Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe how a potentiometer is used to compare the emf's of two cells by the combination method.
उत्तर १
A stable emf E battery is used to create a potential gradient `"V"/"L"` along the potentiometer wire,
where V = potential difference across length L of the wire.
The positive terminal of cell 1 is connected to the potentiometer's higher potential terminal A, while the negative terminal is connected to the galvanometer G via the reversing key. The galvanometer's other terminal is connected to a pencil jockey. Cell 2 is connected across the remaining two opposite terminals of the reversing key. The other terminal of the galvanometer is connected to a pencil jockey.
The emf E1 should be greater than the emf E2; this can be fine-tuned through trial and error. In positions 1-1, two plugs are inserted into the reversing key. In this case, the two cells help each other, resulting in a net emf of E1 + E2.
The jockey taps along the wire to find null point D. If the null point is located at a distance of l1 from A,
E1 + E2 = l1 (V/L)
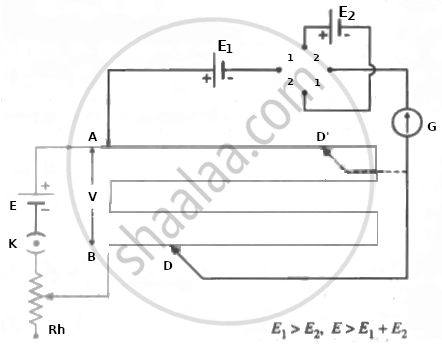
Comparison of two emf's using a potentiometer by the combination method (the sum and difference method)
For the same potential gradient (without changing the rheostat setting), the plugs are now inserted into positions 2-2. (instead of 1-1). The emf E2 then opposes E1 and the net emf is E1 - E2. The new null point D' is, say, a distance l2 from A and
E1 - E2 = l2 (V/L)
∴ `("E"_1 + "E"_2)/("E"_1 - "E"_2) = "l"_1/"l"_2`
∴ `"E"_1/"E"_2 = ("l"_1 + "l"_2)/("l"_1 - "l"_2)`
Here, the emf E should be greater than E1 + E2. Using the rheostat, the experiment is repeated for different potential gradients.
उत्तर २
- The emfs of two cells can be compared using the sum and difference method.
- When two cells are connected such that the positive terminal of the first cell is connected to the negative terminal of the second cell, the emf of the two cells are added up and the effective emf of the combination of two cells is E1 + E2. This method of connecting two cells is called the sum method.
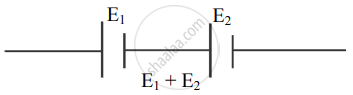
Sum method - When two cells are connected such that their negative terminals are together or their positive terminals are connected together, then their emf oppose each other. The effective emf of the combination of two cells is E1 – E2 (Considering E1 > E2). This method of connecting two cells is called the difference method.
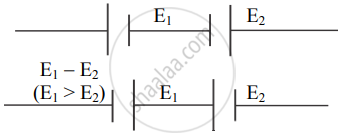
Difference method - The circuit for the sum and difference method is connected, as shown in the below figure. When keys K1 and K3 are closed, the cells E1 and E2 are in the sum mode. The null point is obtained using the jockey.
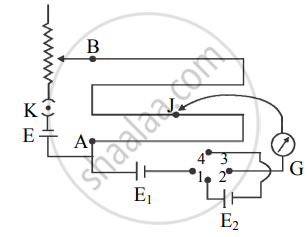
- Let l1 be the length of the wire between the null point and point A.
This corresponds to the emf (E1 + E2).
∴ E1 + E2 = K l1 ….(1)
where K is the potential gradient along the potentiometer wire. - Now the keys K1 and K3 are kept open and keys K2 and K4 are closed. In this case, the two cells are in the difference mode.
- Again the null point is obtained. Let l2 be the length of the wire between the null point and point A.
This corresponds to emf (E1 - E2).
∴ E1 - E2 = Kl2 ….(2) - Dividing equation (1) by equation (2),
`("E"_1 + "E"_2)/("E"_1 - "E"_2) = "l"_1/"l"_2`
By componendo and dividendo method,
`(("E"_1 + "E"_2) + ("E"_1 - "E"_2))/(("E"_1 + "E"_2) - ("E"_1 - "E"_2)) = ("l"_1 + "l"_2)/("l"_1 - "l"_2)`
∴ `"E"_1/"E"_2 = ("l"_1 + "l"_2)/("l"_1 - "l"_2)`
Thus, emf of two cells can be compared using sum and difference method.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the principle of working of a potentiometer.
