Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
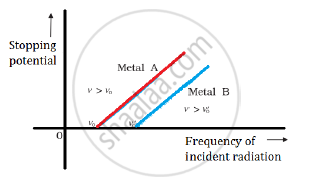
Define (i) stopping potential and (ii) threshold frequency, using Einstein’s equation and drawing necessary plot between relevant quantities.
Solution
Stopping potential: For a particular frequency of incident radiation, the minimum negative (retarding) potential V0 for which the photocurrent stops or becomes zero is called the cut-off or stopping potential.
Threshold frequency: The minimum frequency required for photoelectrons to be emitted from a metal surface is called the threshold frequency.
The graph between stopping potential and frequency of incident radiation is shown below:
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When radiations of wavelength λ1 and λ2 are incident on certain photosensitive, such that E1 > E2 . Then Planck's constant 'h' is ......................... .
(C = Velocity of light).
The photoelectric threshold wavelength of a metal is 230 nm. Determine the maximum kinetic energy in joule and in eV of the ejects electron for the metal surface when it is exposed to a radiation of wavelength 180 nm.
[Planck’s constant : h = 6.63 * 10-34 Js, Velocity of light : C = 3 * 108 m/s.]
State two important properties of photon which are used to write Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
A proton and a deuteron are accelerated through the same accelerating potential. Which one of the two has less momentum?
Give reasons to justify your answer.
Write its S.I. unit of (intensity of radiation)
The work function for a metal surface is 2.2eV. If the light of wavelength 5000Å is incident on the surface of the metal, find the threshold frequency and incident frequency. Will there be an emission of photoelectrons or not? (c = 3 x 108 m/ s, 1eV = 1.6x10-19 J , h = 6.63 x 10-34 J.s.)
Write the basic features of photon picture of electromagnetic radiation on which Einstein’s photoelectric equation is based.
In an inelastic collision, which of the following does not remain conserved?
According to Einstein's photoelectric equation, the plot of the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons from a metal Vs the frequency of the incident radiation gives as straight the whose slope:
How does stopping potential in photoelectric emission vary if the intensity of the incident radiation increases?
