Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe with the help of a neat circuit diagram how you will determine the internal resistance of a cell by using a potentiometer. Derive the necessary formula.
Explain the use of a potentiometer to determine the internal resistance of a cell.
उत्तर
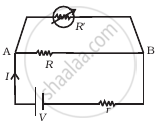
- The experimental setup for this method consists of a potentiometer wire AB connected in series with a cell of emf ε, the key K1, and rheostat as shown in the figure.

- Terminal A is at a higher potential than Terminal B. A cell of emf ε1 whose internal resistance r is to be determined is connected to the potentiometer wire through a galvanometer G and the jockey J.
- A resistance box R is connected across cell ε1 through the key K2. The key K1 is closed and K2 is open.
- The circuit now consists of cell ε, cell ε1, and the potentiometer wire. The null point is then obtained.
- Let l1 be the length of the potentiometer wire between the null point and point A. This length corresponds to emf ε1.
∴ ε1 = kl1 ….(1)
where K is the potential gradient of the potentiometer wire which is constant. - Now both the keys K1 and K2 are closed so that the circuit consists of cell ε, cell ε1, the resistance box, the galvanometer, and the jockey. Some resistance R is selected from the resistance box and a null point is obtained.
- The length of the wire l2 between the null point and point A is measured. This corresponds to the voltage between the null point and point A.
∴ V = kl2 ….(2)
Dividing equation (1) by equation (2),
∴ `"ε"_1/"V" = ("k""l"_1)/("k""l"_2) = "l"_1/"l"_2` .....(3) - Consider the loop PQSTP,
ε1 = IR + Ir and V = IR
∴ `"ε"_1/"V" = ("IR" + "Ir")/("IR") = ("R" + "r")/"R" = "l"_1/"l"_2` ....….[From equation (3)]
⇒ r = R`("l"_1/"l"_2 - 1)`
The above equation is used to determine the internal resistance of the cell.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A potentiometer wire has resistance of per unit length of 0.1 Ω/m. A cell of e.m.f. 1.5 V balances against a 300 cm length of the wire. Find the current in the potentiometer wire.
State the principle of working of a potentiometer.
Accuracy of potentiometer can be easily increased by ______.
Write two factors by which current sensitivity of a potentiometer can be increased.
Figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.40 Ω maintaining a potential drop across the resistor wire AB. A standard cell which maintains a constant emf of 1.02 V (for very moderate currents up to a few mA) gives a balance point at 67.3 cm length of the wire. To ensure very low currents drawn from the standard cell, very high resistance of 600 kΩ is put in series with it, which is shorted close to the balance point. The standard cell is then replaced by a cell of unknown emf ε and the balance point found similarly, turns out to be at 82.3 cm length of the wire.
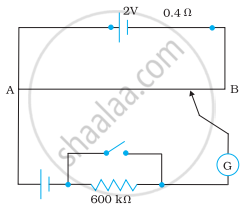
(a) What is the value ε?
(b) What purpose does the high resistance of 600 kΩ have?
(c) Is the balance point affected by this high resistance?
(d) Is the balance point affected by the internal resistance of the driver cell?
(e) Would the method work in the above situation if the driver cell of the potentiometer had an emf of 1.0 V instead of 2.0 V?
(f) Would the circuit work well for determining an extremely small emf, say of the order of a few mV (such as the typical emf of a thermo-couple)? If not, how will you modify the circuit?
In the given circuit, with steady current, calculate the potential drop across the capacitor and the charge stored in it.

(i) State the principle on which a potentiometer works. How can a given potentiometer be made more sensitive?

