Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write the name.
The phase in which solid substances are converted into liquid.
Solution
The phase in which solid substances are converted into liquid- Melting
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the energy absorbed during the phase change called?
Explain the following:
The heat supplied to a substance during it change of state, does not cause any rise in its temperature.
The S.I. unit of specific latent heat is ______.
A molten metal of mass 150 g is kept at its melting point 800℃. When it is allowed to freeze at the same temperature, it gives out 75,000 J of heat energy.
- What is the specific latent heat of the metal?
- If the specific heat capacity of metal is 200 J kg-1 K-1, how much additional heat energy will the metal give out in cooling to -50℃?
A refrigerator converts 100g of water at 20℃ to ice at – 10℃ in 73.5 min. Calculate the average rate of heat extraction in watt. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 J kg-1 K-1, specific latent heat of ice is 336 J g-1 and the specific heat capacity of ice is 2.1 J kg-1 K-1.
During transformation of liquid phase to solid phase, the latent heat is ______.
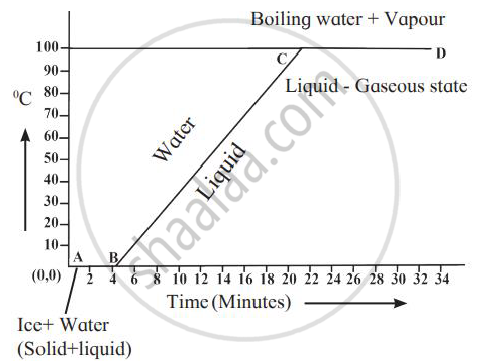
Explain the following temperature vs time graph.
Explain the meaning of the term latent heat. State its S. I. unit.
When 1 g of ice at 0 °C melts to form 1 g of water at 0 °C then, is the latent heat absorbed by the ice or given out by it?
Give one consequence of the high specific latent heat of fusion of ice.
The specific latent heat of vaporisation of steam is 2260 J/g. Comment on this.
Why does evaporation causes cooling and why is water used in hot water bottles?
What do you understand by the ‘latent heat of vaporization’ of a substance?
Steam at 100°C is passed over 1000 g of ice at 0°C. After some time, 600 g of ice at 0°C is left and 450 g of water at 0°C is formed. Calculate the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam (Given: specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg°C, specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336,000 J/kg.)
If pressure increases, the melting point of a substance ______.
During reheating, ice is converted to water at a temperature of 0 °C.
Specific latent heat of a substance ______.
