Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Distinguish between a conductor and a semi conductor on the basis of energy band diagram
उत्तर
Distinction between conductor and insulator:
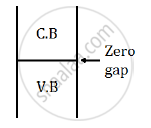
Conductor: In a conductor, the valance band is either partially filled or completely filled.
It has zero forbidden energy gap between the conduction band and the valance band.
The energy band diagram can be represented as shown below:
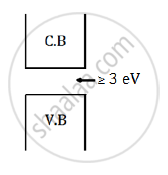
Insulator: In an insulator, the valance band is completely filled and the conduction band is empty.
The forbidden energy gap between the conduction band and the valance band is greater than or equal to 3 eV
The energy band diagram can be represented as shown below:
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw separate energy band diagram for conductors, semiconductors and insulators and
label each of them.
Distinguish between a conductor, a semiconductor and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams.
There are energy bands in a solid. Do we have really continuous energy variation in a band ro do we have very closely spaced but still discrete energy levels?
We have valence electrons and conduction electrons in a semiconductor. Do we also have 'valence holes' and 'conduction holes'?
A semiconductor is doped with a donor impurity.
Suppose the energy liberated in the recombination of a hole-electron pair is converted into electromagnetic radiation. If the maximum wavelength emitted is 820 nm, what is the band gap?
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
The product of the hole concentration and the conduction electron concentration turns out to be independent of the amount of any impurity doped. The concentration of conduction electrons in germanium is 6 × 1019 per cubic metref conduction electrons increases to 2 × 1023 per cubic metre. Find the concentration of the holes in the doped germanium.. When some phosphorus impurity is doped into a germanium sample, the concentration o
The conductivity of an intrinsic semiconductor depends on temperature as σ = σ0e−ΔE/2kT, where σ0 is a constant. Find the temperature at which the conductivity of an intrinsic germanium semiconductor will be double of its value at T = 300 K. Assume that the gap for germanium is 0.650 eV and remains constant as the temperature is increased.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
If the lattice constant of this semiconductor is decreased, then which of the following is correct?
An n-type semiconductor is
