Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solution
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State two factors upon which the rate of emission of thermions depends.
State the effect of an increase of impurities on the melting point of ice.
1 g ice of 0℃ melts to form 1 g water at 0℃. State whether the latent heat is absorbed or given out by ice.
A refrigerator converts 100g of water at 20℃ to ice at – 10℃ in 73.5 min. Calculate the average rate of heat extraction in watt. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 J kg-1 K-1, specific latent heat of ice is 336 J g-1 and the specific heat capacity of ice is 2.1 J kg-1 K-1.
A thermally insulated pot has 150 g ice at temperature 0°C. How much steam of 100°C has to be mixed to it, so that water of temperature 50°C will be obtained? (Given : latent heat of melting of ice = 80 cal/g, latent heat of vaporization of water = 540 cal/g, specific heat of water = 1 cal/g °C)
Water expands on reducing its temperature below ______°C.
What do you mean by the statement?
'The specific latent heat capacity of fusion of ice is 336 J per g'?
Define the following terms:
(i) Specific latent heat,
(ii) Specific latent heat of fusion.
What is the name given to the energy absorbed during a phase change?
Explain the statement; “The specific latent heat of vaporization of wafer is 2260 × 103 J/kg”.
What do you understand by the ‘latent heat of vaporization’ of a substance?
If pressure increases, the melting point of a substance ______.
Write the name.
Products obtained when sugar is heated.
1 kg of dry air at a temperature of 40 °C can hold a maximum of 49 g of water vapour.
Define specific latent heat capacity
Who introduced the term latent heat?
Give some practical applications of specific latent heat of ice.
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for a substance:
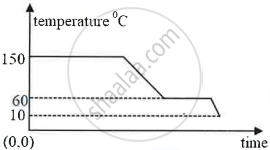
- State the temperatures at which the substance condenses.
- The temperature range in which the substance is in liquid state.
- Why do we prefer ice to ice-cold water for cooling a drink?
