Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When two cells of emf's E1 and E2 are connected in series so as to assist each other, their balancing length on a potentiometer wire is found to be 2.7 m. When the cells are connected in series so as to oppose each other, the balancing length is found to be 0.3 m. Compare the emf's of the two cells.
उत्तर
Data: l1 = 2.7 m (cells assisting),
l2 = 0.3 m (cells opposing)
`"E"_1 + "E"_2 = "Kl"_1` and `"E"_1 - "E"_2 = "Kl"_2`
∴ `("E"_1 + "E"_2)/("E"_1 - "E"_2) = "Kl"_1/"Kl"_2`
∴`"E"_1/"E"_2 = ("l"_1 + "l"_2)/("l"_1 - "l"_2) = (2.7 + 0.3)/(2.7 - 0.3) = 3/2.4 = 30/24` = 1.25
The ratio of the emf's of the two cells is 1.25.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write two factors by which current sensitivity of a potentiometer can be increased.
Figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.40 Ω maintaining a potential drop across the resistor wire AB. A standard cell which maintains a constant emf of 1.02 V (for very moderate currents up to a few mA) gives a balance point at 67.3 cm length of the wire. To ensure very low currents drawn from the standard cell, very high resistance of 600 kΩ is put in series with it, which is shorted close to the balance point. The standard cell is then replaced by a cell of unknown emf ε and the balance point found similarly, turns out to be at 82.3 cm length of the wire.
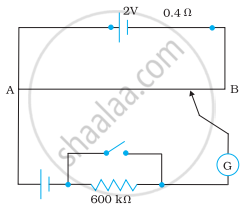
(a) What is the value ε?
(b) What purpose does the high resistance of 600 kΩ have?
(c) Is the balance point affected by this high resistance?
(d) Is the balance point affected by the internal resistance of the driver cell?
(e) Would the method work in the above situation if the driver cell of the potentiometer had an emf of 1.0 V instead of 2.0 V?
(f) Would the circuit work well for determining an extremely small emf, say of the order of a few mV (such as the typical emf of a thermo-couple)? If not, how will you modify the circuit?
Figure 3.34 shows a potentiometer circuit for comparison of two resistances. The balance point with a standard resistor R = 10.0 Ω is found to be 58.3 cm, while that with the unknown resistance X is 68.5 cm. Determine the value of X. What might you do if you failed to find a balance point with the given cell of emf ε?
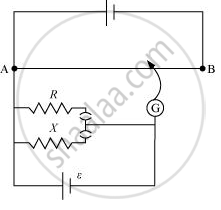
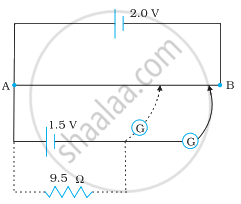
Figure shows a 2.0 V potentiometer used for the determination of internal resistance of a 1.5 V cell. The balance point of the cell in open circuit is 76.3 cm. When a resistor of 9.5 Ω is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to 64.8 cm length of the potentiometer wire. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.
SI unit of potential gradient is _______.
(a) V cm
(b) `V/"cm"`
(c) Vm
(d) `V/m`
In a potentiometer experiment, balancing length is found to be 120 cm for a cell E1 of emf 2V. What will be the balancing length for another cell E2 of emf 1.5V? (No other changes are made in the experiment.)
In the given circuit, with steady current, calculate the potential drop across the capacitor and the charge stored in it.

State the principle of a potentiometer. Define potential gradient. Obtain an expression for potential gradient in terms of resistivity of the potentiometer wire.
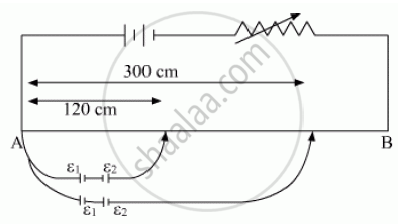
Figure shows a long potentiometer wire AB having a constant potential gradient. The null points for the two primary cells of emfs ε1 and ε2 connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of l1 = 120 cm and l2 = 300 cm from the end A. Determine (i) ε1/ε2 and (ii) position of null point for the cell ε1 only.

Write two possible causes for one sided deflection in a potentiometer experiment.
Describe briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of a cell.
In the figure a long uniform potentiometer wire AB is having a constant potential gradient along its length. The null points for the two primary cells of emfs ε1 and ε2 connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of 120 cm and 300 cm from the end A. Find (i) ε1/ ε2 and (ii) position of null point for the cell ε1.
How is the sensitivity of a potentiometer increased?
Two students ‘X’ and ‘Y’ perform an experiment on potentiometer separately using the circuit given below:
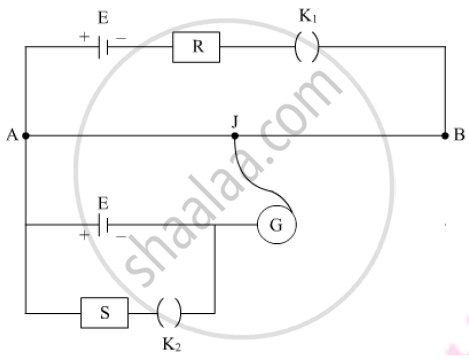
Keeping other parameters unchanged, how will the position of the null point be affected if
(i) ‘X’ increases the value of resistance R in the set-up by keeping the key K1 closed and the Key K2 opens?
(ii) ‘Y’ decreases the value of resistance S in the set-up, while the key K2 remains open and they K1 closed?
Justify.
Would you prefer a voltmeter or a potentiometer to measure the emf of a battery?
The potentiometer wire AB shown in the figure is 40 cm long. Where should the free end of the galvanometer be connected on AB, so that the galvanometer may show zero deflection?

Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a potentiometer to measure the internal resistance ‘r’ of a cell. Write the working formula (derivation is not required).
Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a potentiometer to compare emfs of two cells. Write the working formula (Derivation not required).
When the balance point is obtained in the potentiometer, a current is drawn from ______.
Define or describe a Potentiometer.
Define potential gradient of the potentiometer wire.
Describe how a potentiometer is used to compare the EMFs of two cells by connecting the cells individually.
A battery of emf 4 volt and internal resistance 1 Ω is connected in parallel with another battery of emf 1 V and internal resistance 1 Ω (with their like poles connected together). The combination is used to send current through an external resistance of 2 Ω. Calculate the current through the external resistance.
A potential drop per unit length along a wire is 5 × 10−3 V/m. If the emf of a cell balances against length 216 cm of this potentiometer wire, find the emf of the cell.
What will be the effect on the position of zero deflection if only the current flowing through the potentiometer wire is decreased?
The resistance of a potentiometer wire is 8 Ω and its length is 8 m. A resistance box and a 2 V battery are connected in series with iL What should be the resistance in the box if it is desired to have a potential drop of 1 µV/mm?
The SI unit of the potential gradient is ______
State any one use of a potentiometer.
The emf of a standard cell is 1.5V and is balanced by a length of 300 cm of a potentiometer with a 10 m long wire. Find the percentage error in a voltmeter that balances at 350 cm when its reading is 1.8 V.
The resistance of the potentiometer wire should ideally be ____________.
In a potentiometer experiment, when the galvanometer shows no deflection, then no current flows through ____________.
A potentiometer is an ideal device for measuring potential difference because ______.
Select the WRONG statement:
A potentiometer wire of Length 10 m is connected in series with a battery. The e.m.f. of a cell balances against 250 cm Length of wire. If length of potentiometer wire is increased by 1 m, the new balancing length of wire will be ____________.
Which of the following is true for a potentiometer?
A cell of e.m.f. 'E' is connected across a resistance 'R'. The potential difference across the terminals of the cell is 90% ofE. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
In the potentiometer experiment, the balancing length with cell E1 of unknown e.m.f. is ℓ1 cm. By shunting the cell E1 with resistance 'R' which is equal to internal resistance (r) of the cell E1, the balancing length ℓ2 is ______
In the potentiometer experiment, the balancing length with a cell E1 of unknown e.m.f. is 'ℓ1' cm. By shunting the cell with resistance R Ω, the balancing length becomes `ℓ_1/2` cm, the internal resistance (r) of a cell is ______
In the potentiometer experiment, cells of e.m.f. E1 and E2 are connected in series (E1 > E2). the balancing length is 64 cm of the wire. If the polarity of E2 is reversed, the balancing length becomes 32 cm. The ratio `E_1/E_2` is ______
A potentiometer wire is 100 cm long and a constant potential difference is maintained across it. Two cells are connected in series first to support one another and then in opposite direction. The balance points are obtained at 50 cm and 10 cm from the positive end of the wire in the two cases. The ratio of emf's is ______.
In a potentiometer of 10 wires, the balance point is obtained on the 7th wire. To shift the balance point to 9th wire, we should ______.
AB is a wire of potentiometer with the increase in the value of resistance R, the shift in the balance point J will be ______.
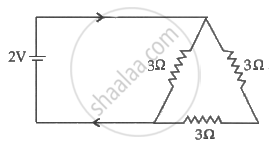
The value of current I in the network shown in fig.
The instrument among the following which measures the e.m.f of a cell most accurately is ______
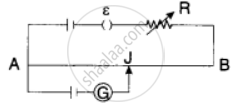
In an experiment with a potentiometer, VB = 10V. R is adjusted to be 50Ω (Figure). A student wanting to measure voltage E1 of a battery (approx. 8V) finds no null point possible. He then diminishes R to 10Ω and is able to locate the null point on the last (4th) segment of the potentiometer. Find the resistance of the potentiometer wire and potential drop per unit length across the wire in the second case.
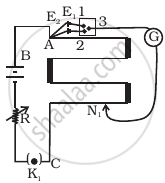
Potential difference between the points A and B in the circuit shown is 16 V, then potential difference across 2Ω resistor is ______ V. volt. (VA > VB)

Two identical thin metal plates has charge q1 and q2 respectively such that q1 > q2. The plates were brought close to each other to form a parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C. The potential difference between them is ______.
What is the value of resistance for an ideal voltmeter?
State dimension of potential gradient.
Draw neat labelled diagram of potentiometer as voltage divider.