Write two factors by which current sensitivity of a potentiometer can be increased.
On what factors does the potential gradient of the wire depend?
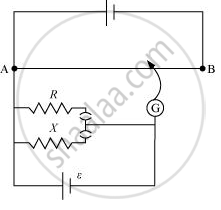
Figure 3.34 shows a potentiometer circuit for comparison of two resistances. The balance point with a standard resistor R = 10.0 Ω is found to be 58.3 cm, while that with the unknown resistance X is 68.5 cm. Determine the value of X. What might you do if you failed to find a balance point with the given cell of emf ε?
SI unit of potential gradient is _______.
(a) V cm
(b) `V/"cm"`
(c) Vm
(d) `V/m`
In the given circuit, with steady current, calculate the potential drop across the capacitor and the charge stored in it.

State the underlying principle of a potentiometer ?
A potentiometer wire of length 1 m has a resistance of 5 Ω. It is connected to a 8 V battery in series with a resistance of 15 Ω. Determine the emf of the primary cell which gives a balance point at 60 cm.
State the principle of a potentiometer. Define potential gradient. Obtain an expression for potential gradient in terms of resistivity of the potentiometer wire.
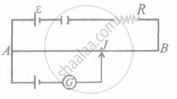
The potentiometer wire AB shown in the figure is 40 cm long. Where should the free end of the galvanometer be connected on AB, so that the galvanometer may show zero deflection?

Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a potentiometer to measure the internal resistance ‘r’ of a cell. Write the working formula (derivation is not required).
Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a potentiometer to compare emfs of two cells. Write the working formula (Derivation not required).
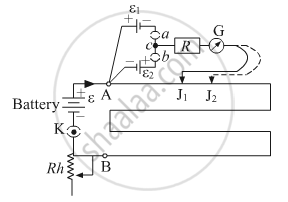
A student uses the circuit diagram of a potentiometer as shown in the figure
(a) for a steady current I passing through the potentiometer wire, he gets a null point for the cell ε1. and not for ε2. Give the reason for this observation and suggest how this difficulty can be resolved.
(b) What is the function of resistance R used in the circuit? How will the change in its value affect the null point?
(c) How can the sensitivity of the potentiometer be increased?
How is potential gradient measured? Explain.
Describe how a potentiometer is used to compare the EMFs of two cells by connecting the cells individually.
When the null point is obtained in the potentiometer, the current is drawn from the ______
State any one use of a potentiometer.
A potentiometer wire is 4m long and potential difference of 3V is maintained between the ends. The emf of the cell, which balances against a length of 100 cm of the potentiometer wire is ____________.
Two cells having unknown emfs E1 and E2 (E1 > E2) are connected in potentiometer circuit, so as to assist each other. The null point obtained is at 490 cm from the higher potential end. When cell E2 is connected, so as to oppose cell E1, the null point is obtained at 90 cm from the same end. The ratio of the emfs of two cells `("E"_1/"E"_2)` is ______.
A 10 m long wire of resistance 20 Q is connected in series with a battery of emf 3 V and a resistance of 10 Ω. The potential gradient along the wire in V/m is ________.
The resistivity of potentiometer wire is 40 × 10-8 ohm - metre and its area of cross-section is 8 × 10-6 m2. If 0.2 ampere current is flowing through the wire, the potential gradient of the wire is ______.
A potentiometer is an ideal device for measuring potential difference because ______.
The length of a potentiometer wire is L. A cell of e.m.f E is balanced at length L/3 from the positive end of the wire. If the length of wire increases by L/2, then the same cell will give balance point at length ____________.
A potentiometer wire of Length 10 m is connected in series with a battery. The e.m.f. of a cell balances against 250 cm Length of wire. If length of potentiometer wire is increased by 1 m, the new balancing length of wire will be ____________.
To determine the internal resistance of a cell by using potentiometer, the null point is at 1 m when cell is shunted by 3 Ω resistance and at a length 1.5 m when cell is shunted by 6 Ω resistance. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
The length of a wire of a potentiometer is 100 cm, and the e.m.f of its standard cell is E volt. It is employed to measure the e.m.f of a battery whose internal resistance is 0.5 `Omega` If the balance point is obtained at `l`= 30 cm from the positive end, the e.m.f of the battery is ____________.
where 'i' is the current in the potentiometer
When two cells of e.m.f 1.5 V and 1.1 V connected in series are balanced on a potentiometer, the balancing length is 260 cm. The balancing length, when they are connected in opposition is (in cm) ____________.
