Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(i) State the principle on which a potentiometer works. How can a given potentiometer be made more sensitive?

Solution
(i) Potentiometer is an apparatus used for measuring the emf of a cell or potential difference between two points in an electric circuit accurately.
Principle of potentiometer
The working of potentiometer is based on the fact that the fall of potential across any portion of the wire is directly proportional to the length of that portion provided the wire is of uniform area of cross-section and a constant current is flowing through it.
If V is the potential drop across the portion of wire of length l whose resistance is R. Then
\[V = I \times R = I \times \frac{\rho l}{A}\]
where A, l and \[\rho\] are respectively the area of cross-section, length and specific resistance of the material of the wire.
\[\frac{V}{l} = I \frac{\rho}{A} = K\]
where K is called the potential gradient, i.e. the fall of potential per unit length of wire.
To make the potentiometer sensitive, the potential gradient should be low. So by increasing the length of the wire,potential gradient reduces as it is inversely proportional to the length of the wire and hence in this the potentiometer can be made more sensitive.
(ii) A potentiometer is called sensitive if fall of potential per unit length i.e potential gradient is small. The slope of V-l graph gives potential gradient which is smaller for the potentiometer B than for potentiometer A. Hence, potentiometer B is more sensitive than A.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the principle of working of a potentiometer.
A potentiometer wire of length 1 m has a resistance of 5 Ω. It is connected to a 8 V battery in series with a resistance of 15 Ω. Determine the emf of the primary cell which gives a balance point at 60 cm.
The potentiometer wire AB shown in the figure is 40 cm long. Where should the free end of the galvanometer be connected on AB, so that the galvanometer may show zero deflection?

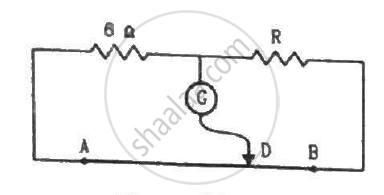
The potentiometer wire AB shown in the figure is 50 cm long. When AD = 30 cm, no deflection occurs in the galvanometer. Find R.
In the potentiometer experiment, the balancing length with cell E1 of unknown e.m.f. is ℓ1 cm. By shunting the cell E1 with resistance 'R' which is equal to internal resistance (r) of the cell E1, the balancing length ℓ2 is ______
In the potentiometer experiment, cells of e.m.f. E1 and E2 are connected in series (E1 > E2). the balancing length is 64 cm of the wire. If the polarity of E2 is reversed, the balancing length becomes 32 cm. The ratio `E_1/E_2` is ______
The sensitivity of the potentiometer can be increased by ______.
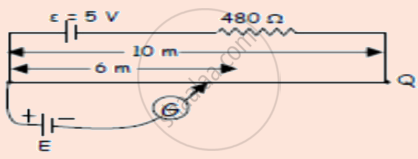
A 10 m long wire of uniform cross-section and 20 Ω resistance is used in a potentiometer. The wire is connected in series with a battery of 5 V along with an external resistance of 480 Ω. If an unknown emf E is balanced at 6.0 m length of the wire, then the value of unknown emf is ______.
A Daniel cell is balanced on 125 cm lengths of a potentiometer wire. Now the cell is short circuited by a resistance 2 Ω and the balance is obtained at 100 cm. The internal resistance of the Daniel cell is ______.
In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell of emf 1.20 V gives a balance point at 36 cm length of wire. This cell is now replaced by another cell of emf 1.80 V. The difference in balancing length of potentiometer wire in above conditions will be ______ cm.
