Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State the principle of a potentiometer. Define potential gradient. Obtain an expression for potential gradient in terms of resistivity of the potentiometer wire.
Solution
Principle
When a constant current is passed through a wire of uniform area of cross-section, the potential drop across any portion of the wire is directly proportional to the length of that portion.
Let V be the potential difference across certain portion of the wire, whose resistance is R. If I is the current through the wire, then \[V = IR\] We know that \[R = \rho\frac{l}{A}\], where l, A and ρ are length, area of cross-section and resistivity of the material of the wire, respectively.
\[\therefore V = I\rho\frac{l}{A}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{V}{l} = \frac{I\rho}{A}\]
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write two factors by which current sensitivity of a potentiometer can be increased.
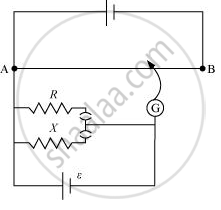
Figure 3.34 shows a potentiometer circuit for comparison of two resistances. The balance point with a standard resistor R = 10.0 Ω is found to be 58.3 cm, while that with the unknown resistance X is 68.5 cm. Determine the value of X. What might you do if you failed to find a balance point with the given cell of emf ε?
What are the disadvantages of a potentiometer?
The potentiometer is more sensitive, when ______.
Sensitivity of a given potentiometer can be decreased by ______.
Potentiometer measures the potential difference more accurately than a voltmeter, because ______.
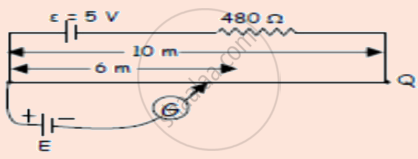
A 10 m long wire of uniform cross-section and 20 Ω resistance is used in a potentiometer. The wire is connected in series with a battery of 5 V along with an external resistance of 480 Ω. If an unknown emf E is balanced at 6.0 m length of the wire, then the value of unknown emf is ______.
Specific resistance of a conductor increase with.
In balanced meter bridge, the resistance of bridge wire is 0.1 Ω cm. Unknown resistance X is connected in left gap and 6 Ω in right gap, null point divides the wire in the ratio 2:3. Find the current drawn from the battery of 5 V having negligible resistance.
What is the value of resistance for an ideal voltmeter?
