Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define potential gradient of the potentiometer wire.
Define Potential Gradient.
What is potential gradient?
उत्तर
The potential gradient is defined as the potential difference per unit length of the potentiometer wire.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the principle of working of a potentiometer.
Accuracy of potentiometer can be easily increased by ______.
Write two factors by which current sensitivity of a potentiometer can be increased.
Figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.40 Ω maintaining a potential drop across the resistor wire AB. A standard cell which maintains a constant emf of 1.02 V (for very moderate currents up to a few mA) gives a balance point at 67.3 cm length of the wire. To ensure very low currents drawn from the standard cell, very high resistance of 600 kΩ is put in series with it, which is shorted close to the balance point. The standard cell is then replaced by a cell of unknown emf ε and the balance point found similarly, turns out to be at 82.3 cm length of the wire.
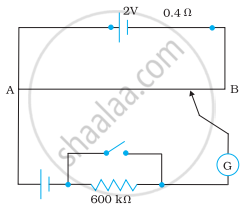
(a) What is the value ε?
(b) What purpose does the high resistance of 600 kΩ have?
(c) Is the balance point affected by this high resistance?
(d) Is the balance point affected by the internal resistance of the driver cell?
(e) Would the method work in the above situation if the driver cell of the potentiometer had an emf of 1.0 V instead of 2.0 V?
(f) Would the circuit work well for determining an extremely small emf, say of the order of a few mV (such as the typical emf of a thermo-couple)? If not, how will you modify the circuit?
State the advantages of potentiometer over voltmeter.
SI unit of potential gradient is _______.
(a) V cm
(b) `V/"cm"`
(c) Vm
(d) `V/m`
In a potentiometer experiment, balancing length is found to be 120 cm for a cell E1 of emf 2V. What will be the balancing length for another cell E2 of emf 1.5V? (No other changes are made in the experiment.)
State the underlying principle of a potentiometer ?
In the given circuit in the steady state, obtain the expressions for (a) the potential drop (b) the charge and (c) the energy stored in the capacitor, C.

Figure shows a long potentiometer wire AB having a constant potential gradient. The null points for the two primary cells of emfs ε1 and ε2 connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of l1 = 120 cm and l2 = 300 cm from the end A. Determine (i) ε1/ε2 and (ii) position of null point for the cell ε1 only.

Describe briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of a cell.
The net resistance of an ammeter should be small to ensure that _______________ .
The potentiometer wire AB shown in the figure is 50 cm long. When AD = 30 cm, no deflection occurs in the galvanometer. Find R.
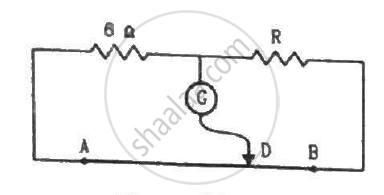
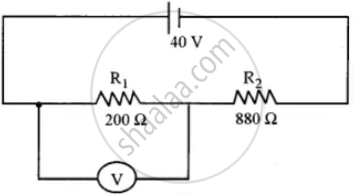
Figure below shows two resistors R1 and R2 connected to a battery having an emf of 40V and negligible internal resistance. A voltmeter having a resistance of. 300 Ω is used to measure the potential difference across R1 Find the reading of the voltmeter.
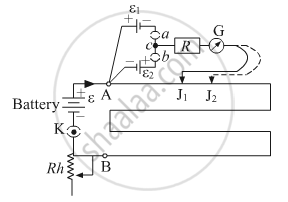
A student uses the circuit diagram of a potentiometer as shown in the figure
(a) for a steady current I passing through the potentiometer wire, he gets a null point for the cell ε1. and not for ε2. Give the reason for this observation and suggest how this difficulty can be resolved.
(b) What is the function of resistance R used in the circuit? How will the change in its value affect the null point?
(c) How can the sensitivity of the potentiometer be increased?
How is potential gradient measured? Explain.
What are the disadvantages of a potentiometer?
Distinguish between a potentiometer and a voltmeter.
Describe how a potentiometer is used to compare the emf's of two cells by the combination method.
When two cells of emf's E1 and E2 are connected in series so as to assist each other, their balancing length on a potentiometer wire is found to be 2.7 m. When the cells are connected in series so as to oppose each other, the balancing length is found to be 0.3 m. Compare the emf's of the two cells.
The emf of a cell is balanced by a length of 120 cm of a potentiometer wire. When the cell is shunted by a resistance of 10 Ω, the balancing length is reduced by 20 cm. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
The SI unit of the potential gradient is ______
What are the disadvantages of a potentiometer over a voltmeter?
A cell of e.m.f 1.5V and negligible internal resistance is connected in series with a potential meter of length 10 m and the total resistance of 20 Ω. What resistance should be introduced in the resistance box such that the potential drop across the potentiometer is one microvolt per cm of the wire?
