Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The band gap for silicon is 1.1 eV. (a) Find the ratio of the band gap to kT for silicon at room temperature 300 K. (b) At what temperature does this ratio become one tents of the value at 300 K? (Silicon will not retain its structure at these high temperatures.)
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
उत्तर
Given:-
Band gap of silicon, E = 1.1 eV
Temperature, T = 300 K
Boltzmann's constant, k = \[8 . 62 \times {10}^{- 5} e\]V/K
(a) We need to find out the ratio of the band gap to kT.
Ratio \[= \frac{1 . 1}{kT}\]
\[= \frac{1 . 1}{8 . 62 \times {10}^{- 5} \times 3 \times {10}^2}\]
\[ = 42 . 53 = 43\]
(b) The new ratio is `1/10` th of the earlier ratio.
i.e. New ratio = 4.253
We know,
Ratio = (Band gap)/(kT)
\[\Rightarrow 4 . 253 = \frac{1 . 1}{8 . 62 \times {10}^{- 5} \times T}\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = \frac{1 . 1}{8 . 62 \times {10}^{- 5} \times 4 . 253}\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = 3000 . 4 K \approx 3000 K\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between a conductor and a semi conductor on the basis of energy band diagram
Draw the necessary energy band diagrams to distinguish between conductors, semiconductors and insulators.
How does the change in temperature affect the behaviour of these materials ? Explain briefly.
Draw separate energy band diagram for conductors, semiconductors and insulators and
label each of them.
Write two characteristic features to distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors ?
How many 1s energy states are present in one mole of sodium vapour? Are they all filled in normal conditions? How many 3s energy states are present in one mole of sodium vapour? Are they all filled in normal conditions?
There are energy bands in a solid. Do we have really continuous energy variation in a band ro do we have very closely spaced but still discrete energy levels?
Let np and ne be the number of holes and conduction electrons in an intrinsic semiconductor.
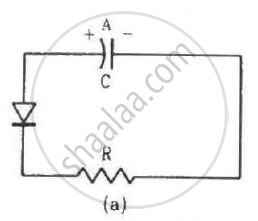
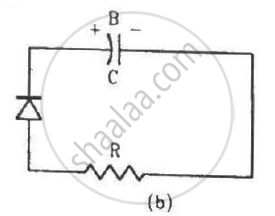
Two identical capacitors A and B are charged to the same potential V and are connected in two circuits at t = 0 as shown in figure. The charges on the capacitors at a time t = CRare, respectively,
An incomplete sentence about transistors is given below:
The emitter−..... junction is __ and the collector−..... junction is __. The appropriate words for the dotted empty positions are, respectively,
In a semiconductor,
(a) there are no free electrons at 0 K
(b) there are no free electrons at any temperature
(c) the number of free electrons increases with temperature
(d) the number of free electrons is less than that in a conductor.
A semiconductor is doped with a donor impurity.
The product of the hole concentration and the conduction electron concentration turns out to be independent of the amount of any impurity doped. The concentration of conduction electrons in germanium is 6 × 1019 per cubic metref conduction electrons increases to 2 × 1023 per cubic metre. Find the concentration of the holes in the doped germanium.. When some phosphorus impurity is doped into a germanium sample, the concentration o
The conductivity of an intrinsic semiconductor depends on temperature as σ = σ0e−ΔE/2kT, where σ0 is a constant. Find the temperature at which the conductivity of an intrinsic germanium semiconductor will be double of its value at T = 300 K. Assume that the gap for germanium is 0.650 eV and remains constant as the temperature is increased.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
The energy of a hydrogen atom in the ground state is −13.6 eV. The energy of a He+ ion in the first excited state will be:
In a semiconductor, the forbidden energy gap between the valence, band and the conduction band is of the order of
In a common base configuration Ie = 1 mA α = 0.95 the value of base current is
With reference to semiconductor physics, answer the following question.
In which material “Forbidden band” is absent?
