Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the maximum wavelength of electromagnetic radiation which can create a hole-electron pair in germanium. The band gap in germanium is 0.65 eV.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
Solution
Given:
Band gap of germanium, E = 0.65 eV
Wavelength of the incident radiation, λ = ?
For the electron‒hole pair creation, the energy of the incident radiation should be at least equal to the band gap of the material.
So,
\[E = \frac{hc}{\lambda}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda = \frac{hc}{E} = \frac{1242 eV - \text{ nm }}{0 . 65 eV}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda = 1910 . 7 \times {10}^{- 9} \text{m}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda \approx 1 . 9 \times {10}^{- 6} \text{m}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Electric conduction in a semiconductor takes place due to
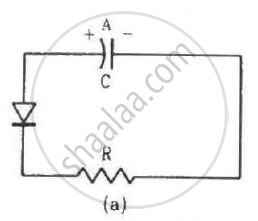
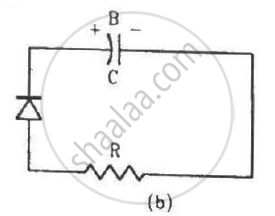
Two identical capacitors A and B are charged to the same potential V and are connected in two circuits at t = 0 as shown in figure. The charges on the capacitors at a time t = CRare, respectively,
In a semiconductor,
(a) there are no free electrons at 0 K
(b) there are no free electrons at any temperature
(c) the number of free electrons increases with temperature
(d) the number of free electrons is less than that in a conductor.
In a pure semiconductor, the number of conduction election 6 × 1019 per cubic metre. How many holes are there in a sample of size 1 cm × 1 mm?
The band gap between the valence and the conduction bands in zinc oxide (ZnO) is 3.2 eV. Suppose an electron in the conduction band combines with a hole in the valence band and the excess energy is released in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Find the maximum wavelength that can be emitted in this process.
Suppose the energy liberated in the recombination of a hole-electron pair is converted into electromagnetic radiation. If the maximum wavelength emitted is 820 nm, what is the band gap?
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
The conductivity of a pure semiconductor is roughly proportional to T3/2 e−ΔE/2kT where ΔE is the band gap. The band gap for germanium is 0.74 eV at 4 K and 0.67 eV at 300 K. By what factor does the conductivity of pure germanium increase as the temperature is raised from 4 K to 300 K?
The product of the hole concentration and the conduction electron concentration turns out to be independent of the amount of any impurity doped. The concentration of conduction electrons in germanium is 6 × 1019 per cubic metref conduction electrons increases to 2 × 1023 per cubic metre. Find the concentration of the holes in the doped germanium.. When some phosphorus impurity is doped into a germanium sample, the concentration o
A semiconducting material has a band gap of 1 eV. Acceptor impurities are doped into it which create acceptor levels 1 meV above the valence band. Assume that the transition from one energy level to the other is almost forbidden if kT is less than 1/50 of the energy gap. Also if kT is more than twice the gap, the upper levels have maximum population. The temperature of the semiconductor is increased from 0 K. The concentration of the holes increases with temperature and after a certain temperature it becomes approximately constant. As the temperature is further increased, the hole concentration again starts increasing at a certain temperature. Find the order of the temperature range in which the hole concentration remains approximately constant.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
With reference to Semiconductor Physics,
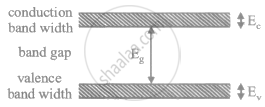
Draw a labelled energy band diagram for a semiconductor.
What is forbidden band?
If the lattice constant of this semiconductor is decreased, then which of the following is correct?
A hole in a. p – type semiconductor is
For germanium crystal, the forbidden gas energy gap
In a semiconductor, the forbidden energy gap between the valence, band and the conduction band is of the order of
Hole are majority charge carrier in
The energy required by an electron to jump the forbidden band in silicon at room temperature is about ______.
With reference to semiconductor physics, answer the following question.
In which material “Forbidden band” is absent?
