Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 8 - Metallugy SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 8 - Metallugy - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-and-technology-1-english-10-standard-ssc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 8: Metallugy
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 8 of Maharashtra State Board SCERT Maharashtra for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Choose the correct option.
Choose the correct option.
Bronze is an alloy of ______.
copper and tin
copper and zinc
tin and zinc
copper, zinc and tin
_______ is an alloy made from iron, carbon and chromium.
brass
bronze
stainless steel
amalgam
_______ is basic oxide.
CO2
K2O
SO2
Al2O3
In electrolytic reduction of alumina _______ is used as a cathode.
sulphur
graphite
platinum
aluminium
Iron is _______.
more reactive than zinc
more reactive than aluminium
less reactive than copper
less reactive than aluminium
If Cu, Fe, Zn, Al elements are arranged in increasing order of their reactivity then the correct order would be which of the following?
Cu, Fe, Zn, Al
Al, Cu, Fe, Zn
Zn, Al, Cu, Fe
Fe, Zn, Al, Cu
Which of the following method is used to prevent the accumulation of greenish layer on brass due to corrosion?
electroplating
anodization
tinning
alloying
In Wilfley table method to separate particles of gangue _______ method is used.
Magnetic
Froth floatation
Leaching
gravitation
Aluminium oxide is _______ oxide.
acidic
basic
neutral
amphoteric
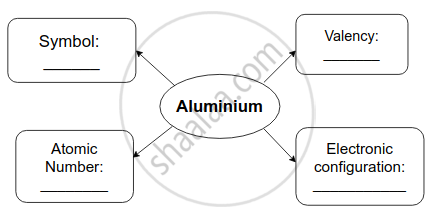
Atomic number of aluminium is _______ and its electronic configuration is _______.
13, (2, 8, 3)
12, (2, 8, 2)
13, (3, 10)
12, (2, 10)
The chemical formula of zinc blend is _______.
ZnSO4
ZnS
ZnCO3
ZnO
Extraction of moderately reactive elements is done by _______ and _______ method.
roasting and calcination
roasting and reduction
separation and calcination
none of these
Corrosion of silver causes a black layer of _______.
Silver nitrate
silver oxide
silver sulphide
silver carbonate
To prevent corrosion of iron and steel _______ method is used.
electroplating
anodization
tinning
galvanizing
In preparation of Aqua regia hydrochloric acid and _______ acid are mixed.
sulphuric acid
nitric acid
carbonic acid
phosphoric acid
The sound of one metal colliding with another makes a noise, this property is called as _______.
good conductors
ductility
sonority
malleability
Ionic compounds are electrically _______.
positively charged
negatively charged
neutral
conductor
_______ is good conductor of heat but bad conductor of electricity.
graphite
diamond
coal
iodine
_______ is the least reactive metal.
silver
sodium
zinc
gold
_______ forms a green colour in the water.
CuSO4
FeSO4
NaCl
all the above
Stainless steel is an alloy of _______.
copper
tin
zinc
iron
When one of the metals in an alloy is mercury the alloy is called _______.
amalgam
sodium amalgam
zinc amalgam
all the above
The minerals from which the metal can be separated economically are called _______.
minerals
ores
gangue
alloy
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Find the correlation.
Find the correlation.
Brass : Aluminium and zinc : : Bronze : ______
Pressure cooker : Anodizing : : Silver plated spoons : _______
In Electrolytic reduction of alumina, Anode : _______ : : Cathode : Graphite lining
Sulphide ores : Roasting : : Carbonate ores : _______
Bauxite : Aluminium ore : : Cassiterite : _______
Metal sheets : Malleable : : Electric wires : _______
Zinc sulphide : Roasting : : zinc carbonate : _______
Rusting of iron : Fe2O3 : : corrosion of copper : ______
Diamond : electric insulator : : _______ : electric conductor
Soft metal : Na : : hard metal : _______
Aluminium: _______: gold : : electric insulator
Bronze : _______ : : Stainless steel : Fe + Cr + C
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Find odd one out.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Sodium
Potassium
Silver
Sulphur
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Boron
Chlorine
Bromine
Fluorine
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Copper
Iron
Mercury
Brass
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Brass
Bronze
Phosphorous
Steel
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Tinning
Alloying
Anodization
