Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe how a potentiometer is used to compare the emf's of two cells by the combination method.
उत्तर १
A stable emf E battery is used to create a potential gradient `"V"/"L"` along the potentiometer wire,
where V = potential difference across length L of the wire.
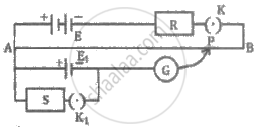
The positive terminal of cell 1 is connected to the potentiometer's higher potential terminal A, while the negative terminal is connected to the galvanometer G via the reversing key. The galvanometer's other terminal is connected to a pencil jockey. Cell 2 is connected across the remaining two opposite terminals of the reversing key. The other terminal of the galvanometer is connected to a pencil jockey.
The emf E1 should be greater than the emf E2; this can be fine-tuned through trial and error. In positions 1-1, two plugs are inserted into the reversing key. In this case, the two cells help each other, resulting in a net emf of E1 + E2.
The jockey taps along the wire to find null point D. If the null point is located at a distance of l1 from A,
E1 + E2 = l1 (V/L)
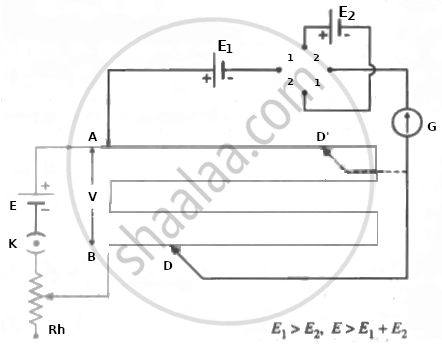
Comparison of two emf's using a potentiometer by the combination method (the sum and difference method)
For the same potential gradient (without changing the rheostat setting), the plugs are now inserted into positions 2-2. (instead of 1-1). The emf E2 then opposes E1 and the net emf is E1 - E2. The new null point D' is, say, a distance l2 from A and
E1 - E2 = l2 (V/L)
∴ `("E"_1 + "E"_2)/("E"_1 - "E"_2) = "l"_1/"l"_2`
∴ `"E"_1/"E"_2 = ("l"_1 + "l"_2)/("l"_1 - "l"_2)`
Here, the emf E should be greater than E1 + E2. Using the rheostat, the experiment is repeated for different potential gradients.
उत्तर २
- The emfs of two cells can be compared using the sum and difference method.
- When two cells are connected such that the positive terminal of the first cell is connected to the negative terminal of the second cell, the emf of the two cells are added up and the effective emf of the combination of two cells is E1 + E2. This method of connecting two cells is called the sum method.
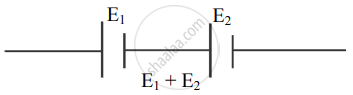
Sum method - When two cells are connected such that their negative terminals are together or their positive terminals are connected together, then their emf oppose each other. The effective emf of the combination of two cells is E1 – E2 (Considering E1 > E2). This method of connecting two cells is called the difference method.
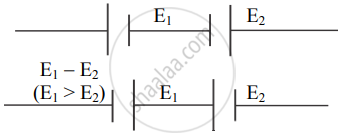
Difference method - The circuit for the sum and difference method is connected, as shown in the below figure. When keys K1 and K3 are closed, the cells E1 and E2 are in the sum mode. The null point is obtained using the jockey.
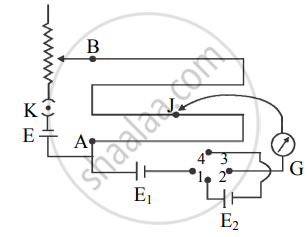
- Let l1 be the length of the wire between the null point and point A.
This corresponds to the emf (E1 + E2).
∴ E1 + E2 = K l1 ….(1)
where K is the potential gradient along the potentiometer wire. - Now the keys K1 and K3 are kept open and keys K2 and K4 are closed. In this case, the two cells are in the difference mode.
- Again the null point is obtained. Let l2 be the length of the wire between the null point and point A.
This corresponds to emf (E1 - E2).
∴ E1 - E2 = Kl2 ….(2) - Dividing equation (1) by equation (2),
`("E"_1 + "E"_2)/("E"_1 - "E"_2) = "l"_1/"l"_2`
By componendo and dividendo method,
`(("E"_1 + "E"_2) + ("E"_1 - "E"_2))/(("E"_1 + "E"_2) - ("E"_1 - "E"_2)) = ("l"_1 + "l"_2)/("l"_1 - "l"_2)`
∴ `"E"_1/"E"_2 = ("l"_1 + "l"_2)/("l"_1 - "l"_2)`
Thus, emf of two cells can be compared using sum and difference method.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the principle of working of a potentiometer.
