Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following questions based on the P–T phase diagram of CO2:
CO2 at 1 atm pressure and temperature – 60 °C is compressed isothermally. Does it go through a liquid phase?
Solution 1
No
The P-T phase diagram for CO2 is shown in the following figure.
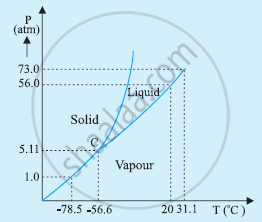
At 1 atm pressure and at –60°C, CO2 lies to the left of –56.6°C (triple point C). Hence, it lies in the region of vaporous and solid phases.
Thus, CO2 condenses into the solid state directly, without going through the liquid state
Solution 2
No, the CO2 does not go through the liquid phase. The point (1.00 atm, – 60°C) is to the lift of the triple-point O and below the sublimation curve OA. Therefore, when CO2 is compressed at this point at constant temperature, the point moves perpendicular to the temperature-axis and enters the solid phase region. Hence, the CO2 vapour condenses to solid directly without going through the liquid phase.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A copper block of mass 2.5 kg is heated in a furnace to a temperature of 500 °C and then placed on a large ice block. What is the maximum amount of ice that can melt? (Specific heat of copper = 0.39 J g–1 K–1; heat of fusion of water = 335 J g–1).
Answer the following question based on the P-T phase diagram of carbon dioxide:
Is CO2 solid, liquid or gas at
- –70 °C under 1 atm,
- –60 °C under 10 atm,
- 15 °C under 56 atm?
Answer the following questions based on the P–T phase diagram of CO2:
What happens when CO2 at 4 atm pressure is cooled from room temperature at constant pressure?
Answer the following questions based on the P–T phase diagram of CO2:
Describe qualitatively the changes in a given mass of solid CO2 at 10 atm pressure and temperature –65 °C as it is heated up to room temperature at constant pressure.
Answer the following questions based on the P–T phase diagram of CO2:
CO2 is heated to a temperature 70 °C and compressed isothermally. What changes in its properties do you expect to observe?
A ‘thermacole’ icebox is a cheap and efficient method for storing small quantities of cooked food in summer in particular. A cubical icebox of side 30 cm has a thickness of 5.0 cm. If 4.0 kg of ice is put in the box, estimate the amount of ice remaining after 6 h. The outside temperature is 45 °C, and coefficient of thermal conductivity of thermacole is 0.01 J s–1 m–1 K–1. [Heat of fusion of water = 335 × 103 J kg–1]
A metal block of heat capacity 80 J°C−1 placed in a room at 20°C is heated electrically. The heater is switched off when the temperature reaches 30°C. The temperature of the block rises at the rate of 2°C s−1 just after the heater is switched on and falls at the rate of 0.2°C s−1 just after the heater is switched off. Assume Newton's law of cooling to hold.
- Find the power of the heater.
- Find the power radiated by the block just after the heater is switched off.
- Find the power radiated by the block when the temperature of the block is 25°C.
- Assuming that the power radiated at 25°C represents the average value in the heating process, find the time for which the heater was kept on.
Answer the following question based on the P-T phase diagram of carbon dioxide:
At what temperature and pressure can the solid, liquid and vapour phases of CO2 co-exist in equilibrium?
Answer the following question based on the P-T phase diagram of carbon dioxide:
What is the effect of decrease of pressure on the fusion and boiling point of CO2?
Answer the following question based on the P-T phase diagram of carbon dioxide:
What are the critical temperature and pressure for CO2? What is their significance?
