Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In an experiment with a potentiometer, VB = 10V. R is adjusted to be 50Ω (Figure). A student wanting to measure voltage E1 of a battery (approx. 8V) finds no null point possible. He then diminishes R to 10Ω and is able to locate the null point on the last (4th) segment of the potentiometer. Find the resistance of the potentiometer wire and potential drop per unit length across the wire in the second case.
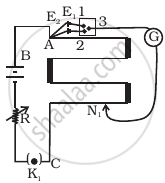
Solution
When emf of the primary cell is less than the potential difference across the wires of potentiometer, only then the null point is obtained.
Equivalent resistance of potentiometer and variable resistor (R = 50Ω) is given by = 50Ω + R'
Equivalent voltage applied across potentiometer = 10V

The current through the main circuit,
`I = V/(50Ω + R^') = 10/(50Ω + R^')`
Potential difference across wire of potentiometer,
Since with 50Ω resistor, null point is not obtained it is possible only when
`(10 xx R^')/(10 + R^') > 8`
⇒ 2R' > 80
⇒ R' > 40
`(10 xx 3/4 R)/(10 + R^') < 8`
⇒ 7.5R' < 80 + 8R'
R' > 160
⇒ 160 < R' < 200
Any R' between 160Ω and 200Ω will achieve.
Since, the null point on the last (4th) segment of the potentiometer, therefore potential drop across 400 cm of wire > 8V.
This imply that potential gradient
k × 400 cm > 8 V
or k × 4 m > 8 V
k > 2 V/m
Similarly, potential drop across 300 cm wire < 8 V.
k × 300 cm > 8 V
or k × 3 m > 8 V
`k > 2 2/3 V/m`
Thus, `2 2/3 V/m > k > V/m`.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a potentiometer experiment, balancing length is found to be 120 cm for a cell E1 of emf 2V. What will be the balancing length for another cell E2 of emf 1.5V? (No other changes are made in the experiment.)
State the working principle of a potentiometer. With the help of the circuit diagram, explain how a potentiometer is used to compare the emf's of two primary cells. Obtain the required expression used for comparing the emfs.
The resistance of a potentiometer wire is 8 Ω and its length is 8 m. A resistance box and a 2 V battery are connected in series with iL What should be the resistance in the box if it is desired to have a potential drop of 1 µV/mm?
If the potential gradient of a wire decreases, then its length ______
Which of the following instruments is not a direct reading instrument?
A potentiometer wire is 10 m long and has resistance of 2`Omega`/m. It is connected in series with a battery of e.m.f 3 V and a resistance of 10 `Omega`. The potential gradient along the wire in V/m is ______.
AB is a wire of potentiometer with the increase in value of resistance R, the shift in the balance point J will be:
A wire of resistance R is cut into two equal part. There parts are then connected in parallel. The equivalent resistance of the combination will be
The emf of the cell of internal resistance 1.275 Ω balances against a length of 217 cm of a potentiometer wire. Find the balancing length when the cell is shunted by a resistance of 15 Ω.
A particle carrying 8 electron charges starts from rest and is accelerated through a potential difference of 9000 V. Calculate the KE acquired by it in keV.
