Commerce (English Medium)
Science (English Medium)
Arts (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2013-2014
Date: March 2014
Advertisements
Figure shows the field lines due to a positive point charge. Give the sign of potential energy difference of a small negative charge between the points Q and P.
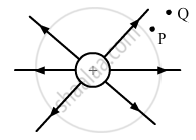
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
In both β− and β+ decay processes, the mass number of a nucleus remains the same, whereas the atomic number Z increases by one in β− decay and decreases by one in β+ decay. Explain giving reason.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Why must electrostatic field at the surface of a charged conductor be normal to the surface at every point? Give reason?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
A triangular loop of wire placed at abc is moved completely inside a magnetic field which is directed normal to the plane of the loop away from the reader to a new position a'b'c'. What is the direction of the current induced in the loop? Give reason.
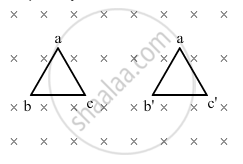
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
An electron in an atom revolves round the nucleus in an orbit of radius r with frequency v. Write the expression for the magnetic moment of the electron.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
A ray of light falls on a transparent sphere with centre C as shown in the figure. The ray emerges from the sphere parallel to the line AB. Find the angle of refraction at A if the refractive index of the material of the sphere is \[\sqrt{3}\].
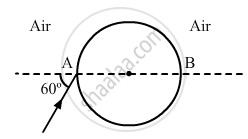
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Arrange the following electromagnetic waves in decreasing order of wavelength:
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Plot a graph showing the variation of photoelectric current with collector plate potential at a given frequency but for two different intensities I1 and I2, where I2 > I1.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
In the circuit shown in the figure, find the total resistance of the circuit and the current in the arm AD.
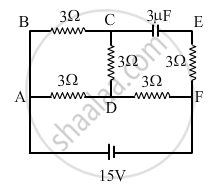
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Figure shows a ray of light passing through a prism. If the refracted ray QR is parallel to the base BC, show that (i) r1 = r2 = A/2 and (ii) angle of minimum deviation, Dm = 2i − A.
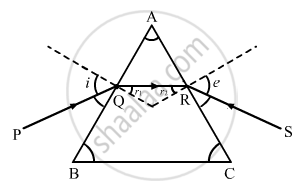
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Draw energy band diagrams of an n-type and p-type semiconductor at temperature T > 0 K. Mark the donor and acceptor energy levels with their energies.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Distinguish between a metal and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams ?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Show that the current leads the voltage in phase by π/2 in an AC circuit containing an ideal capacitor ?
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Two very small identical circular loops, (1) and (2), carrying equal currents I are placed vertically (with respect to the plane of the paper) with their geometrical axes perpendicular to each other as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field produced at the point O.
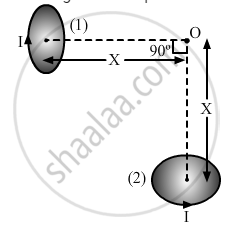
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
How does oscillating charge produce electromagnetic waves?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Sketch a schematic diagram depicting oscillating electric and magnetic fields of an em wave propagating along + z-direction ?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Give two points to distinguish between a paramagnetic and a diamagnetic substance ?
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Identify the gate equivalent to the circuit shown in the figure. Write its truth table.
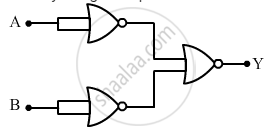
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Define the term modulation. Draw a block diagram of a simple modulator for obtaining AM signal ?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
A circuit is set up by connecting inductance L = 100 mH, resistor R = 100 Ω and a capacitor of reactance 200 Ω in series. An alternating emf of \[150\sqrt{2}\] V, 500/π Hz is applies across this series combination. Calculate the power dissipated in the resistor.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Advertisements
Why is zener diode fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n-sides of the junction?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Draw the circuit diagram of zener diode as a voltage regulator and briefly explains its working ?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
How is a photodiode fabricated?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Briefly explain its working. Draw its V - I characteristics for two different intensities of illumination ?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Two long straight parallel conductors 'a' and 'b', carrying steady currents Ia and Ib are separated by a distance d. Write the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field produced by the conductor 'a' at the points along the conductor 'b'. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, what is the nature and magnitude of the force between the two conductors?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Show with the help of a diagram how the force between the two conductors would change when the currents in them flow in the opposite directions?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Describe briefly how the Davisson-Germer experiment demonstrated the wave nature of electrons.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
An electron is accelerated from rest through a potential V. Obtain the expression for the de-Broglie wavelength associated with it ?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
A point charge (+Q) is kept in the vicinity of an uncharged conducting plate. Sketch the electric field lines between the charge and the plate?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Two infinitely large plane thin parallel sheets having surface charge densities σ1 and σ2 (σ1 > σ2) are shown in the figure. Write the magnitudes and directions of the net fields in the regions marked II and III.
