Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Suppose the energy liberated in the recombination of a hole-electron pair is converted into electromagnetic radiation. If the maximum wavelength emitted is 820 nm, what is the band gap?
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
Solution
Given:
Wavelength, `lambda = 820 "nm"`
The minimum energy released in the recombination of a conduction band electron with a valence band hole is equal to the band gap of the material.
Band gap, \[E = \frac{hc}{\lambda}\]
\[\Rightarrow E = \frac{1240}{820}\frac{eV - \text{ nm}}{\text{ nm} }\]
\[ \Rightarrow E = 1 . 5 \text{ eV }\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Distinguish between a conductor and a semi conductor on the basis of energy band diagram
There are energy bands in a solid. Do we have really continuous energy variation in a band ro do we have very closely spaced but still discrete energy levels?
When an electron goes from the valence band to the conduction band in silicon, its energy is increased by 1.1 eV. The average energy exchanged in a thermal collision is of the order of kT which is only 0.026 eV at room temperature. How is a thermal collision able to take some to the electrons from the valence band to the conduction band?
Electric conduction in a semiconductor takes place due to
An electric field is applied to a semiconductor. Let the number of charge carries be nand the average drift speed by v. If the temperature is increased,
Let np and ne be the number of holes and conduction electrons in an intrinsic semiconductor.
When an impurity is doped into an intrinsic semiconductor, the conductivity of the semiconductor
Two identical capacitors A and B are charged to the same potential V and are connected in two circuits at t = 0 as shown in figure. The charges on the capacitors at a time t = CRare, respectively,
The impurity atoms with which pure silicon may be doped to make it a p-type semiconductor are those of
(a) phosphorus
(b) boron
(c) antimony
(d) aluminium.
The electrical conductivity of pure germanium can be increased by
(a) increasing the temperature
(b) doping acceptor impurities
(c) doping donor impurities
(d) irradiating ultraviolet light on it.
In a pure semiconductor, the number of conduction election 6 × 1019 per cubic metre. How many holes are there in a sample of size 1 cm × 1 mm?
Indium antimonide has a band gap of 0.23 eV between the valence and the conduction band. Find the temperature at which kT equals the band gap.
Find the maximum wavelength of electromagnetic radiation which can create a hole-electron pair in germanium. The band gap in germanium is 0.65 eV.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
If the lattice constant of this semiconductor is decreased, then which of the following is correct?
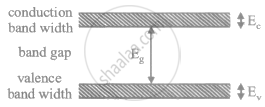
An n-type semiconductor is
A semiconductor is cooled from T.K to T2K its resistance will
In a common base configuration Ie = 1 mA α = 0.95 the value of base current is
The reaction between α and β parameter of a transistor is given by
Hole are majority charge carrier in
Draw the energy band diagrams for conductors, semiconductors and insulators. Which band determines the electrical conductivity of a solid? How is the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor affected with rise in its temperature? Explain.
