Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The impurity atoms with which pure silicon may be doped to make it a p-type semiconductor are those of
(a) phosphorus
(b) boron
(c) antimony
(d) aluminium.
Solution
(b) boron
(d) aluminium
A p-type semiconductor is formed by doping an intrinsic semiconductor with a trivalent atom (atom having valency 3). As phosphorous and boron have three valence electrons, they can be doped with silicon to make a p-type semiconductor.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw the necessary energy band diagrams to distinguish between conductors, semiconductors and insulators.
How does the change in temperature affect the behaviour of these materials ? Explain briefly.
Draw energy band diagrams of an n-type and p-type semiconductor at temperature T > 0 K. Mark the donor and acceptor energy levels with their energies.
Write two characteristic features to distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors ?
When an electron goes from the valence band to the conduction band in silicon, its energy is increased by 1.1 eV. The average energy exchanged in a thermal collision is of the order of kT which is only 0.026 eV at room temperature. How is a thermal collision able to take some to the electrons from the valence band to the conduction band?
We have valence electrons and conduction electrons in a semiconductor. Do we also have 'valence holes' and 'conduction holes'?
An electric field is applied to a semiconductor. Let the number of charge carries be nand the average drift speed by v. If the temperature is increased,
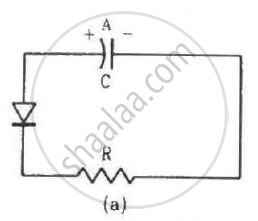
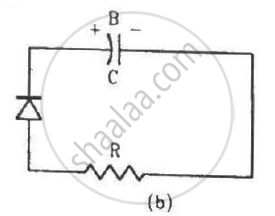
Two identical capacitors A and B are charged to the same potential V and are connected in two circuits at t = 0 as shown in figure. The charges on the capacitors at a time t = CRare, respectively,
Calculate the number of states per cubic metre of sodium in 3s band. The density of sodium is 1013 kgm−3. How many of them are empty?
The band gap between the valence and the conduction bands in zinc oxide (ZnO) is 3.2 eV. Suppose an electron in the conduction band combines with a hole in the valence band and the excess energy is released in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Find the maximum wavelength that can be emitted in this process.
Suppose the energy liberated in the recombination of a hole-electron pair is converted into electromagnetic radiation. If the maximum wavelength emitted is 820 nm, what is the band gap?
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
Find the maximum wavelength of electromagnetic radiation which can create a hole-electron pair in germanium. The band gap in germanium is 0.65 eV.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
The conductivity of a pure semiconductor is roughly proportional to T3/2 e−ΔE/2kT where ΔE is the band gap. The band gap for germanium is 0.74 eV at 4 K and 0.67 eV at 300 K. By what factor does the conductivity of pure germanium increase as the temperature is raised from 4 K to 300 K?
The product of the hole concentration and the conduction electron concentration turns out to be independent of the amount of any impurity doped. The concentration of conduction electrons in germanium is 6 × 1019 per cubic metref conduction electrons increases to 2 × 1023 per cubic metre. Find the concentration of the holes in the doped germanium.. When some phosphorus impurity is doped into a germanium sample, the concentration o
The conductivity of an intrinsic semiconductor depends on temperature as σ = σ0e−ΔE/2kT, where σ0 is a constant. Find the temperature at which the conductivity of an intrinsic germanium semiconductor will be double of its value at T = 300 K. Assume that the gap for germanium is 0.650 eV and remains constant as the temperature is increased.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
In a common-base circuit calculate the change in the base current if that in the emitter current is αmA and a = 0.98
In a common base configuration Ie = 1 mA α = 0.95 the value of base current is
Draw the energy band diagrams for conductors, semiconductors and insulators. Which band determines the electrical conductivity of a solid? How is the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor affected with rise in its temperature? Explain.
- Assertion (A): In insulators, the forbidden gap is very large.
- Reason (R): The valence electrons in an atom of an insulator are very tightly bound to the nucleus.
With reference to semiconductor physics, answer the following question.
In which material “Forbidden band” is absent?
