Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In a p-n junction diode, the current I can be expressed as
I = `"I"_0 exp ("eV"/(2"k"_"BT") - 1)`
where I0 is called the reverse saturation current, V is the voltage across the diode and is positive for forward bias and negative for reverse bias, and I is the current through the diode, kBis the Boltzmann constant (8.6×10−5 eV/K) and T is the absolute temperature. If for a given diode I0 = 5 × 10−12 A and T = 300 K, then
(a) What will be the forward current at a forward voltage of 0.6 V?
(b) What will be the increase in the current if the voltage across the diode is increased to 0.7 V?
(c) What is the dynamic resistance?
(d) What will be the current if reverse bias voltage changes from 1 V to 2 V?
Solution
a) In a p-n junction diode, the expression for current is given as:
I = `"I"_0 exp("eV"/(2"k"_"B" "T") - 1)`
Where,
I0 = Reverse saturation current = 5 × 10−12 A
T = Absolute temperature = 300 K
kB = Boltzmann constant = 8.6 × 10−5 eV/K = 1.376 × 10−23 J K−1
V = Voltage across the diode
(a) Forward voltage, V = 0.6 V
= `5 xx 10^(-12)[exp ((1.6xx 10^(-19) xx 0.6)/(1.376 xx 10^(-23) xx 300))-1]`
∴ Current, I
`= 5 xx 10^(-12) xx exp [22.36] = 0.0256 A`
Therefore, the forward current is about 0.0256 A.
(b) For forward voltage, V’ = 0.7 V, we can write:
I' =`5 xx 10^(-12) [exp ((1.6 xx 10^(-19) xx 0.7)/(1.376 xx 10^(-23) xx 300)) - 1]`
`= 5 xx 10^(-12) xx exp [26.25] = 1.257` A
Hence, the increase in current, ΔI = I' − I
= 1.257 − 0.0256 = 1.23 A
(c) Dynamic resistance = `"Change in voltage"/"Change in Current"`
`= (0.7 - 0.6)/1.23 = 0.1/1.23 = 0.081 "Ω"`
(d) If the reverse bias voltage changes from 1 V to 2 V, then the current (I) will almost remain equal to I0 in both cases. Therefore, the dynamic resistance in the reverse bias will be infinite.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A zener diode is fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n- sides of the junction. Explain, why?
Explain, with the help of a circuit diagram, the working of a photo-diode. Write briefly how it is used to detect the optical signals.
Explain, with the help of a circuit diagram, the working of n-p-n transistor as a common emitter amplifier.
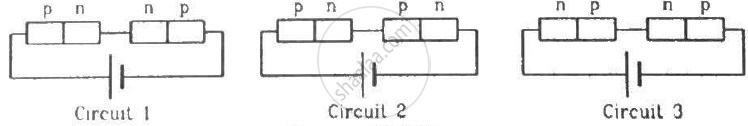
Two identical p-n junction may be connected in series with a battery in three ways. The potential difference across the two p-n junctions are equal in
In a p-n junction with open ends,
(a) there is no systematic motion of charge carries
(b) holes and conduction electrons systematically go from the p-side to n-side and from the n-side to p-side respectively
(c) there is no net charge transfer between the two sides
(d) there is a constant electric field near the junction.
In a p-n junction,
(a) new holes and conduction electrons are produced continuously throughout the material
(b) new holes and conduction electrons are produced continuously throughout the material except in the depletion region
(c) holes and conduction electrons recombine continuously throughout the material
(d) holes and conduction electrons recombine continuously throughout the material except in the depletion region.
When a p-n junction is reverse-biased, the current becomes almost constant at 25 µA. When it is forward-biased at 200 mV, a current of 75 µA is obtained. Find the magnitude of diffusion current when the diode is
(a) unbiased,
(b) reverse-biased at 200 mV and
(c) forward-biased at 200 mV.
The drift current in a p-n junction is 20.0 µA. Estimate the number of electrons crossing a cross section per second in the depletion region.
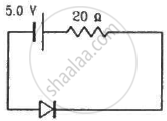
Calculate the current through the circuit and the potential difference across the diode shown in figure. The drift current for the diode is 20 µA.
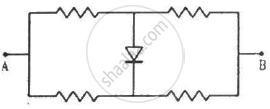
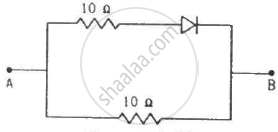
Each of the resistance shown in figure has a value of 20 Ω. Find the equivalent resistance between A and B. Does it depend on whether the point A or B is at higher potential?
Find the currents through the resistance in the circuits shown in figure.
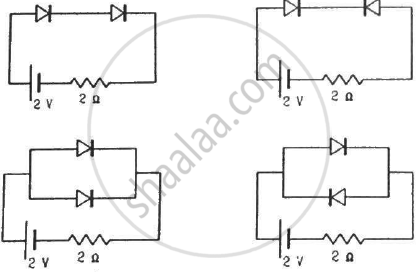
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
What are the readings of the ammeters A1 and A2 shown in figure. Neglect the resistance of the meters.
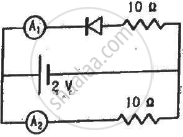
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Draw the current-voltage characteristics for the device show in figure between the terminals A and B.
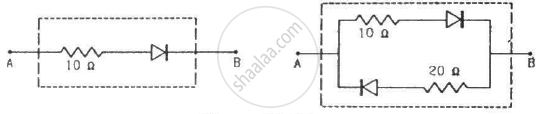
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Find the equivalent resistance of the network shown in figure between the points A and B.
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
A diode, a resistor and a 50 Hz AC source are connected in series. The number of current pulses per second through the resistor is __________ .
Choose the correct option.
Current through a reverse-biased p-n junction increases abruptly at:
Answer in detail.
Discuss the effect of external voltage on the width of depletion region of a p-n junction.
The formation of the depletion region in a p-n junction diode is due to ______.
