Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 5 - Heat SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 5 - Heat - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-and-technology-1-english-10-standard-ssc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 5: Heat
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 5 of Maharashtra State Board SCERT Maharashtra for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Heat Choose the correct option.
Choose the correct option.
If pressure increases, the melting point of a substance ______.
does not change
decreases
increases
remains constant
The vapour content in the air is measured using a physical quantity called ____________.
Absolute humidity
Relative humidity
Dew point
Humidity
Humid and dry nature of air depends on the ______.
amount of vapor in the air
amount of vapor to make the air saturated
temperature of the air
all of the above
Vapours in air condenses to form ______.
fog
snowfall
rainfall
All of the above
When the temperature of water decreases below 4 °C it’s volume _______.
decreases
increases
remains same
none of these
In a region with a cold climate the aquatic animals can survive at 4 °C, because _______.
ice floating on water is insulator
the heat from water cannot transfer to the atmosphere
anomalous behaviour of water
All the above
From the options given below the specific heat of _______ is maximum.
copper
silver
iron
mercury
Ice-ball is prepared from shredded ice again. This is the example of _______.
melting
condensation
regelation
freezing
The SI unit of specific heat is _______.
kcal
cal
cal/g °C
J/kg °C
_______ apparatus is used to study the anomalous behaviour of water.
calorimeter
Joule’s apparatus
Hope’s apparatus
Thermos flask
_______ heat is necessary to raise 1 kg of water from 14.5 °C to 15.5 °C.
4180 joule
1 kjoule
calorie
4180 calorie
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Heat Find the correlation.
Find the correlation.
When ice is converted into water : constant temperature : : before the water evaporates : _______
Relative humidity greater than 60% : humid air : : relative humidity less than 60% : _______
While studying anomalous behaviour of water in Hope’s apparatus, the upper temperature of the thermometer : 0 °C : : lower temperature of the thermometer : _______
The density of water is high at 4 °C : anomalous behaviour of water : : shredded ice converted into solid ice balls : _______
Specific latent heat of vaporisation : J/kg : : specific heat : _______
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Heat Find odd one out.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
cal/g
cal/g °C
kcal/kg °C
erg/g °C
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Joule
erg
Calorie
Newton
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Rainbow
Earthquake
Sunset
Sunrise
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Heat Answer in one sentence.
Answer the following question in one sentence.
Define boiling point of a liquid.
What is meant by regelation?
How fog is formed?
What is a dew point temperature?
What does the existence of drops of water on the leaves of a tree in the morning indicate?
Which temperature segment is chosen when determining the unit of heat? Why?
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Heat Match the columns
Match the columns.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1) Specific latent heat of fusion | a) Air saturated with vapour |
| 2) Specific latent heat of vaporisation | b) Solid converts into liquid |
| 3) Dew point temperature | c) liquid converts into gas |
Match the columns.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1) Absolute humidity | a) J or cal |
| 2) Latent heat | b) J/kg °C |
| 3) Specific heat capacity | c) kJ/kg |
| 4) Heat | d) no unit |
| e) kg/m3 |
Match the columns.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1) Dry air | a) 4 °C |
| 2) Humid air | b) Relative humidity 100% |
| 3) Saturated air/Dew point temperature | c) Relative humidity below 60% |
| 4) Maximum density of water | d) Relative humidity above 60% |
| e) – 4 °C |
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Heat Write the name
Write the name.
Products obtained when sugar is heated.
Write the name.
The phase in which solid substances are converted into liquid.
Write the name.
The amount of heat absorbed at constant temperature by unit mass of a liquid to convert into gaseous phase.
Write the name.
Conversion of ice into liquid due to applied pressure and the reconverts to ice once the pressure is removed.
Write the name.
The instrument used to study anomalous behaviour of water.
Write the name.
The instrument used to measure the specific heat capacity of a substance using mixture method.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Heat Right or Wrong sentence
The dew point temperature does not depend on the amount of vapor in the air.
Right
Wrong
The specific heat capacity of water is 1 cal/g °C.
Right
Wrong
The latent heat of vaporisation is a term referred for the conversion of gas into liquid.
Right
Wrong
Calorimeters are used to study anomalous behaviour of water.
Right
Wrong
During reheating, ice is converted to water at a temperature of 0 °C.
Right
Wrong
1 kg of dry air at a temperature of 40 °C can hold a maximum of 49 g of water vapour.
Right
Wrong
Calorimeters are used to measure specific heat capacity.
Right
Wrong
All metals have the same specific heat capacity.
Right
Wrong
Humidity relative to dew point temperature is 100%.
Right
Wrong
The unit of absolute humidity is kg/m3.
Right
Wrong
1 calorie is 4.81 joules.
Right
Wrong
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Heat Write scientific reasons
In cold regions, in winter the pipes for water supply break.
Write scientific reason.
Even if boiling water is constantly heated, its temperature does not rise.
Write scientific reason.
Use a pressure cooker to cook food in cold air.
Write scientific reason.
In the cold regions, snow falls in winter.
Write scientific reason.
The bottom of some steel utensils used for cooking is copper.
Drops of water can be seen accumulating on the glass of vehicles in the early hours of winter.
