Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two identical p-n junction may be connected in series with a battery in three ways. The potential difference across the two p-n junctions are equal in
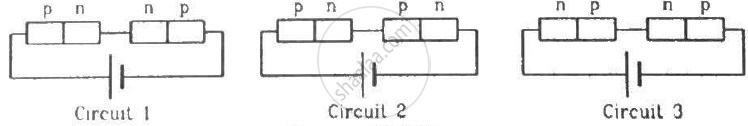
Options
circuit 1 and circuit 2
circuit 2 and circuit 3
circuit 3 and circuit 1
circuit 1 only.
Solution
circuit 2 and circuit 3
In circuit 1, one diode is forward biassed and the other diode is reverse biassed.
The forward-biassed diode offers zero resistance (ideally) to the current flow, so it can be replaced by a short circuit. The voltage drop across the first diode will be zero. The second diode is reverse biassed, so it can be replaced by an open circuit; hence, the voltage drop across this diode will be maximum.
In circuit 2, both the diodes are forward biassed, so they can be replaced by short circuits; hence, the voltage drop across both of them will be minimum and equal.
In circuit 3, both the diodes are reverse biassed, so both can be replaced by open circuits; hence, the voltage drop across both of them will be maximum and equal.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a p-n junction diode, the current I can be expressed as
I = `"I"_0 exp ("eV"/(2"k"_"BT") - 1)`
where I0 is called the reverse saturation current, V is the voltage across the diode and is positive for forward bias and negative for reverse bias, and I is the current through the diode, kBis the Boltzmann constant (8.6×10−5 eV/K) and T is the absolute temperature. If for a given diode I0 = 5 × 10−12 A and T = 300 K, then
(a) What will be the forward current at a forward voltage of 0.6 V?
(b) What will be the increase in the current if the voltage across the diode is increased to 0.7 V?
(c) What is the dynamic resistance?
(d) What will be the current if reverse bias voltage changes from 1 V to 2 V?
A zener diode is fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n- sides of the junction. Explain, why?
Mention the important considerations required while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED). What should be the order of band gap of an LED if it is required to emit light in the visible range?
The drift current in a reverse-biased p-n junction is increased in magnitude if the temperature of the junction is increased. Explain this on the basis of creation of hole-electron pairs.
The drift current in a p-n junction is
The diffusion current in a p-n junction is
In a p-n junction with open ends,
(a) there is no systematic motion of charge carries
(b) holes and conduction electrons systematically go from the p-side to n-side and from the n-side to p-side respectively
(c) there is no net charge transfer between the two sides
(d) there is a constant electric field near the junction.
The drift current in a p-n junction is 20.0 µA. Estimate the number of electrons crossing a cross section per second in the depletion region.
Find the currents through the resistance in the circuits shown in figure.
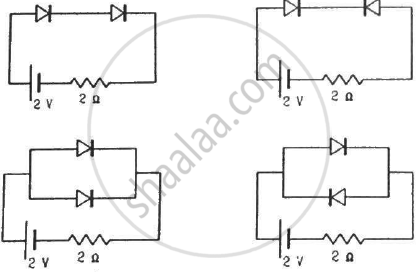
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
What are the readings of the ammeters A1 and A2 shown in figure. Neglect the resistance of the meters.
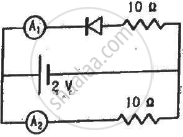
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Find the current through the resistance R in figure if (a) R = 12Ω (b) R = 48Ω.
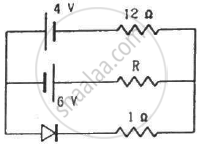
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Draw the current-voltage characteristics for the device show in figure between the terminals A and B.
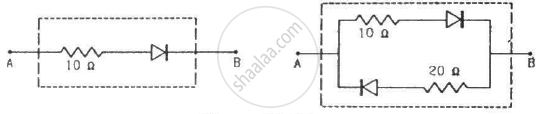
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Find the equivalent resistance of the network shown in figure between the points A and B.
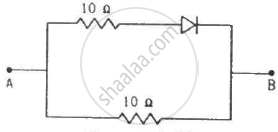
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
A diode, a resistor and a 50 Hz AC source are connected in series. The number of current pulses per second through the resistor is __________ .
In a semiconductor diode, the barrier potential offers opposition to only ______.
The formation of the depletion region in a p-n junction diode is due to ______.
During the formation of a p-n junction ______.
