Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the size, nature and position of the image formed by a convex lens when an object is placed beyond 2f in front of the lens.
Solution
Image formation diagram:
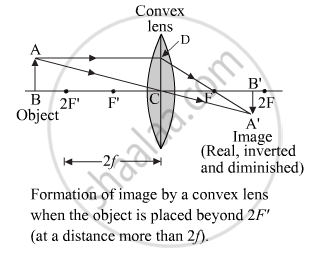
Image properties:
Image – between F and 2F
Nature of image – real and inverted
Size of Image – diminished
RELATED QUESTIONS
To find the image-distance for varying object-distances in case of a convex lens, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object placed very far from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image of the screen.
(a) In which direction – towards or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) What happens to the size of image – does it increase or decrease?
(c) What happen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
Write one condition where it does not bend when entering a medium of different optical density.
Where should an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size as the object is obtained using a convex lens?
f the image formed by a convex lens is of the same size as that of the object, what is the position of the image with respect to the lens?
What type of lens is shown in the diagram on the right? What will happen to the parallel rays of light? Show by completing the ray diagram.
A beam of parallel light rays is incident through the holes on one side of a box and emerges out through the holes on its opposite side as shown in the diagram below:
Which of the following could be inside the box?
(a) a rectangular glass block
(b) a concave lens
(c) a convex lens
(d) a glass prism
Define the term principal axis of a lens.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as in searchlight.
Why do we say that the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of a convex lens can be regarded as a sort of ‘turning points’ as far as the nature of the image formed by it is concerned?
