Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the uses of a potentiometer.
उत्तर १
The applications of the potentiometer discussed above are used in a laboratory. Some practical applications of the potentiometer are given below.
- Voltage divider: The potentiometer can be used as a voltage divider to change the output voltage of a voltage supply.
- Audio control: Sliding potentiometers are commonly used in modem low-power audio systems as audio control devices. Both sliding (faders) and rotary potentiometers (knobs) are regularly used for frequency attenuation, loudness control and for controlling different characteristics of audio signals.
- Potentiometer as a sensor: lf the slider of the potentiometer is connected to the moving part of a machine, it can work as a motion sensor. A small displacement of the moving part causes a change in potential which is further amplified using an amplifier circuit. The potential difference is calibrated in terms of displacement of the moving part.
- To measure the emf (for this, the emf of the standard cell and potential gradient must be known).
- To compare the emfs of two cells.
- To determine a cell's internal resistance.
उत्तर २
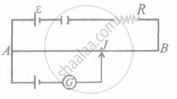
a. Potentiometer as a voltage Divider:
1. The potentiometer can be used as a voltage divider to continuously change the output voltage of a voltage supply. 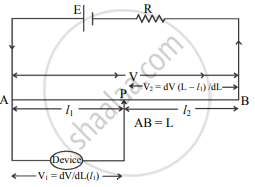
2. As shown in the above figure, potential V is set up between points A and B of a potentiometer wire.
3. One end of a device is connected to positive point A and the other end is connected to a slider that can move along wire AB.
4. The voltage V gets divided in the proportion of lengths l1 and l2, such that
V1 = `("dV"("l"))/("dL")` and
V2 = `("dV"("L" - "l"_1))/("dL")`
b. Potentiometer as an audio control:
1. Sliding potentiometers are commonly used in modern low-power audio systems as audio control devices.
2. Both sliding (faders) and rotary potentiometers (knobs) are regularly used for frequency attenuation, loudness control, and for controlling different characteristics of audio signals.
c. Potentiometer as a sensor:
1. If the slider of a potentiometer is connected to the moving part of a machine, it can work as a motion sensor.
2. A small displacement of the moving part causes changes in potential which is further amplified using an amplifier circuit.
3. The potential difference is calibrated in terms of the displacement of the moving part.
संबंधित प्रश्न
A potentiometer wire has resistance of per unit length of 0.1 Ω/m. A cell of e.m.f. 1.5 V balances against a 300 cm length of the wire. Find the current in the potentiometer wire.
Write two factors by which current sensitivity of a potentiometer can be increased.
On what factors does the potential gradient of the wire depend?
(i) State the principle on which a potentiometer works. How can a given potentiometer be made more sensitive?

Write two possible causes for one sided deflection in a potentiometer experiment.
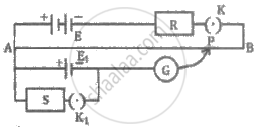
Write the principle of working of a potentiometer. Describe briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of a given cell.
The potentiometer wire AB shown in the figure is 40 cm long. Where should the free end of the galvanometer be connected on AB, so that the galvanometer may show zero deflection?

In a potentiometer experiment, the balancing length with a resistance of 2Ω is found to be 100 cm, while that of an unknown resistance is 500 cm. Calculate the value of the unknown resistance.
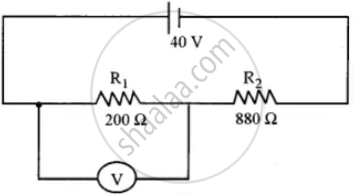
Figure below shows two resistors R1 and R2 connected to a battery having an emf of 40V and negligible internal resistance. A voltmeter having a resistance of. 300 Ω is used to measure the potential difference across R1 Find the reading of the voltmeter.
Define or describe a Potentiometer.
Distinguish between a potentiometer and a voltmeter.
Describe how a potentiometer is used to compare the EMFs of two cells by connecting the cells individually.
Describe with the help of a neat circuit diagram how you will determine the internal resistance of a cell by using a potentiometer. Derive the necessary formula.
A battery of emf 4 volt and internal resistance 1 Ω is connected in parallel with another battery of emf 1 V and internal resistance 1 Ω (with their like poles connected together). The combination is used to send current through an external resistance of 2 Ω. Calculate the current through the external resistance.
A potential drop per unit length along a wire is 5 × 10−3 V/m. If the emf of a cell balances against length 216 cm of this potentiometer wire, find the emf of the cell.
When the null point is obtained in the potentiometer, the current is drawn from the ______
A voltmeter has a resistance of 100 Ω. What will be its reading when it is connected across a cell of emf 6 V and internal resistance 20 Ω?
What are the disadvantages of a potentiometer over a voltmeter?
The emf of a standard cell is 1.5V and is balanced by a length of 300 cm of a potentiometer with a 10 m long wire. Find the percentage error in a voltmeter that balances at 350 cm when its reading is 1.8 V.
