Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the following:
The heat supplied to a substance during it change of state, does not cause any rise in its temperature.
उत्तर
Heat supplied to a substance during its change of state, does not cause any rise in its temperature because this is latent heat of phase change which is required to change the phase only.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the energy absorbed during the phase change called?
Write the approximate value of specific latent heat of ice.
The specific latent heat of fusion of water is ______.
What is meant by latent heat? How will the state of matter transform if latent heat is given off?
Liquid ammonia is used in ice factory for making ice from water. If water at 20°C is to be converted into 2 kg ice at 0°C, how many grams of ammonia are to be evaporated? (Given: The latent heat of vaporization of ammonia = 341 cal/g)
Explain the following temperature Vs. time graph:
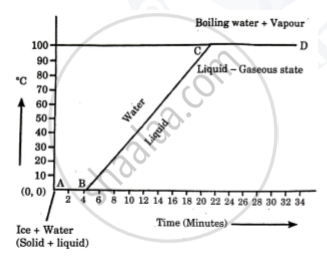
What do you mean by the statement?
'The specific latent heat capacity of fusion of ice is 336 J per g'?
Define the following terms:
(i) Latent heat,
(ii) Latent heat of fusion of ice.
Define the following terms:
(i) Specific latent heat,
(ii) Specific latent heat of fusion.
Define specific latent heat of vaporization of a substance.
Why does weather become pleasant when it starts freezing in cold countries?
Define the term ‘specific latent heat of fusion’ of a substance.
The specific latent heat of vaporisation of steam is 2260 J/g. Comment on this.
What do you understand by the ‘latent heat of vaporization’ of a substance?
Steam at 100°C is passed over 1000 g of ice at 0°C. After some time, 600 g of ice at 0°C is left and 450 g of water at 0°C is formed. Calculate the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam (Given: specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg°C, specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336,000 J/kg.)
Define specific latent heat capacity
Who introduced the term latent heat?
Give some practical applications of specific latent heat of ice.
Specific latent heat of a substance ______.
The amount of heat energy required to melt a given mass of a substance at its melting point without any rise in its temperature is called as the ______.
