Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The drift current in a reverse-biased p-n junction is increased in magnitude if the temperature of the junction is increased. Explain this on the basis of creation of hole-electron pairs.
Solution
When the temperature of a reverse-biassed p‒n junction is increased, the breaking of bonds takes place because of the increase in the thermal energy of the charge carriers. Drift current is due to the flow of the minority carriers across the junction. So, when a p‒n junction is reverse biassed, the applied voltage supports the flow of minority charge carriers across the junction. Thus, the drift current increases with increase in temperature in a reverse-biassed p‒n junction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a p-n junction diode, the current I can be expressed as
I = `"I"_0 exp ("eV"/(2"k"_"BT") - 1)`
where I0 is called the reverse saturation current, V is the voltage across the diode and is positive for forward bias and negative for reverse bias, and I is the current through the diode, kBis the Boltzmann constant (8.6×10−5 eV/K) and T is the absolute temperature. If for a given diode I0 = 5 × 10−12 A and T = 300 K, then
(a) What will be the forward current at a forward voltage of 0.6 V?
(b) What will be the increase in the current if the voltage across the diode is increased to 0.7 V?
(c) What is the dynamic resistance?
(d) What will be the current if reverse bias voltage changes from 1 V to 2 V?
Write the two processes that take place in the formation of a p-n junction.
A zener diode is fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n- sides of the junction. Explain, why?
Explain briefly with the help of necessary diagrams, the forward biasing of a p-n junction diode. Also draw characteristic curves.
Explain briefly with the help of necessary diagrams, the reverse biasing of a p-n junction diode. Also draw characteristic curves.
Mention the important considerations required while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED). What should be the order of band gap of an LED if it is required to emit light in the visible range?
Explain, with the help of a circuit diagram, the working of n-p-n transistor as a common emitter amplifier.
How is a zener diode fabricated so as to make it a special purpose diode? Draw I-V characteristics of zener diode and explain the significance of breakdown voltage.
Explain briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a p-n junction diode works as a half wave rectifier.
A hole diffuses from the p-side to the n-side in a p-n junction. This means that
In a p-n junction,
(a) new holes and conduction electrons are produced continuously throughout the material
(b) new holes and conduction electrons are produced continuously throughout the material except in the depletion region
(c) holes and conduction electrons recombine continuously throughout the material
(d) holes and conduction electrons recombine continuously throughout the material except in the depletion region.
The potential barrier existing across an unbiased p-n junction is 0.2 volt. What minimum kinetic energy a hole should have to diffuse from the p-side to the n-side if (a) the junction is unbiased, (b) the junction is forward-biased at 0.1 volt and (c) the junction is reverse-biased at 0.1 volt?
When a p-n junction is reverse-biased, the current becomes almost constant at 25 µA. When it is forward-biased at 200 mV, a current of 75 µA is obtained. Find the magnitude of diffusion current when the diode is
(a) unbiased,
(b) reverse-biased at 200 mV and
(c) forward-biased at 200 mV.
Consider a p-n junction diode having the characteristic \[i - i_0 ( e^{eV/kT} - 1) \text{ where } i_0 = 20\mu A\] . The diode is operated at T = 300 K . (a) Find the current through the diode when a voltage of 300 mV is applied across it in forward bias. (b) At what voltage does the current double?
Find the currents through the resistance in the circuits shown in figure.
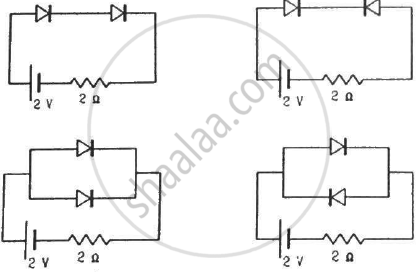
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
A diode, a resistor and a 50 Hz AC source are connected in series. The number of current pulses per second through the resistor is __________ .
Choose the correct option.
Current through a reverse-biased p-n junction increases abruptly at:
The depletion layer in the p-n junction diode is caused by ______.
The formation of the depletion region in a p-n junction diode is due to ______.
