Advertisements
Advertisements
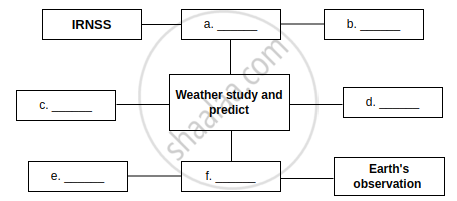
Question
Complete the Following table.
| Sr. no. | Type of Satellite | The names of Indian Satellite and launcher |
| (1) | Navigational Satellite | Satellite: ______ |
| Launcher: ______ | ||
| (2) | Earth Observation Satellite | Satellite: ______ |
| Launcher: ______ |
Solution
| Sr. no. | Type of Satellite | The names of Indian Satellite and launcher |
| (1) | Navigational Satellite | Satellite: IRNSS |
| Launcher: PSLV | ||
| (2) | Earth Observation Satellite | Satellite: IRS |
| Launcher: PSLV |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Fill in the blank and explain the statement with reasoning:
If the height of the orbit of a satellite from the earth surface is increased, the tangential velocity of the satellite will ......
Answer the question:
What is meant by the orbit of a satellite? On what basis and how are the orbits of artificial satellites classified?
Why are geostationary satellites not useful for studies of polar regions?
Complete the following table.

Solve the problem.
How much time a satellite in an orbit at height 35780 km above earth's surface would take, if the mass of the earth would have been four times its original mass?
Considering first correlation, complete the second.
Hubble telescope : At 569 km above the earth’s surface
Orbit of Hubble telescope : .............................
A group of students from COEP Pune sent a small satellite _______ through ISRO in 2016.
The function of a satellite launcher is based on Newton's second law of motion.
Calculate the critical velocity of the satellite to be located at 35780 km above the surface of earth.
What is Medium Earth Orbit?
Observe the figure and write the answers.

- Name the outer orbit.
- Which satellites revolve in low earth orbits?
- Which various orbits are given in the figure?
- Give an example of a launch vehicle based on Newton’s third law.
Numerical problem.
At an orbital height of 400 km, find the orbital period of the satellite.
What is microgravity?
Geostationary satellites are not useful for studies of the polar region.
Complete the following equations:
The orbit of a satellite is exactly 35780 km above the earth's surface and its tangential velocity is 3.08 km/s.
How much time the satellite will take to complete one revolution around the earth?
(Radius of earth = 6400 km.)
