Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define equipotential surface.
Solution
The surfaces on which no work has to be done in order to move a charge is called equipotential surface.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A regular hexagon of side 10 cm has a charge 5 µC at each of its vertices. Calculate the potential at the centre of the hexagon.
The top of the atmosphere is at about 400 kV with respect to the surface of the earth, corresponding to an electric field that decreases with altitude. Near the surface of the earth, the field is about 100 Vm−1. Why then do we not get an electric shock as we step out of our house into the open? (Assume the house to be a steel cage so there is no field inside!)
Draw the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole.
Find the amount of work done in rotating an electric dipole of dipole moment 3.2 x 10- 8Cm from its position of stable equilibrium to the position of unstable equilibrium in a uniform electric field if intensity 104 N/C.
A particle of mass 'm' having charge 'q' is held at rest in uniform electric field of intensity 'E'. When it is released, the kinetic energy attained by it after covering a distance 'y' will be ______.
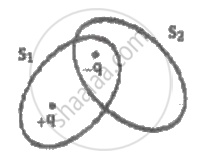
S1 and S2 are the two imaginary surfaces enclosing the charges +q and -q as shown. The electric flux through S1 and S2 are respectively ______.
Equipotentials at a great distance from a collection of charges whose total sum is not zero are approximately.
- The potential at all the points on an equipotential surface is same.
- Equipotential surfaces never intersect each other.
- Work done in moving a charge from one point to other on an equipotential surface is zero.
Consider a uniform electric field in the ẑ direction. The potential is a constant ______.
- in all space.
- for any x for a given z.
- for any y for a given z.
- on the x-y plane for a given z.
Equipotential surfaces are shown in figure. Then the electric field strength will be ______.