In the potentiometer experiment, the balancing length with cell E1 of unknown e.m.f. is ℓ1 cm. By shunting the cell E1 with resistance 'R' which is equal to internal resistance (r) of the cell E1, the balancing length ℓ2 is ______
In the experiment to determine the internal resistance of a cell (E1) using a potentiometer, the resistance drawn from the resistance box is 'R'. The potential difference across the balancing length of the wire is equal to the terminal potential difference (V) of the cell. The value of internal resistance (r) of the cell is ______
If the length of potentiometer wire is increased, then the length of the previously obtained balance point will ______.
In a potentiometer experiment when three cells A, B, C are connected in series the balancing length is found to be 740 cm. If A and B are connected in series, the balancing length is 440 cm and when B and C are connected in series, it is 540 cm. The e.m.f. of A, B, and C cells EA, EB, EC are respectively (in volt) ______
A potentiometer wire is 4 m long and a potential difference of 3 V is maintained between the ends. The e.m.f. of the cell which balances against a length of 100 cm of the potentiometer wire is ______
In the potentiometer experiment, cells of e.m.f. E1 and E2 are connected in series (E1 > E2). the balancing length is 64 cm of the wire. If the polarity of E2 is reversed, the balancing length becomes 32 cm. The ratio `E_1/E_2` is ______
The sensitivity of the potentiometer can be increased by ______.
A potentiometer is an accurate and versatile device to make electrical measurements of E.M.F. because the method involves ______.
AB is a wire of potentiometer with the increase in value of resistance R, the shift in the balance point J will be:
In a potentiometer circuit, a cell of EMF 1.5 V gives balance point at 36 cm length of wire. If another cell of EMF 2.5 V replaces the first cell, then at what length of the wire, the balance point occurs?
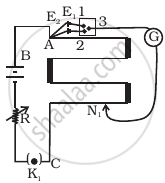
In an experiment with a potentiometer, VB = 10V. R is adjusted to be 50Ω (Figure). A student wanting to measure voltage E1 of a battery (approx. 8V) finds no null point possible. He then diminishes R to 10Ω and is able to locate the null point on the last (4th) segment of the potentiometer. Find the resistance of the potentiometer wire and potential drop per unit length across the wire in the second case.
For the circuit shown, with R1 = 1.0 Ω, R2 = 2.0 Ω, E1 = 2 V, and E2 = E3 = 4 V, the potential difference between the points 'a' and 'b' is approximately (in V) ______.
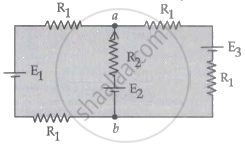
Potential difference between the points A and B in the circuit shown is 16 V, then potential difference across 2Ω resistor is ______ V. volt. (VA > VB)

As a cell age, its internal resistance increases. A voltmeter of resistance 270 Ω connected across an old dry cell reads 1.44 V. However, a potentiometer at the balance point gives a voltage measurement of the cell as 1.5 V. Internal resistance of the cell is ______ Ω.
Two cells of same emf but different internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in series with a resistance R. The value of resistance R, for which the potential difference across second cell is zero, is ______.
In potentiometer experiment, null point is obtained at a particular point for a cell on potentiometer wire x cm long. If the length of the potentiometer wire is increased without changing the cell, the balancing length will ______. (Driving source is not changed)
What should be the diameter of a soap bubble such that the excess pressure inside it is 51.2 Pa? [Surface tension of soap solution = 3.2 × 10−2 N/m]
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Internal resistance of a cell using a potentiometer.
State dimension of potential gradient.
Draw neat labelled diagram of potentiometer as voltage divider.
Three identical cells each of emf 'e' are connected in parallel to form a battery. What is the emf of the battery?
The Figure below shows a potentiometer circuit in which the driver cell D has an emf of 6 V and internal resistance of 2 Ω. The potentiometer wire AB is 10 m long and has a resistance of 28 Ω. The series resistance RS is of 2 Ω.
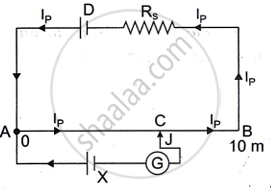
- The current Ip flowing in the potentiometer wire AB when the jockey (J) does not touch the wire AB.
- emf of the cell X if the balancing length AC is 4.5 m.
In a potentiometer, a cell is balanced against 110 cm when the circuit is open. A cell is balanced at 100 cm when short-circuited through a resistance of 10 Ω. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
