Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A potential drop per unit length along a wire is 5 × 10−3 V/m. If the emf of a cell balances against length 216 cm of this potentiometer wire, find the emf of the cell.
उत्तर
Data: K = 5 × 10-3 `"V"/"m"`, L = 216 cm = 216 × 10-2 m
E = KL
∴ E = 5 × 10-3 × 216 ×10-2
= 1080 × 10-5
= 0.01080 V
The emf of the cell is 0.01080 volL
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the principle of working of a potentiometer.
On what factors does the potential gradient of the wire depend?
Figure 3.34 shows a potentiometer circuit for comparison of two resistances. The balance point with a standard resistor R = 10.0 Ω is found to be 58.3 cm, while that with the unknown resistance X is 68.5 cm. Determine the value of X. What might you do if you failed to find a balance point with the given cell of emf ε?
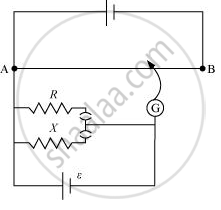
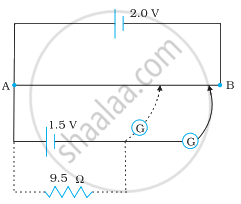
Figure shows a 2.0 V potentiometer used for the determination of internal resistance of a 1.5 V cell. The balance point of the cell in open circuit is 76.3 cm. When a resistor of 9.5 Ω is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to 64.8 cm length of the potentiometer wire. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.
In the given circuit in the steady state, obtain the expressions for (a) the potential drop (b) the charge and (c) the energy stored in the capacitor, C.

State the working principle of a potentiometer. With the help of the circuit diagram, explain how a potentiometer is used to compare the emf's of two primary cells. Obtain the required expression used for comparing the emfs.
Describe briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of a cell.
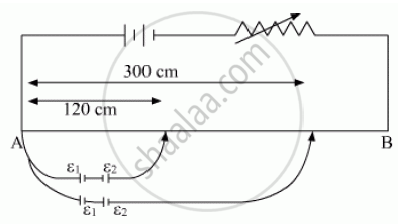
In the figure a long uniform potentiometer wire AB is having a constant potential gradient along its length. The null points for the two primary cells of emfs ε1 and ε2 connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of 120 cm and 300 cm from the end A. Find (i) ε1/ ε2 and (ii) position of null point for the cell ε1.
How is the sensitivity of a potentiometer increased?
Write the principle of working of a potentiometer. Describe briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of a given cell.
The potentiometer wire AB shown in the figure is 40 cm long. Where should the free end of the galvanometer be connected on AB, so that the galvanometer may show zero deflection?

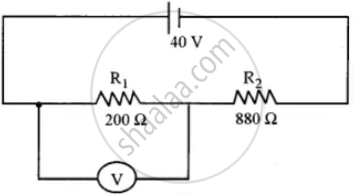
Figure below shows two resistors R1 and R2 connected to a battery having an emf of 40V and negligible internal resistance. A voltmeter having a resistance of. 300 Ω is used to measure the potential difference across R1 Find the reading of the voltmeter.
What are the disadvantages of a potentiometer?
Describe with the help of a neat circuit diagram how you will determine the internal resistance of a cell by using a potentiometer. Derive the necessary formula.
Find the equivalent resistance between the terminals of A and B in the network shown in the figure below given that the resistance of each resistor is 10 ohm.
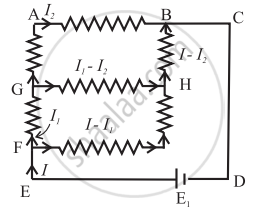
What will be the effect on the position of zero deflection if only the current flowing through the potentiometer wire is decreased?
The emf of a cell is balanced by a length of 120 cm of a potentiometer wire. When the cell is shunted by a resistance of 10 Ω, the balancing length is reduced by 20 cm. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
State any one use of a potentiometer.
A cell of e.m.f 1.5V and negligible internal resistance is connected in series with a potential meter of length 10 m and the total resistance of 20 Ω. What resistance should be introduced in the resistance box such that the potential drop across the potentiometer is one microvolt per cm of the wire?
The emf of a standard cell is 1.5V and is balanced by a length of 300 cm of a potentiometer with a 10 m long wire. Find the percentage error in a voltmeter that balances at 350 cm when its reading is 1.8 V.
A potentiometer wire is 4m long and potential difference of 3V is maintained between the ends. The emf of the cell, which balances against a length of 100 cm of the potentiometer wire is ____________.
Two cells having unknown emfs E1 and E2 (E1 > E2) are connected in potentiometer circuit, so as to assist each other. The null point obtained is at 490 cm from the higher potential end. When cell E2 is connected, so as to oppose cell E1, the null point is obtained at 90 cm from the same end. The ratio of the emfs of two cells `("E"_1/"E"_2)` is ______.
A 10 m long wire of resistance 20 Q is connected in series with a battery of emf 3 V and a resistance of 10 Ω. The potential gradient along the wire in V/m is ________.
