Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
During transformation of liquid phase to solid phase, the latent heat is ______.
उत्तर
During transformation of liquid phase to solid phase, the latent heat is released.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the energy absorbed during the phase change called?
Write the approximate value of specific latent heat of ice.
Which has more heat: 1 g ice at 0℃ or 1g water 0℃? Give reason.
Explain the following:
The surrounding become pleasantly warm when water in a lake starts freezing in cold countries.
What is meant by latent heat? How will the state of matter transform if latent heat is given off?
Define the following terms:
(i) Specific latent heat,
(ii) Specific latent heat of fusion.
What is the name given to the energy absorbed during a phase change?
Define specific latent heat of vaporization of a substance.
Explain why water is used in hot water bottles for fomentation and also as a universal coolant.
Derive an expression for the amount of heat given out or taken up, when its temperature falls or rises by t°C.
If there is no Heat loss to the surroundings, the heat released by the condensation of m1 g of steam at 100°C into water at 100°C can be used to convert m2 g of ice at 0°C into water at 0°C.
(i) Find:
(a) The heat lost by steam in terms of m1
(b) The heat gained by ice in terms of m2
(ii) Form a heat equation find the ratio of m2 : m1
Specific latent heat of vaporization of steam = 2268 kJ/kg
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 kJ/kg
Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg°C
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Write the name.
The phase in which solid substances are converted into liquid.
During reheating, ice is converted to water at a temperature of 0 °C.
Calculate the amount of heat required to convert 200g of ice at 0°C into the water at 0°C Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 Jg-1
Observe the following graph and answer the following questions:

- What does the graph represent?
- What does the line AB represent?
- What does the line BC represent?
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for a substance:
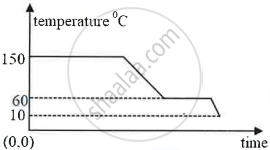
- State the temperatures at which the substance condenses.
- The temperature range in which the substance is in liquid state.
- Why do we prefer ice to ice-cold water for cooling a drink?
20 g of ice at 0°C absorbs 10,920 J of heat energy to melt and change to water at 50°C. Calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. Specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg-1 K-1.
