Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
(i) State the principle on which a potentiometer works. How can a given potentiometer be made more sensitive?

उत्तर
(i) Potentiometer is an apparatus used for measuring the emf of a cell or potential difference between two points in an electric circuit accurately.
Principle of potentiometer
The working of potentiometer is based on the fact that the fall of potential across any portion of the wire is directly proportional to the length of that portion provided the wire is of uniform area of cross-section and a constant current is flowing through it.
If V is the potential drop across the portion of wire of length l whose resistance is R. Then
\[V = I \times R = I \times \frac{\rho l}{A}\]
where A, l and \[\rho\] are respectively the area of cross-section, length and specific resistance of the material of the wire.
\[\frac{V}{l} = I \frac{\rho}{A} = K\]
where K is called the potential gradient, i.e. the fall of potential per unit length of wire.
To make the potentiometer sensitive, the potential gradient should be low. So by increasing the length of the wire,potential gradient reduces as it is inversely proportional to the length of the wire and hence in this the potentiometer can be made more sensitive.
(ii) A potentiometer is called sensitive if fall of potential per unit length i.e potential gradient is small. The slope of V-l graph gives potential gradient which is smaller for the potentiometer B than for potentiometer A. Hence, potentiometer B is more sensitive than A.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
On what factors does the potential gradient of the wire depend?
Figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.40 Ω maintaining a potential drop across the resistor wire AB. A standard cell which maintains a constant emf of 1.02 V (for very moderate currents up to a few mA) gives a balance point at 67.3 cm length of the wire. To ensure very low currents drawn from the standard cell, very high resistance of 600 kΩ is put in series with it, which is shorted close to the balance point. The standard cell is then replaced by a cell of unknown emf ε and the balance point found similarly, turns out to be at 82.3 cm length of the wire.
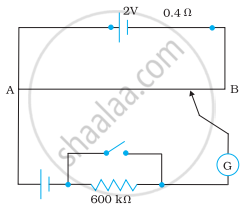
(a) What is the value ε?
(b) What purpose does the high resistance of 600 kΩ have?
(c) Is the balance point affected by this high resistance?
(d) Is the balance point affected by the internal resistance of the driver cell?
(e) Would the method work in the above situation if the driver cell of the potentiometer had an emf of 1.0 V instead of 2.0 V?
(f) Would the circuit work well for determining an extremely small emf, say of the order of a few mV (such as the typical emf of a thermo-couple)? If not, how will you modify the circuit?
In a potentiometer experiment, balancing length is found to be 120 cm for a cell E1 of emf 2V. What will be the balancing length for another cell E2 of emf 1.5V? (No other changes are made in the experiment.)
In the given circuit in the steady state, obtain the expressions for (a) the potential drop (b) the charge and (c) the energy stored in the capacitor, C.

The net resistance of an ammeter should be small to ensure that _______________ .
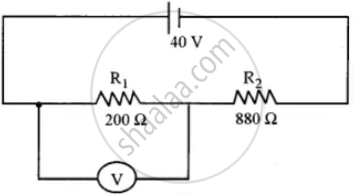
Figure below shows two resistors R1 and R2 connected to a battery having an emf of 40V and negligible internal resistance. A voltmeter having a resistance of. 300 Ω is used to measure the potential difference across R1 Find the reading of the voltmeter.
What will be the effect on the position of zero deflection if only the current flowing through the potentiometer wire is increased?
A potentiometer wire of Length 10 m is connected in series with a battery. The e.m.f. of a cell balances against 250 cm Length of wire. If length of potentiometer wire is increased by 1 m, the new balancing length of wire will be ____________.
In the experiment to determine the internal resistance of a cell (E1) using a potentiometer, the resistance drawn from the resistance box is 'R'. The potential difference across the balancing length of the wire is equal to the terminal potential difference (V) of the cell. The value of internal resistance (r) of the cell is ______
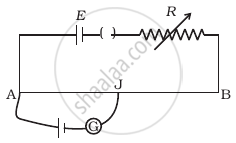
AB is a potentiometer wire (Figure). If the value of R is increased, in which direction will the balance point J shift?