Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Show that the current leads the voltage in phase by π/2 in an AC circuit containing an ideal capacitor ?
Solution
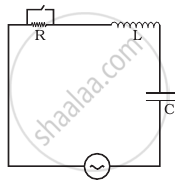
Let us consider a capacitor C connected to an AC source as shown below.

Let the AC voltage applied be
`v = v_msinωt`
`∴ v = q/C`
Applying Kirchhoff’s loop rule, we have:
` v_msinωt q/C`
`i = (dq)/dt`
`∴ i = (d)/dt( v_mCsinωt) `
`ωCv_mcos(ωt)`
`cos ωt = sinωt+π/2`
`∴ i = i_msin(ωt+π/2)`
`i_m = ωCv_m`
`i =(v_m)/((1/(ωC)))`
RELATED QUESTIONS
A transformer is designed to convert an AC voltage of 220 V to an AC voltage of 12 V. If the input terminals are connected to a DC voltage of 220 V, the transformer usually burns. Explain.
A capacitor acts as an infinite resistance for ______.
An AC source producing emf ε = ε0 [cos (100 π s−1)t + cos (500 π s−1)t] is connected in series with a capacitor and a resistor. The steady-state current in the circuit is found to be i = i1 cos [(100 π s−1)t + φ1) + i2 cos [(500π s−1)t + ϕ2]. So,
A bulb rated 60 W at 220 V is connected across a household supply of alternating voltage of 220 V. Calculate the maximum instantaneous current through the filament.
A transformer has 50 turns in the primary and 100 in the secondary. If the primary is connected to a 220 V DC supply, what will be the voltage across the secondary?
A.C. power is transmitted from a power house at a high voltage as ______.
A capacitor has capacitance C and reactance X, if capacitance and frequency become double, then reactance will be ______.
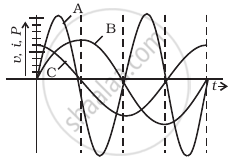
A device ‘X’ is connected to an a.c source. The variation of voltage, current and power in one complete cycle is shown in figure.
- Which curve shows power consumption over a full cycle?
- What is the average power consumption over a cycle?
- Identify the device ‘X’.
In the LCR circuit shown in figure, the ac driving voltage is v = vm sin ωt.
- Write down the equation of motion for q (t).
- At t = t0, the voltage source stops and R is short circuited. Now write down how much energy is stored in each of L and C.
- Describe subsequent motion of charges.