Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State the uses of a potentiometer.
Solution 1
The applications of the potentiometer discussed above are used in a laboratory. Some practical applications of the potentiometer are given below.
- Voltage divider: The potentiometer can be used as a voltage divider to change the output voltage of a voltage supply.
- Audio control: Sliding potentiometers are commonly used in modem low-power audio systems as audio control devices. Both sliding (faders) and rotary potentiometers (knobs) are regularly used for frequency attenuation, loudness control and for controlling different characteristics of audio signals.
- Potentiometer as a sensor: lf the slider of the potentiometer is connected to the moving part of a machine, it can work as a motion sensor. A small displacement of the moving part causes a change in potential which is further amplified using an amplifier circuit. The potential difference is calibrated in terms of displacement of the moving part.
- To measure the emf (for this, the emf of the standard cell and potential gradient must be known).
- To compare the emfs of two cells.
- To determine a cell's internal resistance.
Solution 2
a. Potentiometer as a voltage Divider:
1. The potentiometer can be used as a voltage divider to continuously change the output voltage of a voltage supply. 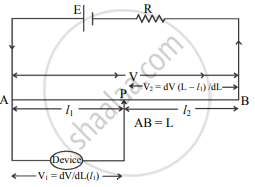
2. As shown in the above figure, potential V is set up between points A and B of a potentiometer wire.
3. One end of a device is connected to positive point A and the other end is connected to a slider that can move along wire AB.
4. The voltage V gets divided in the proportion of lengths l1 and l2, such that
V1 = `("dV"("l"))/("dL")` and
V2 = `("dV"("L" - "l"_1))/("dL")`
b. Potentiometer as an audio control:
1. Sliding potentiometers are commonly used in modern low-power audio systems as audio control devices.
2. Both sliding (faders) and rotary potentiometers (knobs) are regularly used for frequency attenuation, loudness control, and for controlling different characteristics of audio signals.
c. Potentiometer as a sensor:
1. If the slider of a potentiometer is connected to the moving part of a machine, it can work as a motion sensor.
2. A small displacement of the moving part causes changes in potential which is further amplified using an amplifier circuit.
3. The potential difference is calibrated in terms of the displacement of the moving part.
RELATED QUESTIONS
A potentiometer wire has resistance of per unit length of 0.1 Ω/m. A cell of e.m.f. 1.5 V balances against a 300 cm length of the wire. Find the current in the potentiometer wire.
Accuracy of potentiometer can be easily increased by ______.
On what factors does the potential gradient of the wire depend?
Figure shows a potentiometer with a cell of 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.40 Ω maintaining a potential drop across the resistor wire AB. A standard cell which maintains a constant emf of 1.02 V (for very moderate currents up to a few mA) gives a balance point at 67.3 cm length of the wire. To ensure very low currents drawn from the standard cell, very high resistance of 600 kΩ is put in series with it, which is shorted close to the balance point. The standard cell is then replaced by a cell of unknown emf ε and the balance point found similarly, turns out to be at 82.3 cm length of the wire.
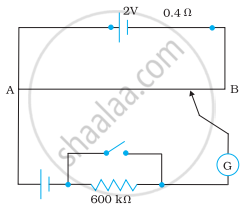
(a) What is the value ε?
(b) What purpose does the high resistance of 600 kΩ have?
(c) Is the balance point affected by this high resistance?
(d) Is the balance point affected by the internal resistance of the driver cell?
(e) Would the method work in the above situation if the driver cell of the potentiometer had an emf of 1.0 V instead of 2.0 V?
(f) Would the circuit work well for determining an extremely small emf, say of the order of a few mV (such as the typical emf of a thermo-couple)? If not, how will you modify the circuit?
State the advantages of potentiometer over voltmeter.
(i) State the principle on which a potentiometer works. How can a given potentiometer be made more sensitive?

In the given circuit in the steady state, obtain the expressions for (a) the potential drop (b) the charge and (c) the energy stored in the capacitor, C.

