Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A cell of e.m.f 1.5V and negligible internal resistance is connected in series with a potential meter of length 10 m and the total resistance of 20 Ω. What resistance should be introduced in the resistance box such that the potential drop across the potentiometer is one microvolt per cm of the wire?
उत्तर
Given:
R = 20 Ω, L = 10 m, E = 1.5 V,
K = 1 μV/cm = 1 × (10-6 /10-2 ) V/ m
= 10-4 V/ m
To find: External resistance (RE)
Formula: K = `"V"/"L"`
Calculation:
Since, I = `"E"/("R" + "R"_"E")`
Also, V = IR = `"ER"/("R" + "R"_"E")`
From formula,
K = `"ER"/(("R" + "R"_"E")"L")`
R + RE = `"ER"/"KL"`
∴ RE = `(1.5 xx 20)/(10^-4 xx 10) - 20 = 30000 - 20`
∴ RE = 29980 Ω
The external resistance should be 29980 Ω.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write two factors by which current sensitivity of a potentiometer can be increased.
On what factors does the potential gradient of the wire depend?
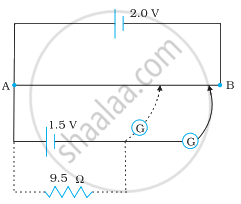
Figure shows a 2.0 V potentiometer used for the determination of internal resistance of a 1.5 V cell. The balance point of the cell in open circuit is 76.3 cm. When a resistor of 9.5 Ω is used in the external circuit of the cell, the balance point shifts to 64.8 cm length of the potentiometer wire. Determine the internal resistance of the cell.
State the advantages of potentiometer over voltmeter.
(i) State the principle on which a potentiometer works. How can a given potentiometer be made more sensitive?

State the underlying principle of a potentiometer ?
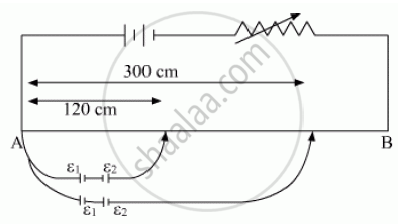
In the figure a long uniform potentiometer wire AB is having a constant potential gradient along its length. The null points for the two primary cells of emfs ε1 and ε2 connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of 120 cm and 300 cm from the end A. Find (i) ε1/ ε2 and (ii) position of null point for the cell ε1.
How is the sensitivity of a potentiometer increased?
When a resistor of 5Ω is connected across the cell, its terminal potential difference is balanced by 150 cm of potentiometer wire and when a resistance of 10 Ω is connected across the cell, the terminal potential difference is balanced by 175 cm same potentiometer wire. Find the balancing length when the cell is in open circuit and the internal resistance of the cell.
The net resistance of a voltmeter should be large to ensure that ______________ .
In a potentiometer experiment, the balancing length with a resistance of 2Ω is found to be 100 cm, while that of an unknown resistance is 500 cm. Calculate the value of the unknown resistance.
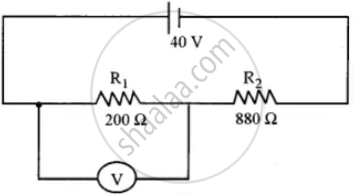
Figure below shows two resistors R1 and R2 connected to a battery having an emf of 40V and negligible internal resistance. A voltmeter having a resistance of. 300 Ω is used to measure the potential difference across R1 Find the reading of the voltmeter.
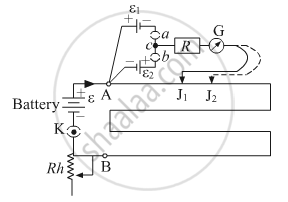
A student uses the circuit diagram of a potentiometer as shown in the figure
(a) for a steady current I passing through the potentiometer wire, he gets a null point for the cell ε1. and not for ε2. Give the reason for this observation and suggest how this difficulty can be resolved.
(b) What is the function of resistance R used in the circuit? How will the change in its value affect the null point?
(c) How can the sensitivity of the potentiometer be increased?
Why should not the jockey be slided along the potentiometer wire?
What will be the effect on the position of zero deflection if only the current flowing through the potentiometer wire is increased?
A potentiometer wire has a length of 1.5 m and a resistance of 10 Ω. It is connected in series with the cell of emf 4 Volt and internal resistance 5 Ω. Calculate the potential drop per centimeter of the wire.
A potential drop per unit length along a wire is 5 × 10−3 V/m. If the emf of a cell balances against length 216 cm of this potentiometer wire, find the emf of the cell.
Why is a potentiometer preferred over a voltmeter for measuring emf?
When the null point is obtained in the potentiometer, the current is drawn from the ______
A voltmeter has a resistance of 100 Ω. What will be its reading when it is connected across a cell of emf 6 V and internal resistance 20 Ω?
What are the disadvantages of a potentiometer over a voltmeter?
A potentiometer wire is 4m long and potential difference of 3V is maintained between the ends. The emf of the cell, which balances against a length of 100 cm of the potentiometer wire is ____________.
The resistance of the potentiometer wire should ideally be ____________.
In a potentiometer experiment, when the galvanometer shows no deflection, then no current flows through ____________.
If the e.m.f of a cell is not constant in the metre bridge experiment, then the ____________.
