Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose the energy liberated in the recombination of a hole-electron pair is converted into electromagnetic radiation. If the maximum wavelength emitted is 820 nm, what is the band gap?
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
उत्तर
Given:
Wavelength, `lambda = 820 "nm"`
The minimum energy released in the recombination of a conduction band electron with a valence band hole is equal to the band gap of the material.
Band gap, \[E = \frac{hc}{\lambda}\]
\[\Rightarrow E = \frac{1240}{820}\frac{eV - \text{ nm}}{\text{ nm} }\]
\[ \Rightarrow E = 1 . 5 \text{ eV }\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between a metal and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams ?
Write two characteristic features to distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors ?
Distinguish between a conductor, a semiconductor and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams.
What is the resistance of an intrinsic semiconductor at 0 K?
Two identical capacitors A and B are charged to the same potential V and are connected in two circuits at t = 0 as shown in figure. The charges on the capacitors at a time t = CRare, respectively,
In a transistor,
The electrical conductivity of pure germanium can be increased by
(a) increasing the temperature
(b) doping acceptor impurities
(c) doping donor impurities
(d) irradiating ultraviolet light on it.
The band gap for silicon is 1.1 eV. (a) Find the ratio of the band gap to kT for silicon at room temperature 300 K. (b) At what temperature does this ratio become one tents of the value at 300 K? (Silicon will not retain its structure at these high temperatures.)
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
When a semiconducting material is doped with an impurity, new acceptor levels are created. In a particular thermal collision, a valence electron receives an energy equal to 2kT and just reaches one of the acceptor levels. Assuming that the energy of the electron was at the top edge of the valence band and that the temperature T is equal to 300 K, find the energy of the acceptor levels above the valence band.
Estimate the proportion of boron impurity which will increase the conductivity of a pure silicon sample by a factor of 100. Assume that each boron atom creates a hole and the concentration of holes in pure silicon at the same temperature is 7 × 1015 holes per cubic metre. Density of silicon 5 × 1028 atoms per cubic metre.
Hydrogen atom in n = 3 state has a lifetime of 10-10 sec. The number of revolutions an electron makes in the n = 3 state before returning to the ground state is ______.
Useful data
`1/(4pi∈_0) = 8.99 xx 10^-34`N m2 C-2; e = 1.60 10-19 C; h = 6.63 10-34 Js; me = 9 × 10-3 kg
A window air conditioner is placed on a table inside a well-insulated apartment, plugged in and turned on. What happens to the average temperature of the apartment?
If the lattice constant of this semiconductor is decreased, then which of the following is correct?
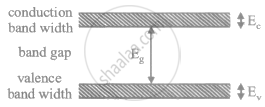
An n-type semiconductor is
For germanium crystal, the forbidden gas energy gap
A semiconductor is cooled from T.K to T2K its resistance will
The valance of an impurity added to germanium crystal in order to convert it into p-type semiconductor is
With reference to semiconductor physics, answer the following question.
In which material “Forbidden band” is absent?