A potentiometer wire is 4m long and potential difference of 3V is maintained between the ends. The emf of the cell, which balances against a length of 100 cm of the potentiometer wire is ____________.
The resistance of the potentiometer wire should ideally be ____________.
In a potentiometer experiment, when the galvanometer shows no deflection, then no current flows through ____________.
The potentiometer is more sensitive, when ______.
A potentiometer is an ideal device for measuring potential difference because ______.
A potentiometer wire of Length 10 m is connected in series with a battery. The e.m.f. of a cell balances against 250 cm Length of wire. If length of potentiometer wire is increased by 1 m, the new balancing length of wire will be ____________.
If the e.m.f of a cell is not constant in the metre bridge experiment, then the ____________.
In the potentiometer experiment, the balancing length with cell E1 of unknown e.m.f. is ℓ1 cm. By shunting the cell E1 with resistance 'R' which is equal to internal resistance (r) of the cell E1, the balancing length ℓ2 is ______
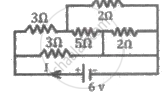
The current drawn from the battery in the given network is ______
(Internal resistance of the battery is neglected)
A wire has a length of 2m and a resistance of 10Ω. It is connected in series with a resistance of 990Ω and a cell of e.m.f. 2V. The potential gradient along the wire will be ______
In the experiment to determine the internal resistance of a cell (E1) using a potentiometer, the resistance drawn from the resistance box is 'R'. The potential difference across the balancing length of the wire is equal to the terminal potential difference (V) of the cell. The value of internal resistance (r) of the cell is ______
A potentiometer wire has a length of 4m and resistance of 5Ω. It is connected in series with 495 Ω resistance and a cell of e.m.f. 4V. The potential gradient along the wire is ______
If the length of potentiometer wire is increased, then the length of the previously obtained balance point will ______.
Two students X and Y perform potentiometer experiment separately and null point was obtained as shown in diagram. During the experiment, ______.
- X increases the value of R (resistance)
- Y decreases the value of S (resistance)
The position of null point obtained by students X and Y respectively.
In a potentiometer experiment when three cells A, B, C are connected in series the balancing length is found to be 740 cm. If A and B are connected in series, the balancing length is 440 cm and when B and C are connected in series, it is 540 cm. The e.m.f. of A, B, and C cells EA, EB, EC are respectively (in volt) ______
In the potentiometer experiment, the balancing length with a cell E1 of unknown e.m.f. is 'ℓ1' cm. By shunting the cell with resistance R Ω, the balancing length becomes `ℓ_1/2` cm, the internal resistance (r) of a cell is ______
In a potentiometer experiment, for measuring internal resistance of a cell, the balance point has been obtained on the fourth wire. The balance point can be shifted to fifth wire by ______.
A potentiometer wire is 100 cm long and a constant potential difference is maintained across it. Two cells are connected in series first to support one another and then in opposite direction. The balance points are obtained at 50 cm and 10 cm from the positive end of the wire in the two cases. The ratio of emf's is ______.
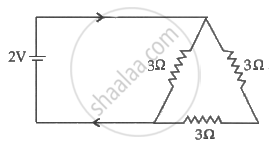
Three resistance each of 4Ω are connected to from a triangle. The resistance b / w two terminal is
The value of current I in the network shown in fig.
The instrument among the following which measures the e.m.f of a cell most accurately is ______
A Daniel cell is balanced on 125 cm lengths of a potentiometer wire. Now the cell is short circuited by a resistance 2 Ω and the balance is obtained at 100 cm. The internal resistance of the Daniel cell is ______.
In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell of emf 1.20 V gives a balance point at 36 cm length of wire. This cell is now replaced by another cell of emf 1.80 V. The difference in balancing length of potentiometer wire in above conditions will be ______ cm.
In potentiometer experiment, null point is obtained at a particular point for a cell on potentiometer wire x cm long. If the length of the potentiometer wire is increased without changing the cell, the balancing length will ______. (Driving source is not changed)
What should be the diameter of a soap bubble such that the excess pressure inside it is 51.2 Pa? [Surface tension of soap solution = 3.2 × 10−2 N/m]
The Figure below shows a potentiometer circuit in which the driver cell D has an emf of 6 V and internal resistance of 2 Ω. The potentiometer wire AB is 10 m long and has a resistance of 28 Ω. The series resistance RS is of 2 Ω.
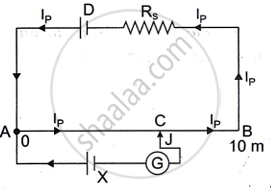
- The current Ip flowing in the potentiometer wire AB when the jockey (J) does not touch the wire AB.
- emf of the cell X if the balancing length AC is 4.5 m.