A cell of e.m.f. 'E' is connected across a resistance 'R'. The potential difference across the terminals of the cell is 90% ofE. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
A potentiometer wire is 10 m long and has resistance of 2`Omega`/m. It is connected in series with a battery of e.m.f 3 V and a resistance of 10 `Omega`. The potential gradient along the wire in V/m is ______.
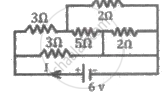
The current drawn from the battery in the given network is ______
(Internal resistance of the battery is neglected)
A wire has a length of 2m and a resistance of 10Ω. It is connected in series with a resistance of 990Ω and a cell of e.m.f. 2V. The potential gradient along the wire will be ______
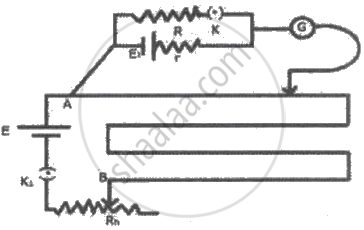
A student connected the circuit as shown in the figure to determine the internal resistance of a cell E1 by potentiometer (E > E1). He is unable to obtain the null point because ______.
Potentiometer measures the potential difference more accurately than a voltmeter, because ______.
It is observed in a potentiometer experiment that no current passes through the galvanometer when the terminals of the cell are connected across a certain length of the potentiometer wire. On shunting the cell by a 2 Ω resistance, the balancing length is reduced to half. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
A potentiometer is an accurate and versatile device to make electrical measurements of E.M.F. because the method involves ______.
The best instrument for accurate measurement of EMF of a cell is ____________.
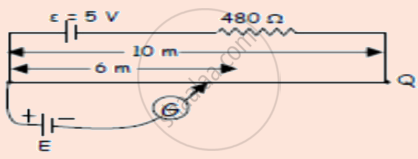
A 10 m long wire of uniform cross-section and 20 Ω resistance is used in a potentiometer. The wire is connected in series with a battery of 5 V along with an external resistance of 480 Ω. If an unknown emf E is balanced at 6.0 m length of the wire, then the value of unknown emf is ______.
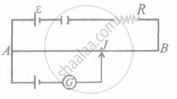
AB is a wire of potentiometer with the increase in value of resistance R, the shift in the balance point J will be:
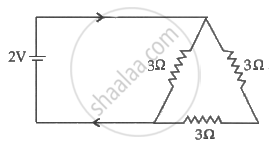
Three resistance each of 4Ω are connected to from a triangle. The resistance b / w two terminal is
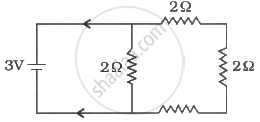
The value of current I in the network shown in fig.
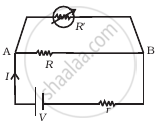
What is the current I in the circuit as show in fig.
Specific resistance of a conductor increase with.
Consider a simple circuit shown in figure ![]() stands for a variable resistance R′. R′ can vary from R0 to infinity. r is internal resistance of the battery (r << R << R0).
stands for a variable resistance R′. R′ can vary from R0 to infinity. r is internal resistance of the battery (r << R << R0).
- Potential drop across AB is nearly constant as R ′ is varied.
- Current through R′ is nearly a constant as R ′ is varied.
- Current I depends sensitively on R′.
- `I ≥ V/(r + R)` always.
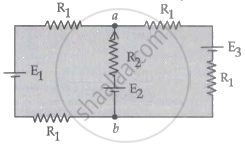
For the circuit shown, with R1 = 1.0 Ω, R2 = 2.0 Ω, E1 = 2 V, and E2 = E3 = 4 V, the potential difference between the points 'a' and 'b' is approximately (in V) ______.
Two identical thin metal plates has charge q1 and q2 respectively such that q1 > q2. The plates were brought close to each other to form a parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C. The potential difference between them is ______.
In potentiometer experiment, null point is obtained at a particular point for a cell on potentiometer wire x cm long. If the length of the potentiometer wire is increased without changing the cell, the balancing length will ______. (Driving source is not changed)
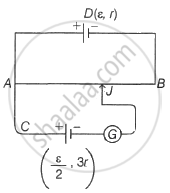
A potentiometer wire AB having length L and resistance 12r is joined to a cell D of emf ε and internal resistance r. A cell C having emt `ε/2` and internal resistance 3r is connected. The length AJ at which the galvanometer as shown in the figure shows no deflection is ______.
What is the value of resistance for an ideal voltmeter?
What will a voltmeter of resistance 200 Ω read when connected across a cell of emf 2 V and internal resistance 2 Ω?
What is the internal resistance of the cell?
Three identical cells each of emf 'e' are connected in parallel to form a battery. What is the emf of the battery?
The Figure below shows a potentiometer circuit in which the driver cell D has an emf of 6 V and internal resistance of 2 Ω. The potentiometer wire AB is 10 m long and has a resistance of 28 Ω. The series resistance RS is of 2 Ω.
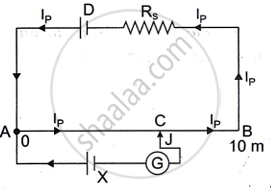
- The current Ip flowing in the potentiometer wire AB when the jockey (J) does not touch the wire AB.
- emf of the cell X if the balancing length AC is 4.5 m.
In a potentiometer, a cell is balanced against 110 cm when the circuit is open. A cell is balanced at 100 cm when short-circuited through a resistance of 10 Ω. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