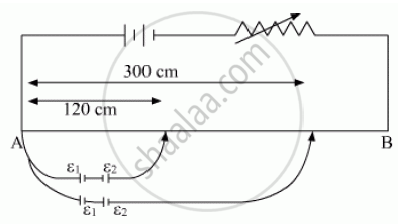
In the figure a long uniform potentiometer wire AB is having a constant potential gradient along its length. The null points for the two primary cells of emfs ε1 and ε2 connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of 120 cm and 300 cm from the end A. Find (i) ε1/ ε2 and (ii) position of null point for the cell ε1.
How is the sensitivity of a potentiometer increased?
Write the principle of working of a potentiometer. Describe briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of a given cell.
Would you prefer a voltmeter or a potentiometer to measure the emf of a battery?
The net resistance of a voltmeter should be large to ensure that ______________ .
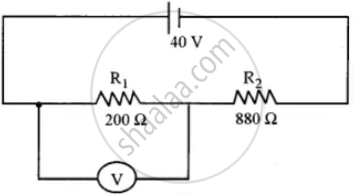
Figure below shows two resistors R1 and R2 connected to a battery having an emf of 40V and negligible internal resistance. A voltmeter having a resistance of. 300 Ω is used to measure the potential difference across R1 Find the reading of the voltmeter.
State the uses of a potentiometer.
A battery of emf 4 volt and internal resistance 1 Ω is connected in parallel with another battery of emf 1 V and internal resistance 1 Ω (with their like poles connected together). The combination is used to send current through an external resistance of 2 Ω. Calculate the current through the external resistance.
What will be the effect on the position of zero deflection if only the current flowing through the potentiometer wire is decreased?
The resistance of a potentiometer wire is 8 Ω and its length is 8 m. A resistance box and a 2 V battery are connected in series with iL What should be the resistance in the box if it is desired to have a potential drop of 1 µV/mm?
When two cells of emf's E1 and E2 are connected in series so as to assist each other, their balancing length on a potentiometer wire is found to be 2.7 m. When the cells are connected in series so as to oppose each other, the balancing length is found to be 0.3 m. Compare the emf's of the two cells.
When the null point is obtained in the potentiometer, the current is drawn from the ______
If the potential gradient of a wire decreases, then its length ______
A voltmeter has a resistance of 100 Ω. What will be its reading when it is connected across a cell of emf 6 V and internal resistance 20 Ω?
What are the disadvantages of a potentiometer over a voltmeter?
Two cells having unknown emfs E1 and E2 (E1 > E2) are connected in potentiometer circuit, so as to assist each other. The null point obtained is at 490 cm from the higher potential end. When cell E2 is connected, so as to oppose cell E1, the null point is obtained at 90 cm from the same end. The ratio of the emfs of two cells `("E"_1/"E"_2)` is ______.
Select the WRONG statement:
Two cells when connected in series are balanced on 8 m on a potentiometer. If the cells are connected with polarities of one of the cell reversed, they balance on 2 m. The ratio of e.m.f's of the two cells is ____________.
A potentiometer wire has length L For given cell of emf E, the balancing length is `"L"/3` from 3 the positive end of the wire. If the length of the potentiometer wire is increased by 50%, then for the same cell, the balance point is obtained at length.
A potentiometer wire of length 100 cm has a resistance of 10 `Omega.` It is connected in series with a resistance and an accumulator of e.m.f 2 V and of negligible internal resistance. A source of e.m.f 10 mV is balanced against a 40 cm length of the potentiometer wire. The value of the external resistance is ____________.
When two cells of e.m.f 1.5 V and 1.1 V connected in series are balanced on a potentiometer, the balancing length is 260 cm. The balancing length, when they are connected in opposition is (in cm) ____________.
A potentiometer is used to measure the potential difference between A and B, the null point is obtained at 0.9 m. Now the potential difference between A and C is measured, the null point is obtained at 0.3 m. The ratio `E_2/E_1` is (E1 > E2) ______

If the length of potentiometer wire is increased, then the length of the previously obtained balance point will ______.
Potentiometer measures the potential difference more accurately than a voltmeter, because ______.
It is observed in a potentiometer experiment that no current passes through the galvanometer when the terminals of the cell are connected across a certain length of the potentiometer wire. On shunting the cell by a 2 Ω resistance, the balancing length is reduced to half. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
A potentiometer wire is 100 cm long and a constant potential difference is maintained across it. Two cells are connected in series first to support one another and then in opposite direction. The balance points are obtained at 50 cm and 10 cm from the positive end of the wire in the two cases. The ratio of emf's is ______.
In a potentiometer of 10 wires, the balance point is obtained on the 7th wire. To shift the balance point to 9th wire, we should ______.
The best instrument for accurate measurement of EMF of a cell is ____________.
AB is a wire of potentiometer with the increase in value of resistance R, the shift in the balance point J will be:
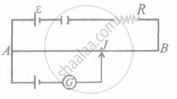
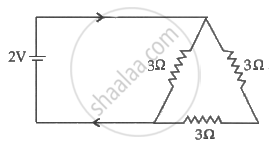
The value of current I in the network shown in fig.
Specific resistance of a conductor increase with.
Consider a simple circuit shown in figure ![]() stands for a variable resistance R′. R′ can vary from R0 to infinity. r is internal resistance of the battery (r << R << R0).
stands for a variable resistance R′. R′ can vary from R0 to infinity. r is internal resistance of the battery (r << R << R0).
- Potential drop across AB is nearly constant as R ′ is varied.
- Current through R′ is nearly a constant as R ′ is varied.
- Current I depends sensitively on R′.
- `I ≥ V/(r + R)` always.
Potential difference between the points A and B in the circuit shown is 16 V, then potential difference across 2Ω resistor is ______ V. volt. (VA > VB)

Two identical thin metal plates has charge q1 and q2 respectively such that q1 > q2. The plates were brought close to each other to form a parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C. The potential difference between them is ______.
Two cells of same emf but different internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in series with a resistance R. The value of resistance R, for which the potential difference across second cell is zero, is ______.
A cell of internal resistance r is connected across an external resistance nr. Then the ratio of the terminal voltage to the emf of the cell is ______.
In balanced meter bridge, the resistance of bridge wire is 0.1 Ω cm. Unknown resistance X is connected in left gap and 6 Ω in right gap, null point divides the wire in the ratio 2:3. Find the current drawn from the battery of 5 V having negligible resistance.
The emf of the cell of internal resistance 1.275 Ω balances against a length of 217 cm of a potentiometer wire. Find the balancing length when the cell is shunted by a resistance of 15 Ω.
What is the effect of decreasing the current through the potentiometer on the null point?
A particle carrying 8 electron charges starts from rest and is accelerated through a potential difference of 9000 V. Calculate the KE acquired by it in keV.
State dimension of potential gradient.
What is the internal resistance of the cell?
In a potentiometer, a cell is balanced against 110 cm when the circuit is open. A cell is balanced at 100 cm when short-circuited through a resistance of 10 Ω. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
