Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
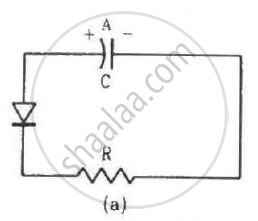
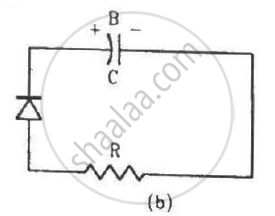
Two identical capacitors A and B are charged to the same potential V and are connected in two circuits at t = 0 as shown in figure. The charges on the capacitors at a time t = CRare, respectively,
पर्याय
VC, VC
VC/e, VC
VC, VC/e
VC/e, VC/e.
उत्तर
In circuit (a), the diode is forward biassed. So, it offers negligible resistance to the flow of current and can thus be replaced by a short circuit. Now, the capacitor charge will leak through the resistance and decay exponentially with time.
Capacitor charge = `(VC)/e`
In circuit (b), the diode is reverse biassed. So, it offers infinite resistance to the current flow and can thus be replaced by an open circuit. As the circuit is open now, no current can flow across the resistance. So, the charge in the capacitor cannot leak through the resistor.
Capacitor charge = VC
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between a conductor and a semi conductor on the basis of energy band diagram
Distinguish between a metal and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams ?
Write two characteristic features to distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors ?
Let np and ne be the number of holes and conduction electrons in an intrinsic semiconductor.
A p-type semiconductor is
When an impurity is doped into an intrinsic semiconductor, the conductivity of the semiconductor
The impurity atoms with which pure silicon may be doped to make it a p-type semiconductor are those of
(a) phosphorus
(b) boron
(c) antimony
(d) aluminium.
The conductivity of a pure semiconductor is roughly proportional to T3/2 e−ΔE/2kT where ΔE is the band gap. The band gap for germanium is 0.74 eV at 4 K and 0.67 eV at 300 K. By what factor does the conductivity of pure germanium increase as the temperature is raised from 4 K to 300 K?
The product of the hole concentration and the conduction electron concentration turns out to be independent of the amount of any impurity doped. The concentration of conduction electrons in germanium is 6 × 1019 per cubic metref conduction electrons increases to 2 × 1023 per cubic metre. Find the concentration of the holes in the doped germanium.. When some phosphorus impurity is doped into a germanium sample, the concentration o
With reference to Semiconductor Physics,
Draw a labelled energy band diagram for a semiconductor.
A window air conditioner is placed on a table inside a well-insulated apartment, plugged in and turned on. What happens to the average temperature of the apartment?
Two radioactive substances A and B have decay constants 3λ and λ respectively. At t = 0 they have the same number of nuclei. The ratio of the number of nuclei of A to those of B will be `1/"e"` after a time interval:
If the lattice constant of this semiconductor is decreased, then which of the following is correct?
The energy of a hydrogen atom in the ground state is −13.6 eV. The energy of a He+ ion in the first excited state will be:
For germanium crystal, the forbidden gas energy gap
In a common-base circuit calculate the change in the base current if that in the emitter current is αmA and a = 0.98
The valance of an impurity added to germanium crystal in order to convert it into p-type semiconductor is
The reaction between α and β parameter of a transistor is given by
Hole are majority charge carrier in
With reference to semiconductor physics, answer the following question.
What is meant by “Forbidden band" of energy levels?
