Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Distinguish between a metal and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams ?
Solution
Metals: (i) For metals, the valence band is completely filled and the conduction band can have two possibilities—either it is partially filled with an extremely small energy gap between the valence and conduction bands or it is empty, with the two bands overlapping each other as shown below:
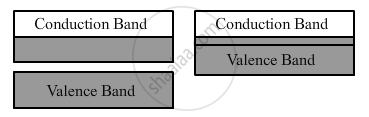
(ii) On applying an small even electric field, metals can conduct electricity.
Insulators: (i) For insulators, the energy gap between the conduction and valence bands is very large. Also, the conduction band is practically empty, as shown below:
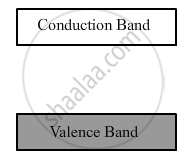
(ii) When an electric field is applied across such a solid, the electrons find it difficult to acquire such a large amount of energy to reach the conduction band. Thus, the conduction band continues to be empty. That is why no current flows through insulators.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw energy band diagrams of an n-type and p-type semiconductor at temperature T > 0 K. Mark the donor and acceptor energy levels with their energies.
There are energy bands in a solid. Do we have really continuous energy variation in a band ro do we have very closely spaced but still discrete energy levels?
When an impurity is doped into an intrinsic semiconductor, the conductivity of the semiconductor
When a semiconducting material is doped with an impurity, new acceptor levels are created. In a particular thermal collision, a valence electron receives an energy equal to 2kT and just reaches one of the acceptor levels. Assuming that the energy of the electron was at the top edge of the valence band and that the temperature T is equal to 300 K, find the energy of the acceptor levels above the valence band.
Suppose the energy liberated in the recombination of a hole-electron pair is converted into electromagnetic radiation. If the maximum wavelength emitted is 820 nm, what is the band gap?
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
Hydrogen atom in n = 3 state has a lifetime of 10-10 sec. The number of revolutions an electron makes in the n = 3 state before returning to the ground state is ______.
Useful data
`1/(4pi∈_0) = 8.99 xx 10^-34`N m2 C-2; e = 1.60 10-19 C; h = 6.63 10-34 Js; me = 9 × 10-3 kg
A window air conditioner is placed on a table inside a well-insulated apartment, plugged in and turned on. What happens to the average temperature of the apartment?
Two radioactive substances A and B have decay constants 3λ and λ respectively. At t = 0 they have the same number of nuclei. The ratio of the number of nuclei of A to those of B will be `1/"e"` after a time interval:
Hole are majority charge carrier in
Which one of the following elements will require the highest energy to take out an electron from them?
Pb, Ge, C and Si
