Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Decide the unit for specific heat capacity.
Solution
- The amount of heat (Q) required to change the temperature of a substance is directly proportional to:
a. the mass of the substance (m).
b. change in temperature of the substance (ΔT).
∴ Q ∝ m and Q ∝ ΔT
∴ Q ∝ mΔT
∴ Q = cmΔT ....(1)
where ‘c’ is specific heat or specific heat capacity of a substance. From equation (1),
c = `"Q"/("m" Delta "T")` ....(2) - SI unit:
As SI unit of heat is J, mass is kg and change in temperature is °C, SI unit of specific heat capacity is J/kg °C - C.G.S. unit:
As CGS unit of heat is calorie, mass is g and change in temperature is °C, CGS unit of specific heat capacity is cal/g °C
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A geyser heats water flowing at the rate of 3.0 litres per minute from 27 °C to 77 °C. If the geyser operates on a gas burner, what is the rate of consumption of the fuel if its heat of combustion is 4.0 × 104 J/g?
Name the S.I. unit of heat.
Name a liquid which has the highest specific heat capacity.
A mass m1 of a substance of specific heat capacity c1 at temperature t1 is mixed with a mass m2 of other substance of specific heat capacity c2 at a lower temperature t2. Deduce the expression for the temperature t of the mixture. State the assumption made, if any.
A heater of power P watt raises the temperature of m kg of a liquid by Δt K in time t s. Express
the specific heat capacity of liquid in terms of above data.
Ice cream appears colder to the mouth than water at 0℃. Give reason.
What is meant by specific heat capacity?
Study the following procedure and answer the questions below:
1. Take 3 spheres of iron, copper and lead of equal mass.
2. Put all the 3 spheres in boiling water in a beaker for some time.
3. Take 3 spheres out of the water. Put them immediately on a thick slab of wax.
4. Note, the depth that each sphere goes into the wax.
i) Which property of substance can be studied with this procedure?
ii) Describe that property in minimum words.
iii) Explain the rule of heat exchange with this property.
What is the unit of heat capacity in CGS system?
What change in heat energy occurs when lead at its melting point
solidifies without change in the temperature?
The SI unit of specific heat is _______.
The molar specific heats of an ideal gas at constant pressure and constant volume are denoted by Cp and Cv respectively. If `gamma = "C"_"p"/"C"_"v"` and R is the universal gas constant, then Cp is equal to ______.
If 'f' is the number of degrees of freedom of a molecule of a gas and ratio of molar specific heats of a gas, ϒ = 1 + `2/"f"` where ϒ = Cp/Cv. The ratio of 'ϒ' for monoatomic gas to 'ϒ' for (rigid) f diatomic gas is ______.
An office room contains about 4000 moles of air. The change in the internal energy of this much air when it is cooled from 34° C to 19° C at a constant pressure of 1.0 atm is (Use `gamma_"air"` = 1.4 and Universal gas constant = 8.314 J / mol K) ____________.
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for 200 g of water. The heat is extracted at the rate of 100 Js-1. Answer the questions that follow:
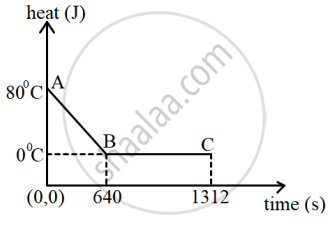
- Calculate specific heat capacity of water.
- Heat released in the region BC.
Two metals A and B have specific heat capacities in the ratio 2:3. If they are supplied same amount of heat then
If specific heat capacity of metal A is 0.26 Jg-1 0C-1 then calculate the specific heat capacity of metal B.
Specific heat capacity C = ______.
Which of the following substances (A, B and C) has the highest specific heat?

Thermal capacities of substances A and B are same. If mass of A is more than mass of B then:
Which substance will have more specific heat capacity?
