Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
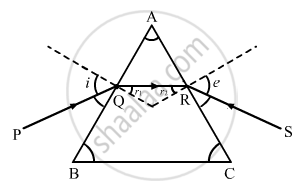
Figure shows a ray of light passing through a prism. If the refracted ray QR is parallel to the base BC, show that (i) r1 = r2 = A/2 and (ii) angle of minimum deviation, Dm = 2i − A.
Solution
(i) When QR is parallel to the base BC, we have: i = e
\[\Rightarrow r_1 = r_2 = r\]
We know that
\[r_1 + r_2 = A\]
\[ \Rightarrow r + r = A \]
\[ \therefore r = A/2\]
(ii) Also, we have:
A + D= i + e
Substituting, D = Dm and e = i
A + Dm= i + i
∴ Dm=2i - A
RELATED QUESTIONS
A ray PQ incident normally on the refracting face BA is refracted in the prism BAC made of material of refractive index 1.5. Complete the path of ray through the prism. From which face will the ray emerge? Justify your answer.
What is a dispersion of light
State any two difference between the primary rainbow and secondary rainbow
For any prism, prove that :
'n' or `mu = sin((A + delta_m)/2)/sin(A/2)`
where the terms have their usual meaning
A prism can produce a minimum deviation δ in a light beam. If three such prisms are combined, the minimum deviation that can be produced in this beam is _______________.
By properly combining two prisms made of different materials, it is possible to
(a) have dispersion without average deviation
(b) have deviation without dispersion
(c) have both dispersion and average deviation
(d) have neither dispersion nor average deviation
The minimum deviations suffered by, yellow and violet beams passing through an equilateral transparent prism are 38.4°, 38.7° and 39.2° respectively. Calculate the dispersive power of the medium.
The deviation produced for violet, yellow and red lights for crown glass are 3.75°, 3.25° and 2.86° respectively. Calculate the dispersive power of the crown glass.
The refractive indices of material for red, violet and yellow colour light are 1.52, 1.62 and 1.59 respectively.
Calculate the dispersive power of the material. If the mean deviation is 40°. What will be the angular dispersion produced by a prism of this material?
What is meant by a thin prism?
