Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
When an impurity is doped into an intrinsic semiconductor, the conductivity of the semiconductor
Options
increases
decreases
remains the same
become zero.
Solution
increases
When an impurity (either a p-type atom or an n-type atom) is doped into an intrinsic semiconductor, it increases the number of charge carriers in the intrinsic semiconductor. As conductivity is directly related to the number of charge carriers, the conductivity of a semiconductor increases with doping.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
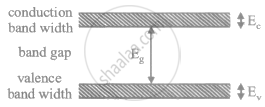
Distinguish between a conductor and a semi conductor on the basis of energy band diagram
Draw energy band diagrams of an n-type and p-type semiconductor at temperature T > 0 K. Mark the donor and acceptor energy levels with their energies.
In semiconductors, thermal collisions are responsible for taking a valence electron to the conduction band. Why does the number of conduction electrons not go on increasing with time as thermal collisions continuously take place?
An electric field is applied to a semiconductor. Let the number of charge carries be nand the average drift speed by v. If the temperature is increased,
Let np and ne be the number of holes and conduction electrons in an intrinsic semiconductor.
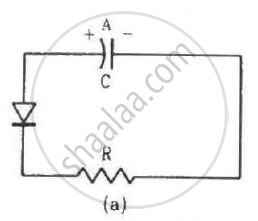
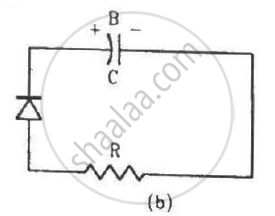
Two identical capacitors A and B are charged to the same potential V and are connected in two circuits at t = 0 as shown in figure. The charges on the capacitors at a time t = CRare, respectively,
The electrical conductivity of pure germanium can be increased by
(a) increasing the temperature
(b) doping acceptor impurities
(c) doping donor impurities
(d) irradiating ultraviolet light on it.
A semiconductor is doped with a donor impurity.
Find the maximum wavelength of electromagnetic radiation which can create a hole-electron pair in germanium. The band gap in germanium is 0.65 eV.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
Let ΔE denote the energy gap between the valence band and the conduction band. The population of conduction electrons (and of the holes) is roughly proportional to e−ΔE/2kT. Find the ratio of the concentration of conduction electrons in diamond to the in silicon at room temperature 300 K. ΔE for silicon is 1.1 eV and for diamond is 6.1 eV. How many conduction electrons are likely to be in one cubic metre of diamond?
Estimate the proportion of boron impurity which will increase the conductivity of a pure silicon sample by a factor of 100. Assume that each boron atom creates a hole and the concentration of holes in pure silicon at the same temperature is 7 × 1015 holes per cubic metre. Density of silicon 5 × 1028 atoms per cubic metre.
With reference to Semiconductor Physics,
Draw a labelled energy band diagram for a semiconductor.
Two radioactive substances A and B have decay constants 3λ and λ respectively. At t = 0 they have the same number of nuclei. The ratio of the number of nuclei of A to those of B will be `1/"e"` after a time interval:
If the lattice constant of this semiconductor is decreased, then which of the following is correct?
The energy of a hydrogen atom in the ground state is −13.6 eV. The energy of a He+ ion in the first excited state will be:
A semiconductor is cooled from T.K to T2K its resistance will
The reaction between α and β parameter of a transistor is given by
Three photo diodes D1, D2 and D3 are made of semiconductors having band gaps of 2.5 eV, 2 eV and 3 eV, respectively. Which 0 ones will be able to detect light of wavelength 6000 Å?
The energy required by an electron to jump the forbidden band in silicon at room temperature is about ______.
