Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe a method for the identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Also write chemical equations of the reactions involved.
Solution
Benzenesulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl), which is also known as Hinsberg’s reagent, reacts with primary and secondary amines to form sulphonamides.
(i) The reaction of benzenesulphonyl chloride with primary amine yields N-ethylbenzenesulphonyl amide.
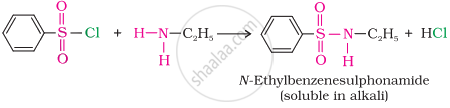
The hydrogen attached to nitrogen in sulphonamide is strongly acidic due to the presence of a strong electron-withdrawing sulphonyl group. Hence, it is soluble in alkali.
(ii) In the reaction with the secondary amine, N, N-diethylbenzenesulphonamide is formed.
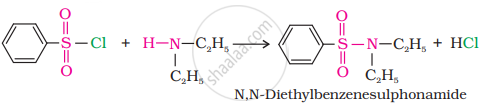
Since N, N-diethylbenzene sulphonamide does not contain any hydrogen atoms attached to nitrogen atoms, it is not acidic and hence insoluble in alkali.
(iii) Tertiary amines do not react with benzenesulphonyl chloride. This property of amines reacting with benzenesulphonyl chloride in a different manner is used for the distinction of primary, secondary and tertiary amines and also for the separation of a mixture of amines. However, these days benzenesulphonyl chloride is replaced by p-toluenesulphonyl chloride.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are 1 - nitropropane, 2-nitropropane and 2-methyl 2- nitropropane are distinguished from each other using nitrous acid?
What is the action of nitrous acid on primary nitroalkane?
Give plausible explanation for each of the following:
Why do primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines?
When primary amine reacts with CHCl3 in alcoholic KOH, the product is _______.
(A) aldehyde
(B) alcohol
(C) cyanide
(D) an isocyanide
What is the action of Benzene Sulphonyl Chloride on primary, secondary and tertiary
amines?
Describe Hinsberg method for the identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Also write the chemical equations of the reactions involved.
Which of the following reactions will not give a primary amine?
On heating an aliphatic primary amine with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide, the organic compound formed is ______.
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling points:
A: Butanamine
B: N, N-Dimethylethanamine
C: N- Etthylethanaminamine
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Tertiary amines are more basic than corresponding secondary and primary amines in gaseous state.
Reason (R): Tertiary amines have three alkyl groups which cause +I effect.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Compound A is converted to B on reaction with CHCl3 and KOH. The compound B is toxic and can be decomposed by C. A, B and C respectively are ______.
Match List I with List II.
| List I | List II | ||
| (A) | Benzenesulphonyl chloride | (I) | Test for primary amines |
| (B) | Hoffmann bromamide reaction | (II) | Anti Saytzeff |
| (C) | Carbylamine reaction | (III) | Hinsberg reagent |
| (D) | Hoffmann orientation | (IV) | Known reaction of Isocyanates |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
A compound 'X' on treatment with Br2/NaOH, provided C3H9N, which gives positive carbylamine test. Compound 'X' is ______.
Give reasons:
(CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in an aqueous solution.
Carbylamine test is the distinguishing test for ______.