Froth floatation
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Zinc coating
Tinning
Electroplating
Calcination
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Na
K
Cu
Li
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Match the columns
Make pairs of substances and their properties
| Substance | Property |
| a. Potassium bromide (KBr) | 1. Combustible |
| b. Gold | 2. Soluble in water |
| c. Sulphur | 3. No chemical reaction |
| d. Neon | 4. High ductility. |
Identify the pairs of metals and their ores from the following.
| Group A | Group B |
| a. Bauxite | i. Mercury |
| b. Cassiterite | ii. Aluminium |
| c. Cinnabar | iii. Tin |
Match the columns.
| Group A | Group B |
| 1. ZnS | a) Copper Sulphide |
| 2. HgS | b) Bauxite |
| c) Cinnabar | |
| d) Zinc blend |
Match the columns.
| Group A | Group B |
| 1) Copper and Zinc | a) Brass |
| 2) Copper and Tin | b) Bronze |
| c) Stainless steel |
Match the columns.
| Group A | Group B |
| 1) Electroplating | a) Pressure cooker |
| 2) Anodising | b) Silver plated spoons |
| c) Coating of tin on copper | |
| d) Coating of Zinc on iron |
Match the columns.
| Group A | Group B |
| 1. Making sheets of metals | a) Sonority |
| 2. Making metal utensils | b) Malleability |
| 3. Making Copper wires | c) Good conductor of heat |
| 4. Making bells from metal | d) Ductility |
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Write the name
Write the name.
The molecular formula of main ore of aluminium –
Write name.
The device used for grinding an ore.
Write the name.
Nonmetal which is a good conductors of electricity.
Write the name.
The reagent which dissolves noble metals.
Write the name.
Metals which are amphoteric in nature.
Write the name.
An alloy of copper and tin-
Write the name.
Two highly reactive metals-
Write the name.
The process of strong heating of carbonate ores in insufficient air–
Write the name.
The process of extraction of aluminium from alumina-
Write the name.
Method used to prevent corrosion of copper.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Right or Wrong sentence
Electrolysis is used to obtain pure metal from impure metal.
Right
Wrong
Ionic compounds are soluble in kerosene.
Right
Wrong
In solid state, ionic compounds conduct electricity.
Right
Wrong
Mercury, silver, gold are highly reactive metals.
Right
Wrong
In the electrolytic method, a layer of highly active metal is applied to a less active metal.
Right
Wrong
In the electrolytic reduction of alumina, the lining of graphite acts as an anode.
Right
Wrong
The electrolysis of alumina involves the use of fluorspar and cryolite to increase the melting point.
Right
Wrong
Cassiterite is a copper ore.
Right
Wrong
Diamond is a hard substance.
Right
Wrong
Gold and silver are active metals.
Right
Wrong
Halogen reacts with acid.
Right
Wrong
Bauxite reacts with sodium hydroxide in the Bayer’s process.
Right
Wrong
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Identify who I am!
Identify who I am!
Carbon allotropes- _______
Identify who I am!
Amphoteric oxide forming metal- _______
Identify who I am!
Ore of Aluminum- ______
Identify who I am!
Metal in Liquid state- _______
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Write scientific reasons
Write scientific reason.
Sodium is always kept in kerosene.
Write scientific reason.
Pine oil is used in froth flotation.
Write scientific reasons.
Lemon or tamarind is used for cleaning copper vessels turned greenish.
Write scientific reason.
Anodes need to be replaced from time to time during the electrolysis of alumina.
Write scientific reason.
Generally the ionic compounds have high melting points.
Write scientific reason.
Anodization method is useful for prevention of the corrosion of the aluminium.
Write scientific reason.
On exposure to air, silver articles turn blackish after some time.
Write scientific reason.
Magnetic separation method is used to separate the magnetic ingredients in the ores.
Write scientific reason.
Coins are made from metals and alloys.
Write scientific reason.
Meena’s mother uses lemon or tamarind for cleaning copper vessels turned greenish.
Write scientific reason.
Sodium is always kept in kerosene.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Solve the following Questions
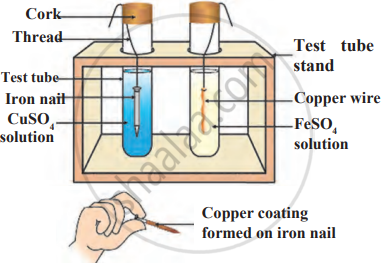