Accuracy of potentiometer can be easily increased by ______.
Write two factors by which current sensitivity of a potentiometer can be increased.
State the advantages of potentiometer over voltmeter.
SI unit of potential gradient is _______.
(a) V cm
(b) `V/"cm"`
(c) Vm
(d) `V/m`
In the given circuit in the steady state, obtain the expressions for (a) the potential drop (b) the charge and (c) the energy stored in the capacitor, C.

A potentiometer wire of length 1 m has a resistance of 5 Ω. It is connected to a 8 V battery in series with a resistance of 15 Ω. Determine the emf of the primary cell which gives a balance point at 60 cm.
State the principle of a potentiometer. Define potential gradient. Obtain an expression for potential gradient in terms of resistivity of the potentiometer wire.
Figure shows a long potentiometer wire AB having a constant potential gradient. The null points for the two primary cells of emfs ε1 and ε2 connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of l1 = 120 cm and l2 = 300 cm from the end A. Determine (i) ε1/ε2 and (ii) position of null point for the cell ε1 only.

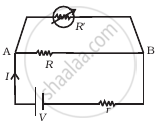
Two students ‘X’ and ‘Y’ perform an experiment on potentiometer separately using the circuit given below:
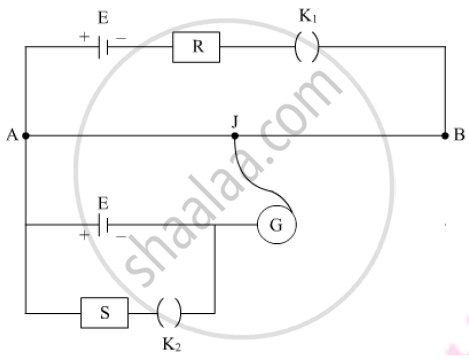
Keeping other parameters unchanged, how will the position of the null point be affected if
(i) ‘X’ increases the value of resistance R in the set-up by keeping the key K1 closed and the Key K2 opens?
(ii) ‘Y’ decreases the value of resistance S in the set-up, while the key K2 remains open and they K1 closed?
Justify.
Write the principle of working of a potentiometer. Describe briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of a given cell.
In a potentiometer experiment, the balancing length with a resistance of 2Ω is found to be 100 cm, while that of an unknown resistance is 500 cm. Calculate the value of the unknown resistance.
Figure below shows two resistors R1 and R2 connected to a battery having an emf of 40V and negligible internal resistance. A voltmeter having a resistance of. 300 Ω is used to measure the potential difference across R1 Find the reading of the voltmeter.
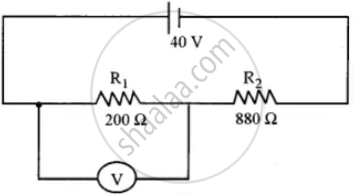
Distinguish between a potentiometer and a voltmeter.
Describe with the help of a neat circuit diagram how you will determine the internal resistance of a cell by using a potentiometer. Derive the necessary formula.
Find the equivalent resistance between the terminals of A and B in the network shown in the figure below given that the resistance of each resistor is 10 ohm.
Why is a potentiometer preferred over a voltmeter for measuring emf?
When the null point is obtained in the potentiometer, the current is drawn from the ______
A voltmeter has a resistance of 100 Ω. What will be its reading when it is connected across a cell of emf 6 V and internal resistance 20 Ω?
What are the disadvantages of a potentiometer over a voltmeter?
The emf of a standard cell is 1.5V and is balanced by a length of 300 cm of a potentiometer with a 10 m long wire. Find the percentage error in a voltmeter that balances at 350 cm when its reading is 1.8 V.
Two cells having unknown emfs E1 and E2 (E1 > E2) are connected in potentiometer circuit, so as to assist each other. The null point obtained is at 490 cm from the higher potential end. When cell E2 is connected, so as to oppose cell E1, the null point is obtained at 90 cm from the same end. The ratio of the emfs of two cells `("E"_1/"E"_2)` is ______.
The resistance of the potentiometer wire should ideally be ____________.
The potentiometer is more sensitive, when ______.
The resistivity of potentiometer wire is 40 × 10-8 ohm - metre and its area of cross-section is 8 × 10-6 m2. If 0.2 ampere current is flowing through the wire, the potential gradient of the wire is ______.