The resistivity of potentiometer wire is 40 × 10-8 ohm - metre and its area of cross-section is 8 × 10-6 m2. If 0.2 ampere current is flowing through the wire, the potential gradient of the wire is ______.
Select the WRONG statement:
A potentiometer wire of Length 10 m is connected in series with a battery. The e.m.f. of a cell balances against 250 cm Length of wire. If length of potentiometer wire is increased by 1 m, the new balancing length of wire will be ____________.
If the e.m.f of a cell is not constant in the metre bridge experiment, then the ____________.
A cell of e.m.f. 'E' is connected across a resistance 'R'. The potential difference across the terminals of the cell is 90% ofE. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
Sensitivity of a given potentiometer can be decreased by ______.
A potentiometer wire is 10 m long and has resistance of 2`Omega`/m. It is connected in series with a battery of e.m.f 3 V and a resistance of 10 `Omega`. The potential gradient along the wire in V/m is ______.
When two cells of e.m.f 1.5 V and 1.1 V connected in series are balanced on a potentiometer, the balancing length is 260 cm. The balancing length, when they are connected in opposition is (in cm) ____________.
In the experiment to determine the internal resistance of a cell (E1) using a potentiometer, the resistance drawn from the resistance box is 'R'. The potential difference across the balancing length of the wire is equal to the terminal potential difference (V) of the cell. The value of internal resistance (r) of the cell is ______
A potentiometer wire has a length of 4m and resistance of 5Ω. It is connected in series with 495 Ω resistance and a cell of e.m.f. 4V. The potential gradient along the wire is ______
A student connected the circuit as shown in the figure to determine the internal resistance of a cell E1 by potentiometer (E > E1). He is unable to obtain the null point because ______.
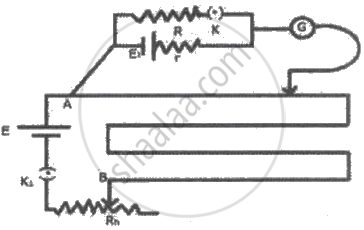
A potentiometer wire of length 'L' and a resistance 'r' are connected in series with a battery of E.M.F. 'E0' and a resistance 'r1'. A cell of unknown E.M.F, 'E' is balanced at a length 'ℓ' of the potentiometer wire. The unknown E.M.F. E is given by ______
In the experiment of potentiometer, at balance point, there is no current in the ______.
In a potentiometer of 10 wires, the balance point is obtained on the 7th wire. To shift the balance point to 9th wire, we should ______.
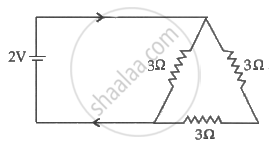
Three resistance each of 4Ω are connected to from a triangle. The resistance b / w two terminal is
The value of current I in the network shown in fig.
Consider a simple circuit shown in figure ![]() stands for a variable resistance R′. R′ can vary from R0 to infinity. r is internal resistance of the battery (r << R << R0).
stands for a variable resistance R′. R′ can vary from R0 to infinity. r is internal resistance of the battery (r << R << R0).
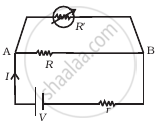
- Potential drop across AB is nearly constant as R ′ is varied.
- Current through R′ is nearly a constant as R ′ is varied.
- Current I depends sensitively on R′.
- `I ≥ V/(r + R)` always.
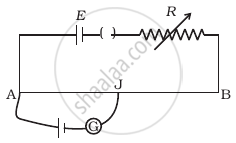
AB is a potentiometer wire (Figure). If the value of R is increased, in which direction will the balance point J shift?
As a cell age, its internal resistance increases. A voltmeter of resistance 270 Ω connected across an old dry cell reads 1.44 V. However, a potentiometer at the balance point gives a voltage measurement of the cell as 1.5 V. Internal resistance of the cell is ______ Ω.
Two identical thin metal plates has charge q1 and q2 respectively such that q1 > q2. The plates were brought close to each other to form a parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C. The potential difference between them is ______.
Two cells of same emf but different internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in series with a resistance R. The value of resistance R, for which the potential difference across second cell is zero, is ______.
In balanced meter bridge, the resistance of bridge wire is 0.1 Ω cm. Unknown resistance X is connected in left gap and 6 Ω in right gap, null point divides the wire in the ratio 2:3. Find the current drawn from the battery of 5 V having negligible resistance.
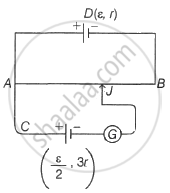
A potentiometer wire AB having length L and resistance 12r is joined to a cell D of emf ε and internal resistance r. A cell C having emt `ε/2` and internal resistance 3r is connected. The length AJ at which the galvanometer as shown in the figure shows no deflection is ______.
The emf of the cell of internal resistance 1.275 Ω balances against a length of 217 cm of a potentiometer wire. Find the balancing length when the cell is shunted by a resistance of 15 Ω.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Internal resistance of a cell using a potentiometer.
Three identical cells each of emf 'e' are connected in parallel to form a battery. What is the emf of the battery?
