Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The impurity atoms with which pure silicon may be doped to make it a p-type semiconductor are those of
(a) phosphorus
(b) boron
(c) antimony
(d) aluminium.
उत्तर
(b) boron
(d) aluminium
A p-type semiconductor is formed by doping an intrinsic semiconductor with a trivalent atom (atom having valency 3). As phosphorous and boron have three valence electrons, they can be doped with silicon to make a p-type semiconductor.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
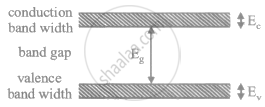
Distinguish between a metal and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams ?
Write two characteristic features to distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors ?
How many 1s energy states are present in one mole of sodium vapour? Are they all filled in normal conditions? How many 3s energy states are present in one mole of sodium vapour? Are they all filled in normal conditions?
What is the resistance of an intrinsic semiconductor at 0 K?
Let np and ne be the number of holes and conduction electrons in an intrinsic semiconductor.
Two identical capacitors A and B are charged to the same potential V and are connected in two circuits at t = 0 as shown in figure. The charges on the capacitors at a time t = CRare, respectively,
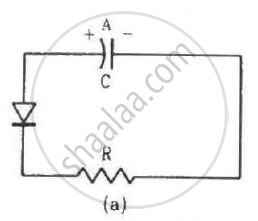
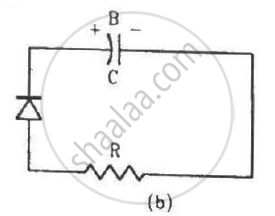
In a transistor,
An incomplete sentence about transistors is given below:
The emitter−..... junction is __ and the collector−..... junction is __. The appropriate words for the dotted empty positions are, respectively,
The electrical conductivity of pure germanium can be increased by
(a) increasing the temperature
(b) doping acceptor impurities
(c) doping donor impurities
(d) irradiating ultraviolet light on it.
Indium antimonide has a band gap of 0.23 eV between the valence and the conduction band. Find the temperature at which kT equals the band gap.
When a semiconducting material is doped with an impurity, new acceptor levels are created. In a particular thermal collision, a valence electron receives an energy equal to 2kT and just reaches one of the acceptor levels. Assuming that the energy of the electron was at the top edge of the valence band and that the temperature T is equal to 300 K, find the energy of the acceptor levels above the valence band.
The conductivity of an intrinsic semiconductor depends on temperature as σ = σ0e−ΔE/2kT, where σ0 is a constant. Find the temperature at which the conductivity of an intrinsic germanium semiconductor will be double of its value at T = 300 K. Assume that the gap for germanium is 0.650 eV and remains constant as the temperature is increased.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
What is forbidden band?
A window air conditioner is placed on a table inside a well-insulated apartment, plugged in and turned on. What happens to the average temperature of the apartment?
If the lattice constant of this semiconductor is decreased, then which of the following is correct?
The reaction between α and β parameter of a transistor is given by
Draw the energy band diagrams for conductors, semiconductors and insulators. Which band determines the electrical conductivity of a solid? How is the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor affected with rise in its temperature? Explain.
