Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If the two ends of a p-n junction are joined by a wire,
Options
there will not be a steady current in the circuit
there will be a steady current from the n-side to the p-side
there will a steady current from the p-side to the n-side
there may or may not be a current depending upon the resistance of the connecting wire
Solution
there will not be a steady current in the circuit
In a p‒n junction, current flows only if it is connected to the battery. If two ends of a p‒njunction are joined by a wire, then there will be diffusion and drift currents in the circuit and they will cancel each other. Hence, no current will flow in the circuit.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a p-n junction diode, the current I can be expressed as
I = `"I"_0 exp ("eV"/(2"k"_"BT") - 1)`
where I0 is called the reverse saturation current, V is the voltage across the diode and is positive for forward bias and negative for reverse bias, and I is the current through the diode, kBis the Boltzmann constant (8.6×10−5 eV/K) and T is the absolute temperature. If for a given diode I0 = 5 × 10−12 A and T = 300 K, then
(a) What will be the forward current at a forward voltage of 0.6 V?
(b) What will be the increase in the current if the voltage across the diode is increased to 0.7 V?
(c) What is the dynamic resistance?
(d) What will be the current if reverse bias voltage changes from 1 V to 2 V?
Write the two processes that take place in the formation of a p-n junction.
Explain briefly with the help of necessary diagrams, the forward biasing of a p-n junction diode. Also draw characteristic curves.
When a p-type impurity is doped in a semiconductor, a large number of holes are created, This does not make the semiconductor charged. But when holes diffuse from the p-side to the n-side in a p-n junction, the n-side gets positively charged. Explain.
The diffusion current in a p-n junction is
Two identical p-n junction may be connected in series with a battery in three ways. The potential difference across the two p-n junctions are equal in
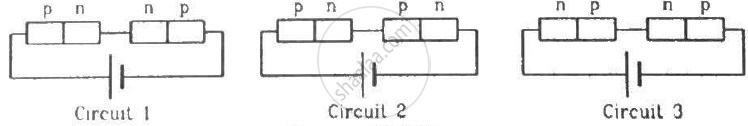
A hole diffuses from the p-side to the n-side in a p-n junction. This means that
Consider a p-n junction diode having the characteristic \[i - i_0 ( e^{eV/kT} - 1) \text{ where } i_0 = 20\mu A\] . The diode is operated at T = 300 K . (a) Find the current through the diode when a voltage of 300 mV is applied across it in forward bias. (b) At what voltage does the current double?
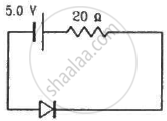
Calculate the current through the circuit and the potential difference across the diode shown in figure. The drift current for the diode is 20 µA.
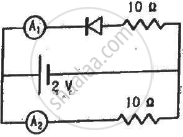
What are the readings of the ammeters A1 and A2 shown in figure. Neglect the resistance of the meters.
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Find the equivalent resistance of the network shown in figure between the points A and B.
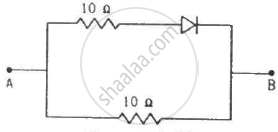
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
A diode, a resistor and a 50 Hz AC source are connected in series. The number of current pulses per second through the resistor is __________ .
Choose the correct option.
Current through a reverse-biased p-n junction increases abruptly at:
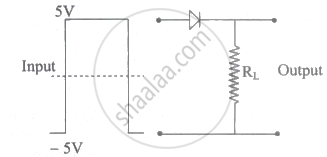
If in a p-n junction diode, a square input signal of 10 V is applied as shown Then the output signal across RL will be ______
In a semiconductor diode, the barrier potential offers opposition to only ______.
The formation of the depletion region in a p-n junction diode is due to ______.
