Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
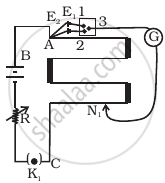
In an experiment with a potentiometer, VB = 10V. R is adjusted to be 50Ω (Figure). A student wanting to measure voltage E1 of a battery (approx. 8V) finds no null point possible. He then diminishes R to 10Ω and is able to locate the null point on the last (4th) segment of the potentiometer. Find the resistance of the potentiometer wire and potential drop per unit length across the wire in the second case.
उत्तर
When emf of the primary cell is less than the potential difference across the wires of potentiometer, only then the null point is obtained.
Equivalent resistance of potentiometer and variable resistor (R = 50Ω) is given by = 50Ω + R'
Equivalent voltage applied across potentiometer = 10V

The current through the main circuit,
`I = V/(50Ω + R^') = 10/(50Ω + R^')`
Potential difference across wire of potentiometer,
Since with 50Ω resistor, null point is not obtained it is possible only when
`(10 xx R^')/(10 + R^') > 8`
⇒ 2R' > 80
⇒ R' > 40
`(10 xx 3/4 R)/(10 + R^') < 8`
⇒ 7.5R' < 80 + 8R'
R' > 160
⇒ 160 < R' < 200
Any R' between 160Ω and 200Ω will achieve.
Since, the null point on the last (4th) segment of the potentiometer, therefore potential drop across 400 cm of wire > 8V.
This imply that potential gradient
k × 400 cm > 8 V
or k × 4 m > 8 V
k > 2 V/m
Similarly, potential drop across 300 cm wire < 8 V.
k × 300 cm > 8 V
or k × 3 m > 8 V
`k > 2 2/3 V/m`
Thus, `2 2/3 V/m > k > V/m`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
On what factors does the potential gradient of the wire depend?
How is potential gradient measured? Explain.
When two cells of emf's E1 and E2 are connected in series so as to assist each other, their balancing length on a potentiometer wire is found to be 2.7 m. When the cells are connected in series so as to oppose each other, the balancing length is found to be 0.3 m. Compare the emf's of the two cells.
The emf of a standard cell is 1.5V and is balanced by a length of 300 cm of a potentiometer with a 10 m long wire. Find the percentage error in a voltmeter that balances at 350 cm when its reading is 1.8 V.
A potentiometer is an ideal device for measuring potential difference because ______.
In the experiment to determine the internal resistance of a cell (E1) using a potentiometer, the resistance drawn from the resistance box is 'R'. The potential difference across the balancing length of the wire is equal to the terminal potential difference (V) of the cell. The value of internal resistance (r) of the cell is ______
In a potentiometer of 10 wires, the balance point is obtained on the 7th wire. To shift the balance point to 9th wire, we should ______.
The best instrument for accurate measurement of EMF of a cell is ____________.
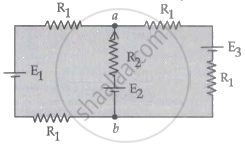
For the circuit shown, with R1 = 1.0 Ω, R2 = 2.0 Ω, E1 = 2 V, and E2 = E3 = 4 V, the potential difference between the points 'a' and 'b' is approximately (in V) ______.
If you are provided a set of resistances 2Ω, 4Ω, 6Ω and 8Ω. Connect these resistances so as to obtain an equivalent resistance of `46/3`Ω.
