Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
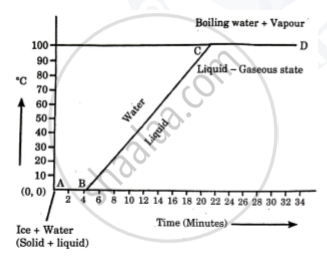
Explain the following temperature vs time graph.

Solution 1
In the given graph, line AB represents conversion of ice into water at constant temperature. When ice is heated, it melts at 0oC and converts into water maintaining constant temperature of 0oC. This constant temperature, at which the ice converts into water is called the melting point of ice. Also, during this transition, the ice absorbs heat energy. This heat energy is utilised for weakening the bonds between the atoms or molecules in the ice to transform itself into liquid. This heat energy absorbed by ice, at constant temperature, to convert it into liquid is called the latent heat of fusion.
Once all the ice is transformed into water, the temperature of water starts rising. It increases upto 100oC. Line BC in the graph represents rise in temperature of water from 0oC to 100oC. Thereafter, even though heat energy is supplied to water, its temperature does not rise. The heat energy is absorbed by water at this temperature and is used to break the bonds between molecules of the liquid and convert the liquid into gaseous state. Thus, during transformation from liquid phase to gas phase, heat energy is absorbed by the liquid, but its temperature does not change. The constant temperature at which the liquid transforms into gaseous state is called the boiling point of the liquid. The heat energy absorbed at constant temperature during transformation of liquid into gas is called the latent heat of vaporization.
Solution 2
- The given temperature v/s time graph demonstrates the behaviour of water when heated continuously and uniformly.
- Line segment AB indicates temperature of ice remaining constant at 0° C for a certain period of time (about 4 minutes).
- This means, amount of heat (latent heat of fusion) supplied to ice is entirely used for changing its state from solid to liquid.
- Thus, line segment AB denotes conversion of ice at 0° C into water at 0° C.
- Line segment BC indicates continuous rise in temperature of water from 0° C to 100° C.
- At point C, boiling point of water is reached and heat energy (latent heat of vaporisation) supplied further is used to convert water into steam.
- During this transformation, temperature remains unchanged as represented by line segment CD.
- Thus, line segment CD denotes conversion of water at 100° C into steam at 100° C.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State two factors upon which the rate of emission of thermions depends.
What is the Greenhouse effect?
What is the energy absorbed during the phase change called?
1 g ice of 0℃ melts to form 1 g water at 0℃. State whether the latent heat is absorbed or given out by ice.
Answer the following:
Explain the role of latent heat in the change of state of a substance.
A thermally insulated pot has 150 g ice at temperature 0°C. How much steam of 100°C has to be mixed to it, so that water of temperature 50°C will be obtained? (Given : latent heat of melting of ice = 80 cal/g, latent heat of vaporization of water = 540 cal/g, specific heat of water = 1 cal/g °C)
Explain the following temperature Vs. time graph:
Explain, why no tracks are left on the ice during ice skating?
Explain the meaning of greenhouse effect.
State the main precautions to be taken in finding the latent heat of steam.
Steam at 100°C is passed over 1000 g of ice at 0°C. After some time, 600 g of ice at 0°C is left and 450 g of water at 0°C is formed. Calculate the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam (Given: specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg°C, specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336,000 J/kg.)
When ice is converted into water : constant temperature : : before the water evaporates : _______
Specific latent heat of vaporisation : J/kg : : specific heat : _______
Match the columns.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1) Specific latent heat of fusion | a) Air saturated with vapour |
| 2) Specific latent heat of vaporisation | b) Solid converts into liquid |
| 3) Dew point temperature | c) liquid converts into gas |
Write scientific reason.
Even if boiling water is constantly heated, its temperature does not rise.
Write scientific reason.
The bottom of some steel utensils used for cooking is copper.
Specific latent heat of a substance ______.
Calculate the total amount of heat energy required to melt 200 g of ice at 0°C to water at 100°C. (Specific latent heat of ice = 336 Jg-1, specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 Jg-1 °C-1)