A potentiometer wire of length 1 m has a resistance of 5 Ω. It is connected to a 8 V battery in series with a resistance of 15 Ω. Determine the emf of the primary cell which gives a balance point at 60 cm.
State the principle of a potentiometer. Define potential gradient. Obtain an expression for potential gradient in terms of resistivity of the potentiometer wire.
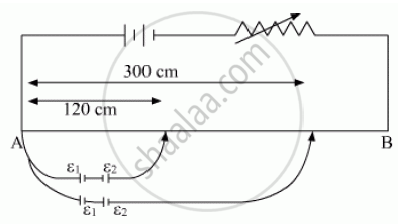
In the figure a long uniform potentiometer wire AB is having a constant potential gradient along its length. The null points for the two primary cells of emfs ε1 and ε2 connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of 120 cm and 300 cm from the end A. Find (i) ε1/ ε2 and (ii) position of null point for the cell ε1.
How is the sensitivity of a potentiometer increased?
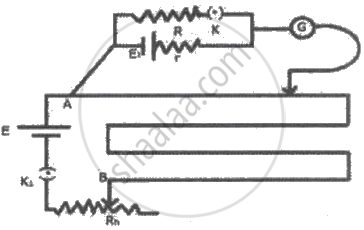
Two students ‘X’ and ‘Y’ perform an experiment on potentiometer separately using the circuit given below:
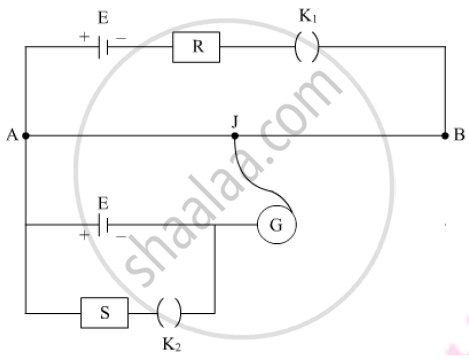
Keeping other parameters unchanged, how will the position of the null point be affected if
(i) ‘X’ increases the value of resistance R in the set-up by keeping the key K1 closed and the Key K2 opens?
(ii) ‘Y’ decreases the value of resistance S in the set-up, while the key K2 remains open and they K1 closed?
Justify.
The net resistance of an ammeter should be small to ensure that _______________ .
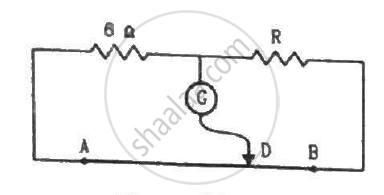
The potentiometer wire AB shown in the figure is 50 cm long. When AD = 30 cm, no deflection occurs in the galvanometer. Find R.
Define or describe a Potentiometer.
Why should not the jockey be slided along the potentiometer wire?
How is potential gradient measured? Explain.
What will be the effect on the position of zero deflection if only the current flowing through the potentiometer wire is increased?
A potentiometer wire has a length of 1.5 m and a resistance of 10 Ω. It is connected in series with the cell of emf 4 Volt and internal resistance 5 Ω. Calculate the potential drop per centimeter of the wire.
A potential drop per unit length along a wire is 5 × 10−3 V/m. If the emf of a cell balances against length 216 cm of this potentiometer wire, find the emf of the cell.
Why is a potentiometer preferred over a voltmeter for measuring emf?
When two cells of emf's E1 and E2 are connected in series so as to assist each other, their balancing length on a potentiometer wire is found to be 2.7 m. When the cells are connected in series so as to oppose each other, the balancing length is found to be 0.3 m. Compare the emf's of the two cells.
The emf of a cell is balanced by a length of 120 cm of a potentiometer wire. When the cell is shunted by a resistance of 10 Ω, the balancing length is reduced by 20 cm. Find the internal resistance of the cell.
The SI unit of the potential gradient is ______
When the null point is obtained in the potentiometer, the current is drawn from the ______
The instrument which can measure terminal potential difference as well as electromotive force (emf) is ______
What is the SI unit of potential gradient?