Two cells when connected in series are balanced on 8 m on a potentiometer. If the cells are connected with polarities of one of the cell reversed, they balance on 2 m. The ratio of e.m.f's of the two cells is ____________.
A potentiometer wire has length L For given cell of emf E, the balancing length is `"L"/3` from 3 the positive end of the wire. If the length of the potentiometer wire is increased by 50%, then for the same cell, the balance point is obtained at length.
If the e.m.f of a cell is not constant in the metre bridge experiment, then the ____________.
Which of the following is true for a potentiometer?
Sensitivity of a given potentiometer can be decreased by ______.
A potentiometer wire is 10 m long and has resistance of 2`Omega`/m. It is connected in series with a battery of e.m.f 3 V and a resistance of 10 `Omega`. The potential gradient along the wire in V/m is ______.
The current drawn from the battery in the given network is ______
(Internal resistance of the battery is neglected)
A wire has a length of 2m and a resistance of 10Ω. It is connected in series with a resistance of 990Ω and a cell of e.m.f. 2V. The potential gradient along the wire will be ______
In the experiment to determine the internal resistance of a cell (E1) using a potentiometer, the resistance drawn from the resistance box is 'R'. The potential difference across the balancing length of the wire is equal to the terminal potential difference (V) of the cell. The value of internal resistance (r) of the cell is ______
Two students X and Y perform potentiometer experiment separately and null point was obtained as shown in diagram. During the experiment, ______.
- X increases the value of R (resistance)
- Y decreases the value of S (resistance)
The position of null point obtained by students X and Y respectively.
A battery is connected with a potentiometer wire. The internal resistance of the battery is negligible. If the length of the potentiometer wire of the same material and radius is doubled then ______.
In a potentiometer of 10 wires, the balance point is obtained on the 7th wire. To shift the balance point to 9th wire, we should ______.
A wire of resistance R is cut into two equal part. There parts are then connected in parallel. The equivalent resistance of the combination will be
In a potentiometer circuit, a cell of EMF 1.5 V gives balance point at 36 cm length of wire. If another cell of EMF 2.5 V replaces the first cell, then at what length of the wire, the balance point occurs?
Consider a simple circuit shown in figure ![]() stands for a variable resistance R′. R′ can vary from R0 to infinity. r is internal resistance of the battery (r << R << R0).
stands for a variable resistance R′. R′ can vary from R0 to infinity. r is internal resistance of the battery (r << R << R0).
- Potential drop across AB is nearly constant as R ′ is varied.
- Current through R′ is nearly a constant as R ′ is varied.
- Current I depends sensitively on R′.
- `I ≥ V/(r + R)` always.
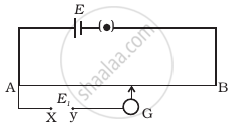
While doing an experiment with potentiometer (Figure) it was found that the deflection is one sided and (i) the deflection decreased while moving from one end A of the wire to the end B; (ii) the deflection increased. while the jockey was moved towards the end B.
- Which terminal + or – ve of the cell E1, is connected at X in case (i) and how is E1 related to E?
- Which terminal of the cell E1 is connected at X in case (ii)?
Potential difference between the points A and B in the circuit shown is 16 V, then potential difference across 2Ω resistor is ______ V. volt. (VA > VB)

A Daniel cell is balanced on 125 cm lengths of a potentiometer wire. Now the cell is short circuited by a resistance 2 Ω and the balance is obtained at 100 cm. The internal resistance of the Daniel cell is ______.
Two identical thin metal plates has charge q1 and q2 respectively such that q1 > q2. The plates were brought close to each other to form a parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C. The potential difference between them is ______.
What is the effect of decreasing the current through the potentiometer on the null point?
A particle carrying 8 electron charges starts from rest and is accelerated through a potential difference of 9000 V. Calculate the KE acquired by it in keV.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Internal resistance of a cell using a potentiometer.
The Figure below shows a potentiometer circuit in which the driver cell D has an emf of 6 V and internal resistance of 2 Ω. The potentiometer wire AB is 10 m long and has a resistance of 28 Ω. The series resistance RS is of 2 Ω.
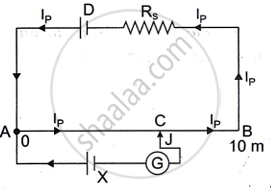
- The current Ip flowing in the potentiometer wire AB when the jockey (J) does not touch the wire AB.
- emf of the cell X if the balancing length AC is 4.5 m.
In a potentiometer, a cell is balanced against 110 cm when the circuit is open. A cell is balanced at 100 cm when short-circuited through a resistance of 10 Ω. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
