Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Correct the sequence of the following steps to explain the process of urine formation.
1. Blood enters the glomerulus under high pressure.
2. The filtrate passes through the thin walls of the Bowman’s capsule into the renal tubule
3. As the filtrate, passes through the tubule, water, and many useful substances are reabsorbed by the walls of the blood capillaries.
4. Water and small solutes are filtered in the Bowman’s capsule.
5. The remaining liquid, along with waste is called urine and is collected in the urinary bladder.
6. Blood containing waste material enters the kidneys through the renal artery.
Solution
1. Blood containing waste material enters the kidneys through the renal artery.
2. Blood enters the glomerulus under high pressure.
3. Water and small solutes are filtered in the Bowman’s capsule.
4. The filtrate passes through the thin walls of the Bowman’s capsule into the renal tubule
5. As the filtrate, passes through the tubule, water, and many useful substances are reabsorbed by the walls of the blood capillaries.
6. The remaining liquid, along with waste is called urine and is collected in the urinary bladder.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Complete the diagram/chart with correct labels/ information. Write the conceptual details regarding it.
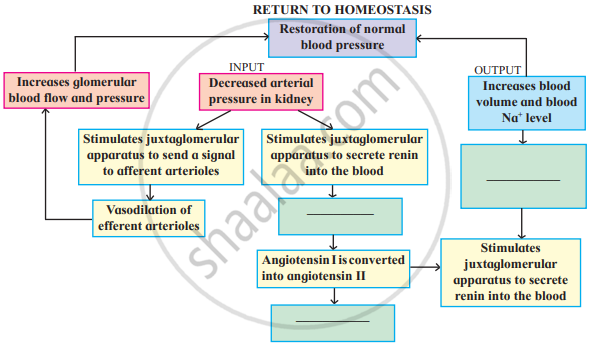
Identify the following structures and explain their significance in renal physiology?
- Juxtaglomerular apparatus
- Podocytes
- Sphincters in the bladder
In acute renal failure the urine output decreases. This condition is called ____________.
Bright's disease is characterized by the following symptoms EXCEPT ______
Dialysis is an imperfect treatment because ______
Ultimate correction for renal failure is:
The condition of accumulation of urea in the blood is termed as ______.
Match the abnormal conditions given in Column A with their explanations given in Column B and Choose the correct option
| Column A | Column B |
| A. Glycosuria | i. Accumulation of uric acid in joints |
| B. Renal calculi | ii. Inflammation in glomeruli |
| C. Glomerular nephritis | iii. Mass of crystallised salts within the kidney |
| D. Gout | iv. Presence of glucose in urine |
Which type of kidney stones are formed due to genetic disorders?
Renal calculi is ______.