A potentiometer wire is 4m long and potential difference of 3V is maintained between the ends. The emf of the cell, which balances against a length of 100 cm of the potentiometer wire is ____________.
Two cells having unknown emfs E1 and E2 (E1 > E2) are connected in potentiometer circuit, so as to assist each other. The null point obtained is at 490 cm from the higher potential end. When cell E2 is connected, so as to oppose cell E1, the null point is obtained at 90 cm from the same end. The ratio of the emfs of two cells `("E"_1/"E"_2)` is ______.
The resistivity of potentiometer wire is 40 × 10-8 ohm - metre and its area of cross-section is 8 × 10-6 m2. If 0.2 ampere current is flowing through the wire, the potential gradient of the wire is ______.
A potentiometer is an ideal device for measuring potential difference because ______.
A potentiometer wire has length L For given cell of emf E, the balancing length is `"L"/3` from 3 the positive end of the wire. If the length of the potentiometer wire is increased by 50%, then for the same cell, the balance point is obtained at length.
If the e.m.f of a cell is not constant in the metre bridge experiment, then the ____________.
To determine the internal resistance of a cell by using potentiometer, the null point is at 1 m when cell is shunted by 3 Ω resistance and at a length 1.5 m when cell is shunted by 6 Ω resistance. The internal resistance of the cell is ______.
When two cells of e.m.f 1.5 V and 1.1 V connected in series are balanced on a potentiometer, the balancing length is 260 cm. The balancing length, when they are connected in opposition is (in cm) ____________.
A wire has a length of 2m and a resistance of 10Ω. It is connected in series with a resistance of 990Ω and a cell of e.m.f. 2V. The potential gradient along the wire will be ______
A student connected the circuit as shown in the figure to determine the internal resistance of a cell E1 by potentiometer (E > E1). He is unable to obtain the null point because ______.
In a potentiometer experiment when three cells A, B, C are connected in series the balancing length is found to be 740 cm. If A and B are connected in series, the balancing length is 440 cm and when B and C are connected in series, it is 540 cm. The e.m.f. of A, B, and C cells EA, EB, EC are respectively (in volt) ______
In the potentiometer experiment, the balancing length with a cell E1 of unknown e.m.f. is 'ℓ1' cm. By shunting the cell with resistance R Ω, the balancing length becomes `ℓ_1/2` cm, the internal resistance (r) of a cell is ______
In the potentiometer experiment, cells of e.m.f. E1 and E2 are connected in series (E1 > E2). the balancing length is 64 cm of the wire. If the polarity of E2 is reversed, the balancing length becomes 32 cm. The ratio `E_1/E_2` is ______
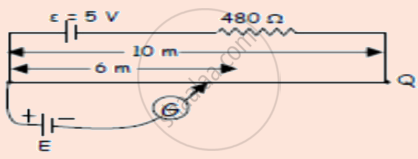
A 10 m long wire of uniform cross-section and 20 Ω resistance is used in a potentiometer. The wire is connected in series with a battery of 5 V along with an external resistance of 480 Ω. If an unknown emf E is balanced at 6.0 m length of the wire, then the value of unknown emf is ______.
Three resistance each of 4Ω are connected to from a triangle. The resistance b / w two terminal is
1°C rise in temperature is observed in a conductor by passing a certain current. If the current is double then the rise in temperature is approximately.
AB is a potentiometer wire (Figure). If the value of R is increased, in which direction will the balance point J shift?
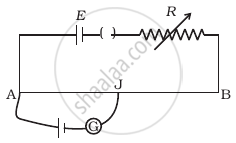
What is the effect of decreasing the current through the potentiometer on the null point?
A particle carrying 8 electron charges starts from rest and is accelerated through a potential difference of 9000 V. Calculate the KE acquired by it in keV.
What should be the diameter of a soap bubble such that the excess pressure inside it is 51.2 Pa? [Surface tension of soap solution = 3.2 × 10−2 N/m]
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Internal resistance of a cell using a potentiometer.
State dimension of potential gradient.
What is the internal resistance of the cell?
Draw neat labelled diagram of potentiometer as voltage divider.
