Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the currents through the resistance in the circuits shown in figure.
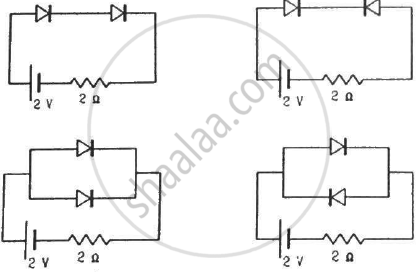
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Solution
We know that under forward bias, an ideal diode acts as a short circuit; and under reverse bias, an ideal diode acts as an open circuit.
(a) Since both the diodes are forward biassed, they can be replaced by short circuits.
Net resistance = 2 Ω
\[i = \frac{2 V}{2 \Omega} = 1 A\]
(b) One diode is forward biassed and the other is reverse biassed; thus, the resistance of one becomes ∞. The circuit becomes open at the position of the second diode, so no current flows through this arm.
\[\therefore i = \frac{2}{2 + \infty} = 0 A\]
(c) Both of them are forward biassed. Thus, the resistance is zero.
We can replace both the resistors by short circuits.
Net resistance = 2 Ω
\[\therefore i = \frac{2}{2} = 1 A\]
(d) One of them is forward biassed and the other is reverse biassed.
Thus, the current passes through the forward-biassed diode and the other acts as open circuit.
\[\therefore i = \frac{2}{2} = 1 A\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a p-n junction diode, the current I can be expressed as
I = `"I"_0 exp ("eV"/(2"k"_"BT") - 1)`
where I0 is called the reverse saturation current, V is the voltage across the diode and is positive for forward bias and negative for reverse bias, and I is the current through the diode, kBis the Boltzmann constant (8.6×10−5 eV/K) and T is the absolute temperature. If for a given diode I0 = 5 × 10−12 A and T = 300 K, then
(a) What will be the forward current at a forward voltage of 0.6 V?
(b) What will be the increase in the current if the voltage across the diode is increased to 0.7 V?
(c) What is the dynamic resistance?
(d) What will be the current if reverse bias voltage changes from 1 V to 2 V?
A zener diode is fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n- sides of the junction. Explain, why?
Explain briefly with the help of necessary diagrams, the reverse biasing of a p-n junction diode. Also draw characteristic curves.
Draw a circuit diagram to study the input and output characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in its common emitter configuration. Draw the typical input and output characteristics.
How is a zener diode fabricated so as to make it a special purpose diode? Draw I-V characteristics of zener diode and explain the significance of breakdown voltage.
Explain briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a p-n junction diode works as a half wave rectifier.
When a p-type impurity is doped in a semiconductor, a large number of holes are created, This does not make the semiconductor charged. But when holes diffuse from the p-side to the n-side in a p-n junction, the n-side gets positively charged. Explain.
The drift current in a reverse-biased p-n junction is increased in magnitude if the temperature of the junction is increased. Explain this on the basis of creation of hole-electron pairs.
The drift current in a p-n junction is
Diffusion current in a p-n junction is greater than the drift current in magnitude
Two identical p-n junction may be connected in series with a battery in three ways. The potential difference across the two p-n junctions are equal in
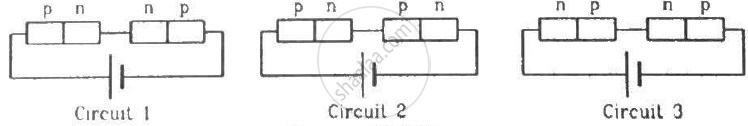
A hole diffuses from the p-side to the n-side in a p-n junction. This means that
Find the current through the resistance R in figure if (a) R = 12Ω (b) R = 48Ω.
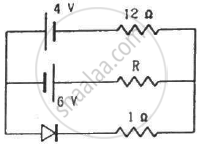
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Draw the current-voltage characteristics for the device show in figure between the terminals A and B.
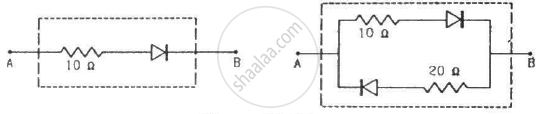
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Find the equivalent resistance of the network shown in figure between the points A and B.
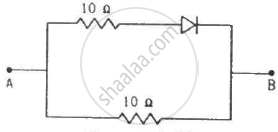
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
A load resistor of 2kΩ is connected in the collector branch of an amplifier circuit using a transistor in common-emitter mode. The current gain β = 50. The input resistance of the transistor is 0.50 kΩ. If the input current is changed by 50µA. (a) by what amount does the output voltage change, (b) by what amount does the input voltage change and (c) what is the power gain?
A diode, a resistor and a 50 Hz AC source are connected in series. The number of current pulses per second through the resistor is __________ .
Answer in detail.
Discuss the effect of external voltage on the width of depletion region of a p-n junction.
The depletion layer in the p-n junction diode is caused by ______.
Zener breakdown occurs in a p-n junction having p and n both:
