Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Distinguish between a metal and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams ?
उत्तर
Metals: (i) For metals, the valence band is completely filled and the conduction band can have two possibilities—either it is partially filled with an extremely small energy gap between the valence and conduction bands or it is empty, with the two bands overlapping each other as shown below:
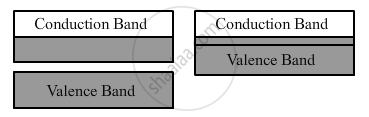
(ii) On applying an small even electric field, metals can conduct electricity.
Insulators: (i) For insulators, the energy gap between the conduction and valence bands is very large. Also, the conduction band is practically empty, as shown below:
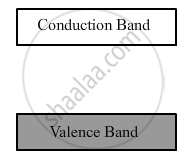
(ii) When an electric field is applied across such a solid, the electrons find it difficult to acquire such a large amount of energy to reach the conduction band. Thus, the conduction band continues to be empty. That is why no current flows through insulators.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between a conductor, a semiconductor and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams.
What is the resistance of an intrinsic semiconductor at 0 K?
Electric conduction in a semiconductor takes place due to
In a transistor,
Find the maximum wavelength of electromagnetic radiation which can create a hole-electron pair in germanium. The band gap in germanium is 0.65 eV.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
The conductivity of an intrinsic semiconductor depends on temperature as σ = σ0e−ΔE/2kT, where σ0 is a constant. Find the temperature at which the conductivity of an intrinsic germanium semiconductor will be double of its value at T = 300 K. Assume that the gap for germanium is 0.650 eV and remains constant as the temperature is increased.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
A semiconducting material has a band gap of 1 eV. Acceptor impurities are doped into it which create acceptor levels 1 meV above the valence band. Assume that the transition from one energy level to the other is almost forbidden if kT is less than 1/50 of the energy gap. Also if kT is more than twice the gap, the upper levels have maximum population. The temperature of the semiconductor is increased from 0 K. The concentration of the holes increases with temperature and after a certain temperature it becomes approximately constant. As the temperature is further increased, the hole concentration again starts increasing at a certain temperature. Find the order of the temperature range in which the hole concentration remains approximately constant.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
A hole in a. p – type semiconductor is
The energy required by an electron to jump the forbidden band in silicon at room temperature is about ______.
With reference to semiconductor physics, answer the following question.
In which material “Forbidden band” is absent?
