Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
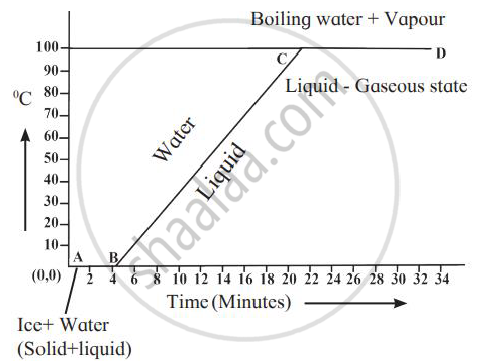
Explain the following temperature vs time graph.

उत्तर १
In the given graph, line AB represents conversion of ice into water at constant temperature. When ice is heated, it melts at 0oC and converts into water maintaining constant temperature of 0oC. This constant temperature, at which the ice converts into water is called the melting point of ice. Also, during this transition, the ice absorbs heat energy. This heat energy is utilised for weakening the bonds between the atoms or molecules in the ice to transform itself into liquid. This heat energy absorbed by ice, at constant temperature, to convert it into liquid is called the latent heat of fusion.
Once all the ice is transformed into water, the temperature of water starts rising. It increases upto 100oC. Line BC in the graph represents rise in temperature of water from 0oC to 100oC. Thereafter, even though heat energy is supplied to water, its temperature does not rise. The heat energy is absorbed by water at this temperature and is used to break the bonds between molecules of the liquid and convert the liquid into gaseous state. Thus, during transformation from liquid phase to gas phase, heat energy is absorbed by the liquid, but its temperature does not change. The constant temperature at which the liquid transforms into gaseous state is called the boiling point of the liquid. The heat energy absorbed at constant temperature during transformation of liquid into gas is called the latent heat of vaporization.
उत्तर २
- The given temperature v/s time graph demonstrates the behaviour of water when heated continuously and uniformly.
- Line segment AB indicates temperature of ice remaining constant at 0° C for a certain period of time (about 4 minutes).
- This means, amount of heat (latent heat of fusion) supplied to ice is entirely used for changing its state from solid to liquid.
- Thus, line segment AB denotes conversion of ice at 0° C into water at 0° C.
- Line segment BC indicates continuous rise in temperature of water from 0° C to 100° C.
- At point C, boiling point of water is reached and heat energy (latent heat of vaporisation) supplied further is used to convert water into steam.
- During this transformation, temperature remains unchanged as represented by line segment CD.
- Thus, line segment CD denotes conversion of water at 100° C into steam at 100° C.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the effect of an increase of impurities on the melting point of ice.
State any two measures to minimize the impact of global warming.
What is the Greenhouse effect?
Write the approximate value of specific latent heat of ice.
1 g ice of 0℃ melts to form 1 g water at 0℃. State whether the latent heat is absorbed or given out by ice.
- Which requires more heat: 1 g ice at 0℃ or 1 g water at 0℃ to raise its temperature to 10℃?
- Explain your answer in part (a).
Explain the following:
The heat supplied to a substance during it change of state, does not cause any rise in its temperature.
A refrigerator converts 100g of water at 20℃ to ice at – 10℃ in 73.5 min. Calculate the average rate of heat extraction in watt. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 J kg-1 K-1, specific latent heat of ice is 336 J g-1 and the specific heat capacity of ice is 2.1 J kg-1 K-1.
During transformation of liquid phase to solid phase, the latent heat is ______.
Liquid ammonia is used in ice factory for making ice from water. If water at 20°C is to be converted into 2 kg ice at 0°C, how many grams of ammonia are to be evaporated? (Given: The latent heat of vaporization of ammonia = 341 cal/g)
Explain the following temperature vs time graph.
Derive an expression for the amount of heat given out or taken up, when its temperature falls or rises by t°C.
If there is no Heat loss to the surroundings, the heat released by the condensation of m1 g of steam at 100°C into water at 100°C can be used to convert m2 g of ice at 0°C into water at 0°C.
(i) Find:
(a) The heat lost by steam in terms of m1
(b) The heat gained by ice in terms of m2
(ii) Form a heat equation find the ratio of m2 : m1
Specific latent heat of vaporization of steam = 2268 kJ/kg
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 kJ/kg
Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg°C
The latent heat of vaporisation is a term referred for the conversion of gas into liquid.
Write scientific reason.
Even if boiling water is constantly heated, its temperature does not rise.
Write scientific reason.
The bottom of some steel utensils used for cooking is copper.
Who introduced the term latent heat?
Give some practical applications of specific latent heat of ice.
2875 J of heat is required to melt 115 g of lead at its melting point. Calculate the specific latent heat capacity of fusion of lead.
20 g of ice at 0°C absorbs 10,920 J of heat energy to melt and change to water at 50°C. Calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. Specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg-1 K-1.