The potentiometer is more sensitive, when ______.
A potentiometer is an ideal device for measuring potential difference because ______.
Two cells when connected in series are balanced on 8 m on a potentiometer. If the cells are connected with polarities of one of the cell reversed, they balance on 2 m. The ratio of e.m.f's of the two cells is ____________.
If the e.m.f of a cell is not constant in the metre bridge experiment, then the ____________.
To determine the internal resistance of a cell by using potentiometer, the null point is at 1 m when cell is shunted by 3 Ω resistance and at a length 1.5 m when cell is shunted by 6 Ω resistance. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
Sensitivity of a given potentiometer can be decreased by ______.
A potentiometer wire of length 100 cm has a resistance of 10 `Omega.` It is connected in series with a resistance and an accumulator of e.m.f 2 V and of negligible internal resistance. A source of e.m.f 10 mV is balanced against a 40 cm length of the potentiometer wire. The value of the external resistance is ____________.
In the given figure, battery E is balanced on 55 cm length of potentiometer wire but when a resistance of 10 `Omega` is connected in parallel with the battery, then it balances on 50 cm length of the potentiometer wire. The internal resistance r of the battery is ____________.
The current drawn from the battery in the given network is ______
(Internal resistance of the battery is neglected)
Two students X and Y perform potentiometer experiment separately and null point was obtained as shown in diagram. During the experiment, ______.
- X increases the value of R (resistance)
- Y decreases the value of S (resistance)
The position of null point obtained by students X and Y respectively.
A potentiometer wire is 4 m long and a potential difference of 3 V is maintained between the ends. The e.m.f. of the cell which balances against a length of 100 cm of the potentiometer wire is ______
A potentiometer wire of length 'L' and a resistance 'r' are connected in series with a battery of E.M.F. 'E0' and a resistance 'r1'. A cell of unknown E.M.F, 'E' is balanced at a length 'ℓ' of the potentiometer wire. The unknown E.M.F. E is given by ______
In the potentiometer experiment, cells of e.m.f. E1 and E2 are connected in series (E1 > E2). the balancing length is 64 cm of the wire. If the polarity of E2 is reversed, the balancing length becomes 32 cm. The ratio `E_1/E_2` is ______
The sensitivity of the potentiometer can be increased by ______.
A battery is connected with a potentiometer wire. The internal resistance of the battery is negligible. If the length of the potentiometer wire of the same material and radius is doubled then ______.
A potentiometer is an accurate and versatile device to make electrical measurements of E.M.F. because the method involves ______.
A potentiometer wire is 100 cm long and a constant potential difference is maintained across it. Two cells are connected in series first to support one another and then in opposite direction. The balance points are obtained at 50 cm and 10 cm from the positive end of the wire in the two cases. The ratio of emf's is ______.
In a potentiometer of 10 wires, the balance point is obtained on the 7th wire. To shift the balance point to 9th wire, we should ______.
AB is a wire of potentiometer with the increase in value of resistance R, the shift in the balance point J will be:
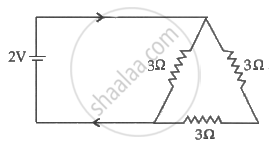
Three resistance each of 4Ω are connected to from a triangle. The resistance b / w two terminal is
The conductivity of super - conductor is
The value of current I in the network shown in fig.
Specific resistance of a conductor increase with.
Consider a simple circuit shown in figure ![]() stands for a variable resistance R′. R′ can vary from R0 to infinity. r is internal resistance of the battery (r << R << R0).
stands for a variable resistance R′. R′ can vary from R0 to infinity. r is internal resistance of the battery (r << R << R0).
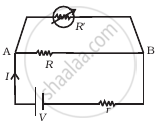
- Potential drop across AB is nearly constant as R ′ is varied.
- Current through R′ is nearly a constant as R ′ is varied.
- Current I depends sensitively on R′.
- `I ≥ V/(r + R)` always.
In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell of emf 1.20 V gives a balance point at 36 cm length of wire. This cell is now replaced by another cell of emf 1.80 V. The difference in balancing length of potentiometer wire in above conditions will be ______ cm.
In potentiometer experiment, null point is obtained at a particular point for a cell on potentiometer wire x cm long. If the length of the potentiometer wire is increased without changing the cell, the balancing length will ______. (Driving source is not changed)
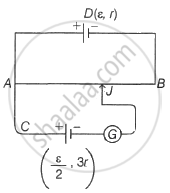
A potentiometer wire AB having length L and resistance 12r is joined to a cell D of emf ε and internal resistance r. A cell C having emt `ε/2` and internal resistance 3r is connected. The length AJ at which the galvanometer as shown in the figure shows no deflection is ______.
What is the value of resistance for an ideal voltmeter?
What will a voltmeter of resistance 200 Ω read when connected across a cell of emf 2 V and internal resistance 2 Ω?
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Internal resistance of a cell using a potentiometer.
State dimension of potential gradient.