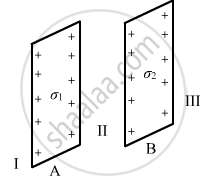
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
When Puja, a student of 10th class, watched her mother washing clothes in the open, she observed coloured soap bubbles and was curious to know why the soap bubbles appear coloured. In the evening when her father, an engineer by profession, came home, she asked him this question. Her father explained to her the basic phenomenon of physics due to which the soap bubbles appear coloured.
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Puja and her father?
(b) State the phenomenon of light involved in the formation of coloured soap bubbles.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Three concentric metallic shells A, B and C or radii a, b and c (a < b < c) have surface charge densities + σ, −σ and + σ, respectively as shown in the figure
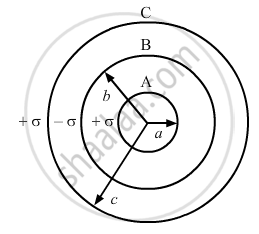
If shells A and C are at the same potential, then obtain the relation between the radii a, b and c.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
A toroidal solenoid with air core has an average radius of 15 cm, area of cross-section 12 cm2 and has 1200 turns. Calculate the self-inductance of the toroid. Assume the field to be uniform across the cross-section of the toroid.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Explain, with the help of a suitable diagram, the space wave mode of propagation. Give two examples in communication systems where this mode is used. What is the frequency range of these waves? Give reason for using this range of frequency.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Distinguish between unpolarised and linearly polarised light.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Advertisements
A partially plane polarised beam of light is passed through a polaroid. Show graphically the variation of the transmitted light intensity with angle of rotation of the polaroid ?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Explain with the help of a diagram how sunlight is polarised by scattering through atmospheric particles ?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Draw a labelled ray diagram of an astronomical telescope to show the image formation of a distant object. Write the main considerations required in selecting the objective and eyepiece lenses in order to have large magnifying power and high resolution of the telescope.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A compound microscope has an objective of focal length 1.25 cm and eyepiece of focal length 5 cm. A small object is kept at 2.5 cm from the objective. If the final image formed is at infinity, find the distance between the objective and the eyepiece ?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Write three characteristic features to distinguish between the interference fringes in Young's double slit experiment and the diffraction pattern obtained due to a narrow single slit.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
A parallel beam of light of wavelength 500 nm falls on a narrow slit and the resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 1 m away. It is observed that the first minimum is a distance of 2.5 mm away from the centre. Find the width of the slit.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Using Bohr's postulates, derive the expression for the total energy of the electron in the stationary states of the hydrogen atom ?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Using Rydberg formula, calculate the wavelengths of the spectral lines of the first member of the Lyman series and of the Balmer series.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Define the terms (i) half-life (T1/2) and (ii) average life (τ). Find out their relationships with the decay constant (λ).
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
A radioactive nucleus has a decay constant λ = 0.3465 (day)–1. How long would it take the nucleus to decay to 75% of its initial amount?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
State the principle of a potentiometer. Define potential gradient. Obtain an expression for potential gradient in terms of resistivity of the potentiometer wire.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Figure shows a long potentiometer wire AB having a constant potential gradient. The null points for the two primary cells of emfs ε1 and ε2 connected in the manner shown are obtained at a distance of l1 = 120 cm and l2 = 300 cm from the end A. Determine (i) ε1/ε2 and (ii) position of null point for the cell ε1 only.

Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Define the term 'drift velocity' of charge carriers in a conductor. Obtain the expression for the current density in terms of relaxation time ?
Chapter:
A 100 V battery is connected to the electric network as shown. If the power consumed in the 2 Ω resistor is 200 W, determine the power dissipated in the 5 Ω resistor.
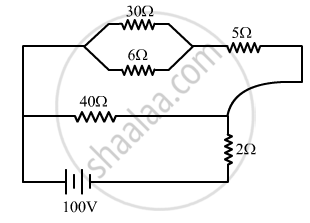
Chapter:
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2013 - 2014
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2014 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
