Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define sliding filament theory of muscle contraction.
Solution 1
Huxley:
By studying striated muscle fibres under an electron microscope, he observed the specific arrangement of actin and myosin rods present in them. Considering this configuration, he proposed the snake fibre or rod creep theory of muscle fibre contraction.
Mechanism of contraction of striated muscles:
Contraction in striated muscles occurs as a result of nerve stimulation. Actin rods slide over myosin rods and enter inside them (towards the centre of the spindle), due to which contraction of the muscle fibre takes place.
Fibre or rod creep theory of muscle contraction:
Under normal conditions, the sarcomere contains ATP and magnesium ions; Calcium ions are also present in minute quantities. Actin rods remain attached to tropomyosin in a way that they cannot attach to myosin rods. When a muscle fibre receives threshold stimulation by a nerve impulse, Ca++ (calcium ions) are released from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of the muscle fibre into the sarcomere. These calcium ions combine with tropomyosin and the actin rods become free. At the same time, energy is released as a result of the decomposition of ATP in water. In the presence of this energy, actin and myosin become active and new bridge bonds are formed. As a result, the actin rods slide over the myosin rods and move towards the centre of the sacmeer. Actin and myosin, together, form actomyosin.
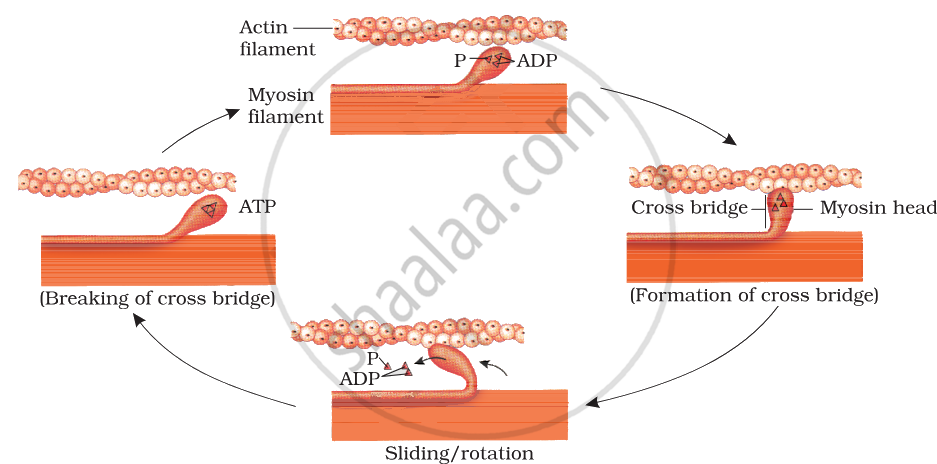
rotation of head and breaking of cross bridge
In this process, the tension of the muscle fibres reduces, which means relaxation takes place. When the stimulation ends, active pumping of calcium ions is pumped into the endothelium. Tropomyosin becomes free, due to which the bridge bonds between actin and myosin are broken. Actin then combines with tropomyosin. The muscle fibre returns to its old state. In cases of death, Ca++ cannot be transported back into the sarcomechanical trap due to the non-formation of ATP. Basically, the muscles remain pale and the body remains motionless.
Energy Supply:
Energy for muscle contraction is supplied by ATP. ATP is produced in muscles as a result of the catabolism of glycogen.
During muscle contraction, energy is obtained from the water decomposition of ATP.
\[\ce{ATP -> [hydrolysis]ADP + Pi + \text{energy}}\]
Another high-energy compound present in muscles is called creatine phosphate. It is also used in ATP production.
\[\ce{ADP + PCr -> ATP + Cr}\]
At rest, creatine phosphate is produced again by ATP.
ATP + Cr → PCr + ADP
In this way, a store of creatine phosphate remains in the muscle, which can provide ATP when needed.
Solution 2
According to the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction, the actin and myosin filaments slide past each other using cross-bridges to shorten the length of the sarcomeres.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions.
Write true or false. If false, change the statement so that it is true:
Actin is present in thin filament
Write true or false. If false, change the statement so that it is true:
H-zone of striated muscle fibre represents both thick and thin filaments.
Write the differences between Actin and Myosin.
Write the difference between:
Red and White muscles
How do you distinguish between a skeletal muscle and a cardiac muscle?
Thin filament of myofibril contains 2 ‘F’ actins and two other proteins namely ______ and ______.
In a muscle fibre Ca++ is stored in ______.
Read the following statements.
- Bands are dark bands and contain myosin
- I bands are light bands and contain actin
- During muscle contraction, the A band contracts.
- The part between the two Z - lines is called a sarcomere.
- The central part of the thin filament, not overlapped by the thick filament is called Hzone.
Of the above statements
In a skeletal muscle, bundles of muscle fibres are held together by ______.
Which of the following statements wrongly represents the nature of smooth muscle?
Match the following and mark the correct option
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Fast muscle fibres | i. Myoglobin |
| B. Slow muscle fibres | ii. Lactic acid |
| C. Actin filament | iii. Contractile unit |
| D. Sarcomere | iv. I-band |
Which one of the following statement is incorrect?
Sarcolemma, sarcoplasm and sarcoplasmic reticulum refer to a particular type of cell in our body. Which is this cell and to what parts of that cell do these names refer to?