Write scientific reason.
During winter season, we may have observed a white trail at the back of the aeroplane flying high in the clear sky or sometimes it may not get formed.
Write scientific reason.
Fish can survive even in frozen ponds in cold regions.
Write scientific reason.
Placing a plastic bottle filled with water in the freezing compartment in the freezer can cause the bottle to explode.
Write scientific reason.
Even the wire moves through the ice slab , the ice slab does not break.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Heat Solve the following Questions
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of Hope’s apparatus.
Name the following diagram appropriately.

Observe the following diagram and write the answers to the questions given below.
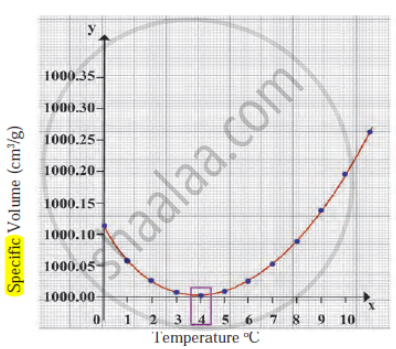
- Which process does the graph represent?
- What is the range of temperature responsible for the behaviour?
How much heat energy is necessary to raise the temperature of 5 kg of water from 20°C to 100°C?
Find the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of a silver container of mass 100 g by 10 °C. (c = 0.056 cal/g °C)
If water of mass 60 g and temperature 60 ˚C is mixed with water of mass 60 g and temperature 40 ˚C, what will be the maximum temperature of the mixture?
Find the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of a piece of iron of mass 500 g by 20 °C. (c = 0.110 cal/g.°C)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Heat Write short notes
Write a short note.
Anomalous behaviour of water
Write a short note.
Specific heat capacity
Write a short note.
Dew point temperature
Write a short note.
Regelation
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Heat Answer the Following
Which principle is used to measure the specific heat capacity of a substance?
Decide the unit for specific heat capacity.
Explain the following:
In cold regions in winter, the rocks crack due to anomalous expansion of water.
Explain how heat capacity of a solid can be determined by the method of mixture.
What is meant by latent heat? How will the state of matter transform if latent heat is given off?
Explain the following:
What is the role of the anomalous behaviour of water in preserving aquatic life in regions of cold climate?
Explain the following:
How can you relate the formation of water droplets on the outer surface of a bottle taken out of refrigerator with formation of dew?
Geeta observed a white trail at the back of aeroplane in a clear sky to answer the question from this incident given below.
- What will be the effect of relative humidity of the air surrounding the plane?
- What will be the effect of relative humidity of the air surrounding the plane is low?
- When the air is dry and humid?
Observe the given picture and answer the following questions.
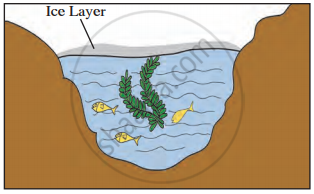
- Which property do you understand in this picture?
- What is the temperature of the water at the surface?
- What is the temperature below the layer of ice on the surface?
Read this activity and answer the following questions.
- Take three spheres of iron, copper and lead. the lead of equal mass.
- Put all the three spheres in boiling water in the beaker for some time.
- Take the three spheres out of the water.
- All the spheres will be at a temperature 100 °C.
- Put them immediately on the thick slab of wax.
- Note, the depth that each of the sphere goes into the wax.
Questions:
- Which property is determined from this activity?
- Give name to that property.
- Explain the term principal of heat exchange with the help of this activity.
The cold object the hot object enclosed in one box of heat-resistant material.
- What changes will occur in the two objects when temperature flows from those objects?
- Which principle can show that the energy exchange takes place between two objects only when kept in isolated system?
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Heat Answer the following questions
Read the passage and answer the questions based on it.
If heat is exchanged between a hot and cold object, the temperature of the cold object goes on increasing due to gain of energy and the temperature of the hot object goes on decreasing due to loss of energy. The change in temperature continues till the temperatures of both objects attain the same value. In this process, the cold object gains heat energy and the hot object loses heat energy. If the system of both the objects is isolated from the environment by keeping it inside a heat-resistant box then no energy can flow from inside the box or come into the box. In this situation, we get the following principle.
Heat energy lost by the hot object = Heat energy gained by the cold object. This is called the ‘Principle of heat exchange’.
- Where does heat transfer take place?
- In such a situation which principle of heat do you perceive?
- How can this principle be explained in short?
- Which property of the substance is measured using this principle?
Explain the following temperature vs time graph.

Solutions for 5: Heat
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 5 - Heat SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 5 - Heat - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-and-technology-1-english-10-standard-ssc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 5 - Heat
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 5 (Heat) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. SCERT Maharashtra textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 5 Heat are Latent Heat and Specific Latent Heat, Regelation, Dew Point and Humidity, Heat and Its Unit, Specific Heat Capacity, Heat Exchange, Measurement of Specific Heat: (Mixing Method) and Calorimeter, Anomalous Behaviour of Water.
Using SCERT Maharashtra Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC solutions Heat exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in SCERT Maharashtra Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC students prefer SCERT Maharashtra Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 5, Heat Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC additional questions for Mathematics Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