When a copper coin is dipped in the solution of silver nitrate, it shows a lustre on its surface. Explain this process with the help of a chemical equation.
Electronic configuration of metal A is 2,8,1. Electronic configuration of metal B is 2,8,8,2. Which of the above metals is more reactive? Explain with reason.
Classify the following metals based on their reactivity.
Cu, Zn, Ca, Mg, Fe, Na, Li, Hg
| More reactive | Moderately reactive | Less reactive |
Write the molecular formulae of the following compound.
Cryolite
Write the molecular formulae of the following compound.
Fluorspar
Write the molecular formulae of the following compound.
Sodium aluminate
Write the molecular formulae of the following compound.
Copper pyrite
Write the molecular formulae of the following compound.
Stannic oxide
Write the molecular formulae of the following compound.
Ferrous tungstate
Explain the concept of Roasting.
Explain the concept of Calcination.
What is an alloy?
Give two examples of alloy.
Explain Bayer’s process.
What is the difference between calcination and roasting?
Draw a neat and labelled diagram for Froth Floatation Process.
Explain the reactions of nonmetals with water with the help of examples.
Explain the characteristics of ionic compounds.
What are amphoteric oxides?
Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Distinguish between
Distinguish between:
Metals - Nonmetals (physical characteristics)
Compare roasting and calcination.
Distinguish between:
Froth floatation - Leaching
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Explain the following reactions with the balanced equations
Explain the following reaction with the balanced equation.
Sodium burns in air
Explain the following reaction with the balanced equation.
Reaction of aluminium with oxygen
Explain the following reaction with the balanced equation.
Magnesium reacts with dil HCl
Explain the following reaction with the balanced equation.
Sulphur burns in air
Explain the following reaction with the balanced equation.
Chlorine dissolved in water
Explain the following reaction with the balanced equation.
Sodium aluminate reacts with water
Write chemical equation for the event.
Iron filings are dropped in aqueous solution of copper sulphate.
Explain the following reaction with the balanced equation.
Ferric oxide is reacted with aluminium.
Write chemical equation for the event.
Electrolysis of alumina is done.
Explain the following reaction with the balanced equation.
Dry aluminium hydroxide is ignited at 1000 °C
Explain the following reaction with the balanced equation.
Zinc sulphide is heated strongly in excess of air
Explain the following reaction with the balanced equation.
Zinc carbonate is heated strongly in limited supply of air
Explain the following reaction with the balanced equation.
Zinc oxide is treated with carbon
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Explain concept with example/explain with the help of balanced equation
Explain concept with example/explain with the help of a balanced equation.
Ionic bond and ionic compounds
Explain concept with example/explain with the help of a balanced equation.
Gangue
Explain concept with example/explain with the help of a balanced equation.
Ores
Explain concept with example/explain with the help of a balanced equation.
Roasting
Explain concept with example/explain with the help of a balanced equation.
Calcination
Explain concept with example/explain with the help of a balanced equation.
Corrosion
Explain concept with example/explain with the help of a balanced equation.
Minerals
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Draw a neat labelled diagram
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
Magnetic separation method.
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
Froth floatation method.
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
Electrolytic reduction of alumina.
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
Hydraulic separation method.
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
Electroplating
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
Anodizing
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Complete flow chart given below
Complete flow chart given below.
Complete flow chart given below.

Complete flow chart given below.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Answer the Following
What is corrosion?
What is rust?
Write a molecular formula for rust.
Observe the following diagram and identify the type of reaction and write observation.
Observe the following diagram and give answers.
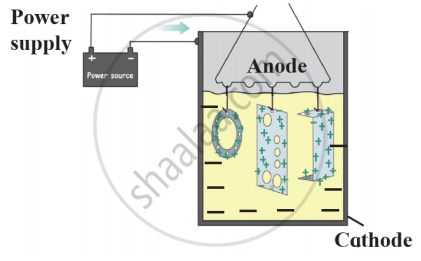
- Name this method of prevention of corrosion.
- For prevention of which metal this method is used?
- What is used as anode in this method?
Explain the hydraulic separation method with a neat labelled diagram.
Observe the following diagram and write answers.

- Name the method.
- Explain the method.
- Give two examples of this method.
Observe the following diagram and write answers.

- Name the method.
- Write anode reaction and cathode reaction.
- Why fluorspar and cryolite are added in the mixture?
Identify the following method of concentration of ores and explain briefly.

Observe the given figure of reactivity series of metals and answer the following questions:

Reactivity series of metals
- Name two metals which react with water.
- Name two moderately reactive metals.
- Name the most highly reactive metal and the most less reactive metal.
Explain the froth floatation method with a neat labelled diagram.
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
According to the reactivity series, zinc is more reactive than iron, iron is more reactive than silver. During study of this, a student dipped the iron nails in silver nitrate solution.
- What is reactivity series?
- What will happen when iron nails are dipped in silver nitrate solution?
- Which type of reaction happens when iron metal reacts with silver nitrate solution?
- What will happen if a zinc rod is used instead of iron nail?
Complete the following flowchart.
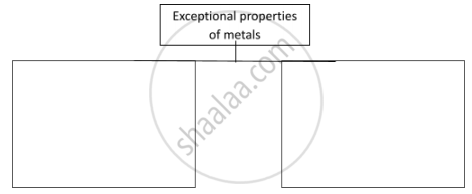
Complete the following flowchart.

Complete the following flow chart.

Write the properties of ionic compounds.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 8 Metallugy Answer the following questions
Explain in brief types of extraction of highly reactive metals according to their reactivity.
Explain in brief types of extraction of moderately reactive metals according to their reactivity.
Explain in brief types of extraction of less reactive metals according to their reactivity.
Explain Bayer’s process of concentration of bauxite with a chemical equation.
Explain in brief electrolytic reduction of alumina with a neat labelled diagram.
Observe the figure and answer the following.

- Write the name of the method.
- What is used as anode and cathode in this method?
- Write the molecular formula and use of cryolite.
- Write anode reaction.
- Write cathode reaction.
Observe the figure and name and explain in brief the following method:

Observe the figure and name and explain in brief the following method:

Answer the questions on the following passage.
The minerals from which the metal can be separated economically are called ores. Ores contain many types of impurities such as soil, sand and rocky substances along with metal compounds. These impurities are called gangue.
Metals can be extracted from their ores by means of various methods of separation. The process of extraction of metal in a pure state from the ores is also a part of metallurgy.
Ores are taken out from the mines and the gangue is usually separated from the ore at the site itself by various methods. Then the ores are carried out to the place where metals are produced. Here metals are extracted in pure form. Then metals are further purified by different methods of purification. This entire process is called metallurgy. Most metals being reactive do not occur in nature in the free state but are found in combined state as their salts such as oxides, carbonates, sulphides, and nitrates. however, the most unreactive metals that are not affected by air, water and other natural factors like silver, gold, platinum, generally occur in a free state. The compounds of metals that occur in nature along with the impurities are called minerals.
- What are ores?
- Which processes are involved in the branch of metallurgy? What is metallurgy?
- Which metals are found in a free state?
- In what forms are metals found in combined state?
- What is gangue?
Explain the difference between Bayer’s process and Hall’s process by explaining the Bayer’s process.
What is corrosion?
Give preventive methods by giving examples of corrosion?
Solutions for 8: Metallugy
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 8 - Metallugy SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 8 - Metallugy - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-and-technology-1-english-10-standard-ssc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 8 - Metallugy
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 8 (Metallugy) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. SCERT Maharashtra textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 8 Metallugy are Types of Element: Metals, Types of Element: Non-metal, Physical Properties of Metals, Extraction of Aluminium, Chemical Properties of Metal, Physical Properties of Non-metal, Chemical Properties of Non-metal, Reactivity Series of Metals, Metallurgy, Extraction of Reactive Metals, Refining of Metals, Ionic Compounds, Reactions of Metal, Basic Principles of Metallurgy, Extraction of Moderately Reactive Metals, Extraction of Less Reactive Metals, Corrosion of Metals, Prevention of Corrosion.
Using SCERT Maharashtra Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC solutions Metallugy exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in SCERT Maharashtra Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC students prefer SCERT Maharashtra Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 8, Metallugy Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC additional questions for Mathematics Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
